9.6 Applications of linear transformation
advertisement
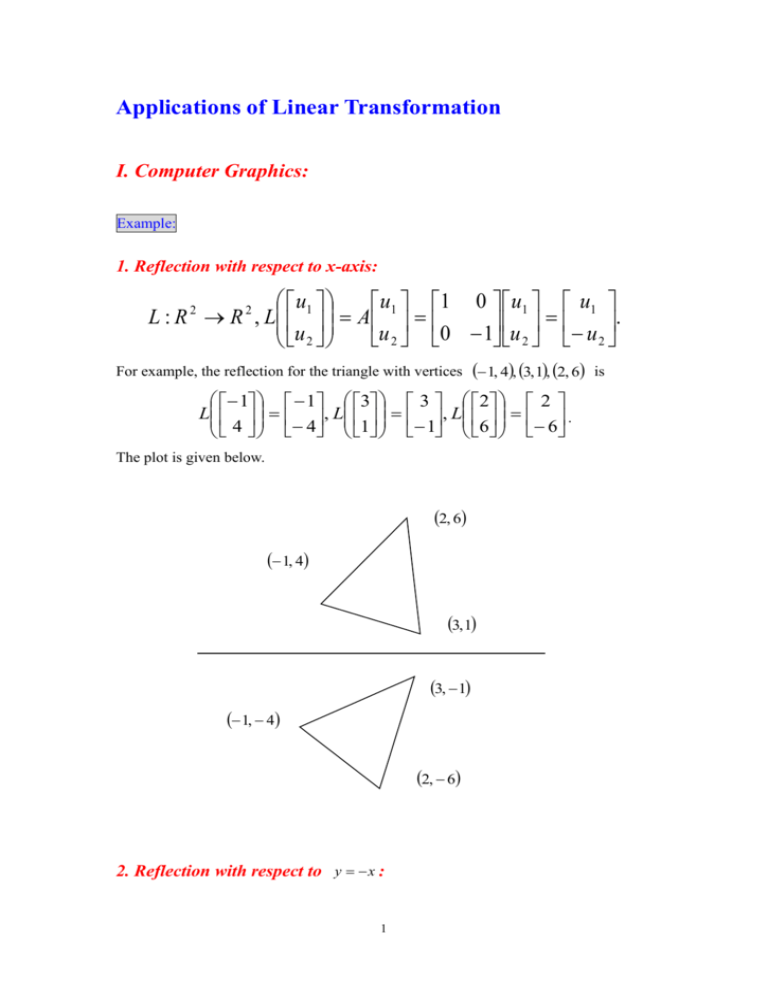
Applications of Linear Transformation I. Computer Graphics: Example: 1. Reflection with respect to x-axis: u L : R 2 R 2 , L 1 u 2 u 1 0 u1 u1 A 1 . u 2 0 1 u 2 u 2 For example, the reflection for the triangle with vertices 1, 4, 3, 1, 2, 6 is 1 1 3 3 2 2 L , L , L . 4 4 1 1 6 6 The plot is given below. 2, 6 1, 4 3, 1 3, 1 1, 4 2, 6 2. Reflection with respect to y x : 1 u1 u1 0 1 u1 u2 L : R R , L A u u . u u 1 0 2 1 2 2 2 2 Thus, the reflection for the triangle with vertices 1, 4, 3, 1, 2, 6 is 1 4 3 1 2 6 L , L , L . 4 1 1 3 6 2 The plot is given below 2, 6 1, 4 3, 1 4, 1 1, 3 6, 2 3. Rotation: u u cos sin u1 L : R 2 R 2 , L 1 A 1 u u u sin cos 2 2 2 For example, as , 2 cos 2 A sin 2 2 0 cos 1 2 sin 1 0 . Thus, the rotation for the triangle with vertices 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1 is 2 0 0 1 0 0 L 0 0, . 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 L 0 1, 0 1 0 and 1 0 1 1 1 L 1 1 . 1 1 0 The plot is given below. 0, 1 1, 1 0, 0 1, 1 1, 0 4. Shear in the x-direction: u1 u1 ku2 L : R R , L , k R. u u 2 2 2 2 For example, as k 2 , u u 2u2 L 1 1 u u 2 2 Thus, the shear for the rectangle with vertices 0, 0, 0, 2, 4, 0, 4, 2 in the x-direction is 0 0 0 4 4 4 4 8 L , L , L , L . 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 3 The plot is given below. 4, 2 0, 2 0, 0 8, 2 4, 0 II. Cryptography: Suppose we want to send the following message to our friend, MEET TOMORROW. For the security, we first code the alphabet as follows: A B … X Y Z 1 2 … 24 25 26 Thus, the code message is MEET TOMORROW M 13 E 5 E 5 T 20 T 20 O 15 M 13 O 15 R 18 R 18 O 15 W 23 The sequence 13 5 5 20 20 15 13 15 18 18 15 23 is the original code message. To encrypt the original code message, we can apply a linear transformation to original code message. Let L : R 3 R 3 , Lx Ax, where 4 1 A 1 0 2 1 1 3 2 . 2 Then, we break the original message into 4 vectors first, 13 20 13 18 5 , 20, 15, 15 , 5 15 18 23 and use the linear transformation to obtain the encrypted code message 13 L 5 5 13 1 2 3 13 38 A 5 1 1 2 5 28 , 5 0 1 2 5 15 20 L 20 15 20 1 2 3 20 105 A20 1 1 2 20 70 15 0 1 2 15 50 13 L 15 18 13 1 2 3 13 97 A15 1 1 2 15 64 , 18 0 1 2 18 51 and 18 L 15 23 18 1 2 3 18 117 A15 1 1 2 15 79 . 23 0 1 2 23 61 Then, we can send the encrypted message code 38 28 15 105 70 50 97 64 51 117 79 61 Suppose our friend wants to encode the encrypted message code. Our friend can find the inverse matrix of A first, 5 1 1 2 3 0 1 1 A 1 1 1 2 2 2 1 0 1 2 1 1 1 and then 1 1 38 13 38 0 A1 28 2 2 1 28 5 , 15 1 1 1 15 5 1 1 105 20 105 0 A1 70 2 2 1 70 20 , 50 1 1 1 50 15 1 1 97 13 97 0 A1 64 2 2 1 64 15 51 1 1 1 51 18 and 1 1 117 18 117 0 A1 79 2 2 1 79 15 61 1 1 1 61 23 Thus, our friend can find the original message code 13 5 5 20 20 15 13 15 18 18 15 23 via the inverse matrix of A. Similarly, if we receive the following message code from our friend 77 54 38 71 49 29 68 51 33 76 48 40 86 53 52 and we know the message from our friend transformed by the same linear transformation 1 2 3 L : R3 R3 , Lx Ax 1 1 2 x. 0 1 2 6 Thus, we first break the message into 5 vectors, 77 71 68 76 86 54, 49, 51, 48, 53 , 38 29 33 40 52 and then the original message code can be obtained by 1 1 77 16 77 0 A1 54 2 2 1 54 8 , 38 1 1 1 38 15 1 1 71 20 71 0 A1 49 2 2 1 49 15 , 29 1 1 1 29 7 1 1 68 18 68 0 A1 51 2 2 1 51 1 , 33 1 1 1 33 16 1 1 76 8 76 0 A1 48 2 2 1 48 16 , 40 1 1 1 40 12 and 1 1 86 1 86 0 A1 53 2 2 1 53 14 . 52 1 1 1 52 19 Thus, the original message from our friend is 16 8 15 20 15 7 18 1 16 8 16 12 1 14 19 P H O T O G R A P H P L A N S PHOTOGRAPH PLANS 7