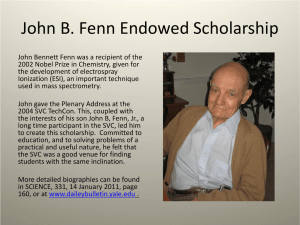
Supplemental Materials
advertisement

Supplemental Material Here, we report: i) the cerebellar activations for the group by task interaction obtained when including the movement parameters as covariates of no interest in the first-level GLM (MNI local maxima: Lobule VIII/posterior vermis, x 8, y -60, z -34, F=7.7, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Crus I, x -14, y -74, z -32, F=6.7, P<0.05, FWE, svc); ii) the cerebellar activations for the correlations with neuropsychological and clinical measures in ET patients (Frontal Assessment Battery [FAB] and disease severity [Fahn Scale], respectively) obtained when including the movement parameters as covariates of no interest in the first-level GLM (FAB, Positive correlations, MNI local maxima: Lobule VI, x -18, y -64, z -24, F=4.7, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Crus I, x -26, y -74, z 26, F=4.3, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Fahn Scale, Negative correlations, MNI local maxima: Crus I, x -30, y -66, z -36, F=5.5, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Lobule VI, x -4, y -72, z -22, F=5.2, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Crus I x 28, y -70, z -30, F=4.1, P<0.05, FWE, svc); iii) the cerebellar activations for the group by task interaction obtained when employing the SUIT approach (including also movement parameters as covariate of no interest in the first-level GLM)(MNI local maxima: Lobule VI, x -38, y -40, z -31, F=8.4, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Crus I, x -16, y -72, z -27, F=7.0, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Lobule VI, x 14, y -70, z -27, F=6.3, P<0.05, FWE, svc)(Supplementary Figure 2); iv) the cerebellar activations for the correlation with neuropsychological and clinical measures in ET patients (Frontal Assessment Battery [FAB] and disease severity [Fahn Scale], respectively) obtained when employing the SUIT approach (including also movement parameters as covariate of no interest in the first-level GLM)(FAB, Positive correlations, MNI local maxima: Lobule VI, x -42, y -66, z -29, F=5.2, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Anterior Vermis, x 4, y -50, z -9, F=5.0, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Posterior Vermis/Lobule VI, x 0, y -59, z -25, F=4.1, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Posterior Vermis/Crus II, x 4, y -76, z -35, F=4.0, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Fahn Scale, Negative correlations, MNI local maxima: Lobule VI, x -40, y -66, z -33, F=4.8, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Lobule VIII/Posterior Vermis, x 10, y -66, z -35, F=4.5, P<0.05, FWE, svc; Crus I, x -32, y -60, z -37, F=4.0, P<0.05, FWE, svc)(Supplementary Figure 3 and 4). Supplementary Figure 1. (A) The activity in the posterior lobe of the cerebellum (Lobule VI)(for the comparison high- vs.- low-load working memory) showed a significant negative correlation with disease severity (Fahn Tremor Rating Scale, Fahn-TRS) in patients with essential tremor (r2 value = -.67, purely included to assist in the interpretation of the slope). (B) Higher-order PsychoPhysiological-Interaction. Individual scores in disease severity in essential tremor patients are negatively correlated with connectivity between the cerebellar source/seed (Crus I/Lobule VI) and the Ventro-Lateral Prefrontal Cortex, VLPFC (r2 value = -.78, purely included to assist in the interpretation of the slope). Correlation lines are shown in black and confidence intervals are shown in red. R, right hemisphere. The color bar represents T statistics. Coordinates (x, z) are in the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. Supplementary Figure 2. The posterior lobe of the cerebellum (Crus I/Lobule VI) showed a significant group by task interaction (analysis of variance, ANOVA)(top part of the figure). A plot of the data from the global maxima in the left Crus I/Lobule VI demonstrated an abnormally enhanced response in patients with essential tremor (ET) compared to controls during high-load working memory (WM) trials (bottom part of the figure). R, right hemisphere. The color bar represents F statistics. Coordinates (y, z) are in the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. Analyses have been performed using the SUIT normalization procedure (Spatially unbiased template of the cerebellum and brainstem, http://www.icn.ucl.ac.uk/motorcontrol/imaging/suit.htm). BOLD, blood oxygenated level dependent. Supplementary Figure 3. Activity in the posterior lobe of the cerebellum (Lobule VI) (high- vs.- low-load working memory contrast) showed a positive correlation with individual scores on a measure of cognitive control (Frontal Assessment Battery scores) in patients with essential tremor (top part of the figure). Correlation line is shown in black and confidence intervals are shown in red. The color bar represents T statistics. Coordinates (y, z) are in the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. Analyses have been performed using the SUIT normalization procedure (Spatially unbiased template of the cerebellum and brainstem, http://www.icn.ucl.ac.uk/motorcontrol/imaging/suit.htm). BOLD, blood oxygenated level dependent. BOLD, blood oxygenated level dependent. Supplementary Figure 4. The activity in the posterior lobe of the cerebellum (Lobule VI)(for the comparison high- vs.- low-load working memory) showed a significant negative correlation with disease severity (Fahn Tremor Rating Scale, Fahn-TRS) in patients with essential tremor. Correlation lines are shown in black and confidence intervals are shown in red. R, right hemisphere. The color bar represents T statistics. Coordinates (x, z) are in the Montreal Neurological Institute (MNI) space. Analyses have been performed using the SUIT normalization procedure (Spatially unbiased template of the cerebellum and brainstem, http://www.icn.ucl.ac.uk/motorcontrol/imaging/suit.htm). BOLD, blood oxygenated level dependent.