Air Quality At CH 15 Prentice Hall p.504-508
advertisement

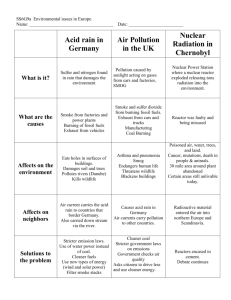
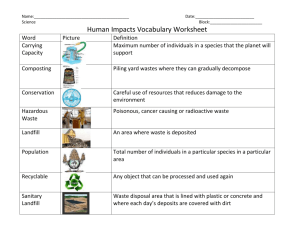
15 At 15. 2ppt Air Quality CH 15 Prentice Hall p.504-508 What is Air Pollution? • A brown haze or unpleasant smell • Pollutants= harmful substances in the air, water or soil. Particles • Air contains particles (pollutants) as well as gases. • Come from both natural sources and human activities. Natural Causes • The Ocean- water evaporates and leaves tiny salt particles in the air. • Particles of mold and plant pollen –blown by the wind. • Forest Fires Natural Causes • Soil Erosion • Dust Storms • Volcanoes- erupt dust, ash and poisonous gases Human Activities • Most is caused by human activities – Burning Fossil Fuels • • • • Oil Gasoline Diesel Fuel Coal • Burning Wood and Coal – releases particles of carbon into the air. – These particles of soot give smoke its dark color. Human Activities • Farming activities and construction release large amounts of soil particles into the air. – Due to soil erosion. • ½ of pollution comes from cars/motor vehicles. • ¼ of pollution comes from factories and power plants that burn coal & oil. Smog • In 1905-smoke and fog combined and formed London-type smog. It occurs when water droplets combine with coal smoke (soot) in humid air. • No longer common in the US. Photochemical “Smog” • Photochemical smog forms a brown haze. – “Photo”= Light – Caused by the action of sunlight on chemicals (nitrogen oxides and hydrocarbons), producing a mix of ozone and other chemicals. • Los Angeles and Mexico City Temperature Inversion • Normally warm air close to the surface is heated and rises carrying pollutants with it and are blown away. Temperature Inversion • During a temp inversion, A layer of warm air that prevents the rising air from escaping and polluted air is trapped and held close to the surface. It becomes concentrated and dangerous. Acid Rain • Forms when nitrogen oxides and other sulfur oxides combine with water in the air to form nitric acid and sulfuric acid. – Rain, sleet, snow, fog and even dry particles carry these two acids. • Acid Rain • Rain is naturally acidic but rain that contains more than normal is classified as acid rain. • Can damage the surface of buildings and statues. • Can also effect living organisms. Improving Air Quality • Many laws and regulations have been passed by the federal and state governments. • Pollution Control Devices required on cars • Power Plants installed filters in smoke stacks to remove smoke. Improving Air Quality • Air quality has improved in the last 30 years. – Major air pollutants have decreased. – Newer cars are less polluting. (hybrid cars) – New power plants are less polluting. • However, more cars are on the road and more power plants burning fossil fuels. • Air in cities is still polluted. Effects of Air Pollution • Dizziness and headaches • Eye, nose, and throat irritation – Cough – Lung Disease • Chest Pains • Allergies – Ragweed pollen causes “hay fever” • Sneezing • Runny nose • Red itchy eyes.