Y7 core Geometry 5
advertisement

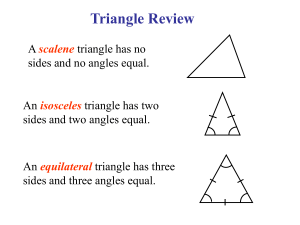
Y7 CORE SUMMER TERM UNIT: Geometry 5 – Constructions and Loci TIME ALLOCATION: 6 Hours PRIOR KNOWLEDGE Be able to measure and draw lines accurately. Be able to calculate scale measurements KEY WORDS STARTER SAS, triangle, quadrilateral, polygon, sketch, construct, adjacent, opposite, parallel, perpendicular, intersect, LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEVEL 4 Use a ruler and protractor to measure and construct acute and obtuse angles to the nearest degree. Use a ruler and protractor to construct a triangle given two angles and the included side (ASA) and given two sides and the included angle (SAS); explore using ICT. MAP ~ Architects' plans and elevations (scale drawings too) ~ What Shape? ~ Visualisation LEARNING OUTCOMES 1. To be able to construct acute and obtuse angles, using a ruler and protractor (or angle measurer). Eg: construct: 6.5 cm 54º 9.8 cm 6.5 cm 2. To be able to construct a triangle given ASA. 54º 9.8 cm 3. To use triangle constructions to construct quadrilaterals: rectangles, parallelograms, squares, rhombi, kites. 54º 54º 4. To be able to use labelling and notation accurately for lines, angles and shapes. Eg: line AB, angle Ŷ or XŶZ , triangle PQR. Begin to identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; solve geometrical problems involving these properties Solve problems involving symmetry properties. To be able to construct triangles given SAS or ASA. Eg 1: Construct ΔABC, if A = 36, B = 58 & AB = 7cm. Eg 2: Construct ΔDEF, if DE = 6cm, EF = 5cm & E = 75. Identify nets for a closed cube. To be able to construct the net for a solid of specified dimensions. Eg: Sketch, and construct the net of a given pyramid. To be able to identify parallel and perpendicular lines. To be able to identify and use geometric properties of: - triangles; - quadrilaterals; To be able to use these properties to solve problems. To be able to identify and use geometric properties of polygons. To be able to identify symmetries of polygons. To be able to identify and visualise symmetries of triangles, quadrilaterals and other polygons. LEVEL 5 Construct the two possible nets for a regular tetrahedron given the length of an edge To use ICT to explore constructions Use a ruler and protractor to construct simple nets of 3-D shapes, e.g. cuboid, regular tetrahedron, square-based pyramid, triangular prism. Construct on plain paper the net for a cuboid Make simple scale drawings with dimensions 2cm, 3cm, 4cm LEVEL 6 Use straight edge and compass to construct the perpendicular from a point to a line Use straight edge and compass to construct the perpendicular from a point to a line Be able to draw simple loci, on paper and using ICT, to produce shapes and paths, e.g. an equilateral triangle ACTIVITIES Design a coat of arms using different constructions Show construction lines Visualise simple paths e.g. Imagine a robot moving so that it is always the same distance from a fixed point. Describe the shape of the path the robot makes ICT Use of logo to draw loci RESOURCES Cube Nets Loci with ants (ppt) Loci of a point (ppt) Loci Puzzle worksheet FUNCTIONAL SKILLS and MPA OPPORTUNITIES Make boxes from nets. Design a kitchen Looking at house plans PLENARIES AND KEY QUESTIONS Why is it important to estimate the size of an angle before measuring it? What important tips would you give to someone about using a protractor? For which constructions is it important to keep the same compass arc (distance between the pencil and the point of your compasses)? Why? How do you go about finding a locus?