A NEW AGE DAWNS Chapter 9 THE MIGHTY ATOM
advertisement

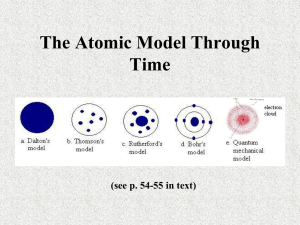
Presented by: Nihal Lashin Omar Sarwat Mohamed Sadek General Knowledge about atoms “All things are made of atoms” the great Caltech physicist Richard Feynman. The basic working arrangements of atoms is the molecule. What is a molecule? Chemists way of thinking: Molecules Vs Elements Properties of an atom: 1. Tiny 2. Durable Long lived (10ˆ35 ) 3. Everywhere 4. Numerous 5. Recycled 6. Indestructible The size of an atom: If you want to see a paramecium- a single celled, fresh water creature which is about 0.002 mm, you have to enlarge it 12 meters across BUT If you want to see an atom in a drop of water you have to enlarge the drop 24 kilometers across ***Can you see how small it is??? The scale of an atom: One ten-millionth of a millimeter. History of atoms: First the idea of atoms developed by the ancient Greeks. Dalton’s contribution: Relative size of an atom 2. Characters of atoms 3. How atoms fit together 1. The Viennese physicist Ernest Mach doubted the existence of atoms… “Atoms cannot be perceived by the senses… they are things of thought” he wrote. • The first real hero of the atomic age is Ernest Rutherford. He received a Nobel Prize for investigations into disintegration of the element. In Manchester University, he did his most important work in determining the structure and the nature of the atom. In 1910 he invented the radiation detector. An atom according to Rutherford was an empty space with a very dense nucleus at the centre. In 1897 J.J. Thomson discovered the electron In 1911 C. T. R. Wilson produced the first particle detector. In 1932 James Chadwick discovered the neutron. The Atom Revealed • In 1910, Rutherford and his assistant Hans Geiger conducted an Experiment which revealed the internal structure of an atom. •Http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5pZj0u _XMbc • We will add some more points after the video to further illustrate the experiment and its conclusion. The structure of an atom as we know now: It’s made of three things: Protons which have a positive charge 2. Electros which have a negative charge 3. Neutrons which have no charge Protons and neutrons are packed inside of the nucleus, while electrons spin around outside. 1. ** Protons give an atom its identity, while neutrons add to its mass.