nuclear fig
advertisement

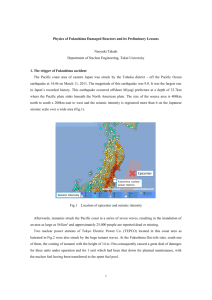
EN EN EN ANNEX 1 Update of the Nuclear Illustrative Programme in the context of the second Strategic Energy Review EN 1 EN Reference Scenario1 Hypothesis 50 Y lifetime2 Hypothesis 60 Y lifetime2 16% 14% 120 12% 100 10% WEO'06 APS scenario Nuclear share, % 80 8% 60 6% 40 4% 1) Sources TREN, IAEA-PLIM, PRIS and b ased on BE+DE phase-out, ES freezing, all decided life extensions and started new b uild (Olk3, Flam2, Cernavoda, Belene1+2 & later Mochovce) 20 2) Sources idem 1, reference scenario with (hypothetical) generalised lifetime extended to 50/60 y or equivalent capacity of new b uilds 0 Nuclear share Installed capacity, GW(e) 140 2% 0% 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 Fig 1: Calculated decrease of nuclear power capacity, in line with the current lifetime information. 18 GWe 12 X : Average : 23 years old 6 146 operational NPPs 4 Under Construction (FI, FR, BG) X 0 Build 5 10 15 20 25 Age (at 31/12/2007) 30 35 40 Source TREN, PRIS Fig 2: Total capacity of Plants under construction & operational vs. age (31/12/2007). EN 2 EN y 40 Oldest Average 35 Youngest 30 25 20 15 10 5 NL (1) UK(19) SE (10) FI (4) BE (7) DE (17) SI (1) ES (8) HU (4) FR (59) LT (1) SK (5) BG (2) CZ (6) RO (2) EU-27(146) 0 Source PRIS, NEA, TREN Member State (Number of plants) Fig 3: Age distribution of operational NPPs in the EU (31/12/2007). EN 3 EN Total U needs Uranium sources of the EU 25 25 U savi ng ( M o x) 20 Imported HEU Imported Stock drawdown 15 U needs Reprocessed U Reprocessed Pu Re-enriched tails 5 EU mining 0 source ESA kt U kt U 15 10 1 20 Imported Nat U 10 5 Indigenous 0 Share of the EU based companies in the global production of U represents about 67% of the 2007 needs of the EU (from WNA, ESA) 25 kt 3500 t (HM)/y source ESA; OECD Brown Book 2008 source ESA; OECD Brown Book 2008 3000 20 15 10 2500 VVER 2000 MOx 1500 CGR 1000 BWR 500 PWR 5 Needs Capacity Needs Capacity 0 0 Conversion² (kt U) Enrichm ent² (kt SW) Fuel Fabrication Needs² Fuel Fabrication Capacity² ² The announced investments in the fuel cycle (conversion, enrichment & fabrication) will maintain the European capacities for the whole fuel cycle, in the upper demand case for 2020, except for the limited VVER fabrication market which is likely to remain 100% Russian. Fig 4: Current annual fuel needs and related covered capacities in the EU. EN 4 EN List of Abbreviations AES-92 APS CANDU CANada Deuterium Uranium design reactor CO2 CSC EDF ELINI EMANI ENEF EPR ESA EU EUR GEN IV Carbon Dioxide GWe HEU IAEA IEA MDEP MOX NDA NEA NPP NPT OECD PLIM PRIS PRIMES PWR SW TEN WEO WNA WENRA VVER EN Recent Russian designed Pressurized water reactor Alternate Policy Scenario (WEO) Convention on Supplementary Compensation for nuclear damage. Electricité de France European Liability Insurance Industry The European Mutual Assurance for the Nuclear Industry European Nuclear Energy Forum European Pressurised Reactors Euratom Supply Agency European Union European Utilities Requirements for Nuclear Safety Generation IV Reactors are nuclear reactor designs currently being researched. 1000 Megawatts of electrical power Highly Enriched Uranium International Atomic Energy Agency International Energy Agency (OECD) Multinational Design Evaluation Programme Mixed Oxide Fuel Nuclear Decommissioning Authority Nuclear Energy Agency (OECD) Nuclear Power Plant Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development Plant Life Management (IAEA) Power Reactor Information System (IAEA) Energy system model supported by a series of research programmes of the European Commission Pressurised Water Reactors Separative Work (enrichment) Trans European Networks World Energy Outlook (IEA two year publication) World Nuclear Association Western European Nuclear Regulators’ Association The Russian abbreviation VVER stands for water-cooled, watermoderated energy reactor. Russian version of PWR reactor. 5 EN Index of Figures EN (1) Fig 1: Calculated decrease of nuclear power capacity, in line with the current lifetime information. (2) Fig 2: Total capacity of Plants under construction & operational vs. age (31/12/2007). (3) Fig 3: Age distribution of operational NPPs in the EU (31/12/2007). (4) Fig 4: Current annual fuel needs and related covered capacities in the EU. 6 EN





![The Politics of Protest [week 3]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005229111_1-9491ac8e8d24cc184a2c9020ba192c97-300x300.png)