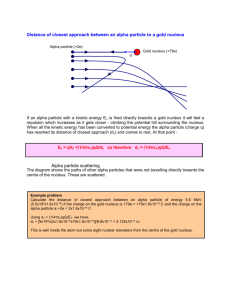
Radioactive Isotope Isotope which is unstable. It emits radiation & changes
advertisement

Isotope which is unstable. It emits radiation & changes into another kind of atom. Radioactive Isotope When one kind of nucleus changes into another kind of nucleus. Transmutation Reaction As stability , energy . Relationship between stability and energy Depends on neutron to proton ratio. Stability All the elements with atomic number > 83 (or beyond Bismuth) Which elements are unstable? Alpha, Beta, Gamma Separated by electric or magnetic fields. Types of Radiation Alpha radiation. Shielding can be paper or cloth. Least penetration power Gamma radiation. Requires lead/concrete shielding. Most penetration power Symbol for alpha radiation 4 2He 4 or 2 Same as the nucleus of a helium atom 4 2He 4 or 2 Mass = 4 amu Charge = +2 4 2He 4 or 2 Symbol for beta particle 0 -1e or 0 -1 or - or Fast moving electron originating from nucleus 0 -1e or 0 -1 or - or Mass = “zero” Charge = -1 0 -1e or 0 -1 or - or Symbol for positron. 0 +1e or 0 +1 or + Mass = “zero.” Charge = +1. Positive electron 0 +1e or 0 +1 or + Symbol for gamma radiation. 0 0 or 0 mass 0 charge 0 0 or Symbol for neutron 1 0n or n Symbol for proton 1 1H or 1 1p Unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle. Atomic # by 2. Mass # by 4. Alpha Decay Unstable nucleus emits an alpha particle. Atomic # by 2. Mass # by 4. 220Fr 87 4 + 216At 2 85 Equation represents natural transmutation. 1 term on reactant side. 220Fr 87 4 + 216At 2 85 Balance nuclear equations using conservation of atomic number & conservation of mass number. 220 220Fr 87 87 = 4 + 216 4 + 216At 2 = 85 2 + 85 Elapsed time Length of H.L. # of Half-Lives Half-Life Map Mass Start mass Elapsed Time 0 Fraction Remaining 1 # of Half Lives 0 1 X H.L. ½ 1 2 X H.L. ¼ 2 3 X H.L. 1/8 3 4 X H.L. 1/16 4 Same as type of particle emitted Decay Mode Weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes. Average Atomic Mass Particle “bullet” hits target nucleus & new isotope is produced. 2 terms on reactant side. Artificial Transmutation Artificial Transmutation target 32S 16 bullet 1 + n 0 32P 15 + 1H 1 Particle “bullet” may be proton or alpha particle. To react with a nucleus, must overcome + + repulsive forces by accelerating bullet to high speeds. Particle “bullet” may be a neutron. Neutrons have no charge, so no repulsive forces to overcome. No acceleration necessary. Artificial Transmutation Fission is division. Large nucleus (U-235 or Pu-239) is split into 2 medium sized nuclei by a neutron bullet. Excess neutrons & a great deal of energy are also produced. Fission Fission 239Pu 94 147Ba + 3 1n + 01n 90 Sr + 38 56 0 Fusion: U for unite and U for sun. Very small nuclei (H & He) are jammed together. Huge amounts of energy are released. Fusion Fusion 1H 1 + 21H 3He 2 a) b) 1n 0 + 235U 92 59Co 27 c) 3He 2 d) 14C 6 142Ba 56 + 01n 60Co 27 + 91Kr 36 14N 7 + -10e 0 fission Artificial transmutation + 11H 4He + 0e 2 + 3 1n + energy +1 fusion Natural transmutation Identify each of the rxns