dalton`s atomic theory of matter
advertisement

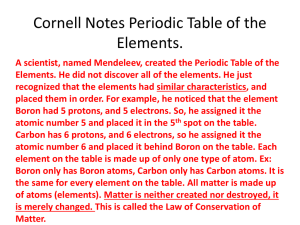
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF GROUPS OF ELEMENTS Elements can be classified using two different schemes. Metal – Nonmetal Scheme (based on physical properties) Metals - most elements are metals - elements on left side of periodic table are metals - characteristics of metals - luster (shine) - high electrical conductivity - high heat conductivity (i. e. low specific heats - ductility – ability of material to be stretched without breaking - malleability – ability of material to be stamped without breaking Nonmetals - elements in the upper right corner of table are nonmetals. - characteristics of nonmetals - poor electrical conductivity (insulator) - poor heat conductivity (insulator) - all of the gaseous elements are nonmetals Metalloids - elements in between metal and nonmetal section of periodic table - properties of metalloids are in between properties of metals and nonmetals - moderate electrical conductivity - as in silicon, which is called a semiconductor since it partially conducts electricity - only B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te, At are metalloids Group Scheme (based on chemical properties) [Section 4.1] Alkali metals – column 1A - first column of periodic table - Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr - all alkali metals may form ions with +1 charge Alkaline earth metals – column 2A - second column of periodic table - Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra - all alkaline earth metals may form ions with +2 charge Transition metals - middle three rows of table - Sc to Zn, Y to Cd, La to Hg - various charges 2 Rare earths - bottom two rows beside table - Ce to Lu, Th to Lr Noble gases – column 8A - last column of periodic table - He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn - essentially unreactive - also called inert gases Halogens – column 7A - second to last column of periodic table - F, Cl, Br, I, At - all halogens may form ions with –1 charge Chalcogens – column 6A - third to last column of periodic table - O, S, Se, Te, Po - all chalcogens may form ions with –2 charge Pnictogens – column 5A - fourth to last column of periodic table - N, P, As, Sb, Bi - N, P are nonmetals with a -3 charge - some pnictogens are metalloids (As, Sb) - Bi is the pnictogen metal (usually +3 charge) Members of groups have similar physical and chemical properties. STRUCTURE OF THE ATOM Atoms have two components. Nucleus - all nuclei have positive charge - contains almost all of the mass of an atom - >99.95% - takes up very little volume in atom Electrons – e- all electrons in the universe are the same - all have –1 charge - electron “orbits” around nucleus, orbit takes up most of space - If nucleus is a penny, then electrons are 75 yards away - i. e., an atom is mostly empty space! 3 STRUCTURE OF NUCLEUS Nucleus has two components. Protons – p+ - all protons in the universe are the same - all protons have +1 charge - all positive charge in nucleus comes from protons - a proton weighs 1 atomic mass unit (amu) (more about this later) - the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom defines the element of the atom Neutrons – n0 - all neutrons in the universe are the same - all neutrons have no charge -i. e., they are neutral. - a neutron weighs 1 amu Atomic Number - Z - every atom has number which defines its identity, which called its atomic number *- atomic number is equal to number of protons* Z = # of p+ Mass Number – A - every atom has number which approximates how heavy it is, which is called its mass number *- mass number is number of protons plus number of neutrons* A = # of p+ + # of n0 ATOMIC SYMBOLS Often specific atoms are given a symbol that includes atomic number and mass number. - Atomic number is written as subscript before elemental symbol. - Mass number is written as superscript before elemental symbol. Example: 42 He 2 = atomic number 4 = mass number Example: An atom has 6 protons and 7 neutrons. Write its chemical symbol. 4 Example: For the atom 37 17 Cl , how many protons neutrons and electrons does it have? Isotope – Two atoms are isotopes if they have same atomic number but different mass numbers - i. e., they have same # p+, but different # n0 - isotopes are the same type of atom, but they have different weights 12 6 C and 13 6 C and 13 6 13 7 C are isotopes N are not isotopes IONS AND IONIC COMPOUNDS Atoms where # e- # p+ are called ions. If there are more e-, ion is called an anion. Ex: Cl- has 17 p+, but 18 eIf there are less e-, ion is called a cation. Ex: Na+ has 11 p+, but 10 eIons are very common in chemistry. Anions and cations attract each other to form ionic compounds. ATOMIC AND MOLECULAR MASSES Average Atomic Mass - If element has more than one naturally occurring isotope, atomic mass is an average of the mass of the isotopes. - Average is performed accounting for the relative natural abundance of each isotope. Example: Copper nuclide abundance 63 Cu 69.17% 65 Cu 30.83% mass(amu) 62.940 64.928 Example: Neon nuclide 20 Ne 21 Ne 22 Ne mass(amu) 19.992 20.994 21.991 abundance 90.48% 0.27% 9.25% 5 DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER 1. All matter is made of fundamental building blocks called atoms that are indivisible. - There is a limit to how small matter can get. 2. Atoms of the same element are identical. - Very roughly, there are 1050 atoms of hydrogen in the universe and they are all the same. 3. Chemical compounds are made from whole number of atoms. - One atom of carbon and one atom of oxygen make carbon monoxide (CO). - One atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen make carbon dioxide (CO2). - We can never put together one atom of carbon and 1½ atoms of oxygen. - no such thing as ½ atom 4. Chemical reactions are the rearrangement of atoms from one substance to another. CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS - three types of chemical compounds 1. Molecular compounds - tightly bound atoms in a single unit - binding between atoms is called covalent bonding 2. Ionic compounds - atoms in compound exist with charges - such atoms are called ions - charges on ions attract each other to form chemical compound - binding between ions is called ionic bonding 3. Intermetallic compounds - atoms in compound exist without charges - binding between atoms is called metallic bonding 6 CHEMICAL FORMULAS - A chemical formula lists all of the elements in a chemical compound. - Number of atoms of each element is always indicated by subscript after element. Carbon dioxide – CO2 - one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen Sodium chloride – NaCl - one atom of sodium and one atom of chlorine Sucrose – C12H22O11 - 12 atoms of carbon, 22 atoms of hydrogen and 11atoms of oxygen Note: Some elements exist as molecules rather than atoms. Gases: H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2 Liquid: Br2 Solid: I2 Mnemonic: Note these 7 molecular elements look approximately like a 7 on the periodic table.