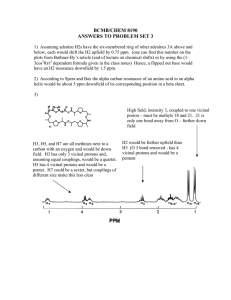
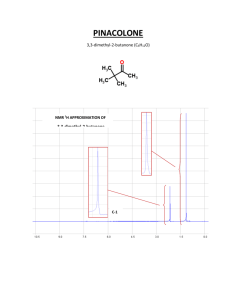
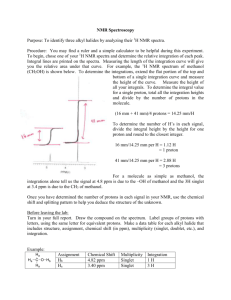
Supplementary data Fig. S1. (A) H. fastigiata growing in wild. Note
advertisement

Supplementary data Fig. S1. A C B D E (A) H. fastigiata growing in wild. Note that these plants grow only for 3 months and attain the height of less than 10 cm; (B) Apical meristem explant; (C) Plantlet formation on the apical meristem explant after 20 days; (D) Initiation of root from the regenerated plantlet; (E) In vitro cultures of Hoppea fastigiata (3-month-old culture). Fig. S2 TLC bioautograph showing AChE inhibitory activity of xanthones in ethanolic extracts of H. fastigiata. Xanthone 3 Xanthone 2 Xanthone 1 (Change in original background (purple colour) indicates the inhibition). [TLC plates were visualized at 312 nm (left) and normal day light after developing to identify AChE inhibitors (right)] Structural identification of compound 3 The LC-ESI-MS of compound 3 generated molecular ion [M+1]+ at m/z 273.1 was subjected to further fragmentation resulting molecular ion [M+H]+ at, m/z 272.9, m/z 257.9, m/z 230, m/z 215.1, m/z 201.1 and m/z 187 which were the indicative of tri-hydroxy mono-methoxy xanthone. The proton NMR spectrum of the sample shows 4 doublets and one singlet peak resonating at 7.60, 6.90, 6.61, 6.33 and 3.91 ppm, respectively using two methanol solvent peaks positioned at 4.78 and 3.31 ppm, as a reference. The chemical shift of doublets is characteristic of aromatic protons. The area integrals showed that the doublets correspond to resonance from a single proton while the singlet has three times greater area and may be assigned to a methyl moiety. The methyl protons are likely to be shifted downfield significantly if attached to an oxygen atom, and therefore can be assigned tentatively to an OCH3 moiety. The TOCSY spectrum showed existence of bond correlations between two pairs of protons. Two of the doublets showed spinspin coupling of ~8.5 Hz which typically arisen from two aromatic protons coupled through three bonds (spin-spin coupling 3J) with zero dihedral angle (cis conformation). Similarly the observed spin-spin coupling of ~2.5 Hz between two other doublets is typical of protons which are four bond coupled. The HSQC spectrum confirmed that all the four doublets are attached to carbons present in aromatic region, resonating at 117.52, 113.91, 93.65, 97.82 ppm, while the carbon of OCH3 protons resonates at 56.30 ppm, that is, in aliphatic region of carbon-13 NMR with reference to methanol peaks resonating at 49.15 ppm (bonded to 3.31 ppm proton peak). The assignment of all protons and carbon resonances were thus obtained un-ambiguously. The ROESY spectrum showed three short contacts; one contact between vicinal coupled protons and two contacts between OCH3 protons and both the four bond coupled protons. The distance of OCH3 protons (considered as a pseudo atom) from 6.61 and 6.33 ppm resonances were found to be 2.29 and 2.44 Ǻ, respectively, obtained from the integral of cross peaks, using distance between vicinal coupled protons resonating at 7.60 and 6.90 ppm to be 2.40 Ǻ as a standard. The remaining aromatic carbons, say at position C5 and C8, may have hydroxyl group attached which cannot be ascertained as their resonance could not observed (even at a temperature of 278 K) due to fast exchange with solvent. Thus the structural identity of compound 3 was confirmed as 1, 3, 5-trihydroxy-8-methoxyxanthone (Fig. 3).