90732 Describe selected properties and applications of
advertisement

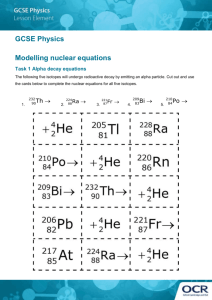
Number AS90732 Version 2 Page 1 of 3 Achievement Standard Subject Reference Science 3.6 Title Describe selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound Level 3 Subfield Science Domain Science – Core Registration date Credits 9 November 2005 4 Assessment Date version published External 9 November 2005 This achievement standard involves describing selected properties and applications of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound, and solving related problems using formulae, graphs and diagrams. Achievement Criteria Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence Describe selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound. Explain selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound. Discuss selected properties and applications of EMR, radioactive decay, sound and ultrasound. Explanatory Notes 1 This achievement standard is derived from Science in the New Zealand Curriculum, Learning Media, Ministry of Education, 1993, achievement objectives 2, 3 and 4 of the Making Sense of the Physical World strand, pp. 86–87. This achievement standard is also related to Pūtaiao i roto i te Marautanga o Aotearoa, Learning Media, Ministry of Education, 1996, Ō Ahupūngao: Te Whē, pp. 50–51. 2 Properties will be selected from for EMR: wave propagation, wave type, wavelength, frequency, period, wave velocity, amplitude, two point source interference, reflection, refraction, diffraction, EMR spectrum, absorption New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 Number AS90732 Version 2 Page 2 of 3 for radioactive decay: alpha and beta particles, gamma rays, conservation of atomic and mass number in alpha, beta and gamma decay, half life, isotopes, ionisation, penetration for sound and ultrasound: wave propagation, wave type, wavelength, frequency, period, wave velocity in different media, amplitude, pitch, loudness, reflection, diffraction, transmission, absorption. 3 Applications will be limited to the aspects of the application, which relate to the properties in Explanatory Note 2. Examples of applications could include: for EMR: shadows and eclipses; radio wave transmission; radio receivers; microwave oven; optical, radio and infrared telescopes; photographic imaging in different parts of the spectrum; medical diagnosis and treatment; radar; speed guns for radioactive decay: Geiger counters, radiometric dating, irradiation of food, sterilisation, medical diagnosis and treatment, smoke detectors, density and thickness measurements for sound and ultrasound: acoustics, ultrasound scanning, Doppler effect, animal communication. 4 Terms Describe requires the student to recognise, name, draw, give characteristics of or an account of. Explain requires the student to provide a reason as to how or why something occurs. Discuss requires the student to show understanding by linking scientific ideas. It may involve students in justifying, relating, evaluating, comparing and contrasting, analysing. 5 The description, explanation and discussion of properties and applications of the phenomena will also involve solving problems using formulae, graphs or diagrams. Recall and use of the following formulae is expected: d c = f, v = f, v = , f = 1 / T t If other formulae are required, they will be provided. 6 Use of graphs or diagrams could include reading information directly from graphs (including interpolation and extrapolation), drawing graphs from given information, or extracting information from a diagram. 7 Standard form, correct units and sensible rounding is expected in solving problems. New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016 Number AS90732 Version 2 Page 3 of 3 Quality Assurance 1 Providers and Industry Training Organisations must be accredited by the Qualifications Authority before they can register credits from assessment against achievement standards. 2 Accredited providers and Industry Training Organisations assessing against achievement standards must engage with the moderation system that applies to those achievement standards. Accreditation and Moderation Action Plan (AMAP) reference 0226 New Zealand Qualifications Authority 2016



![Jiye Jin-2014[1].3.17](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485437_1-38483f116d2f44a767f9ba4fa894c894-300x300.png)