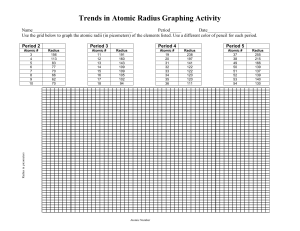
CHEMISTRY 3.4 Name: WORKSHEET FOUR RADII OF ATOMS
advertisement
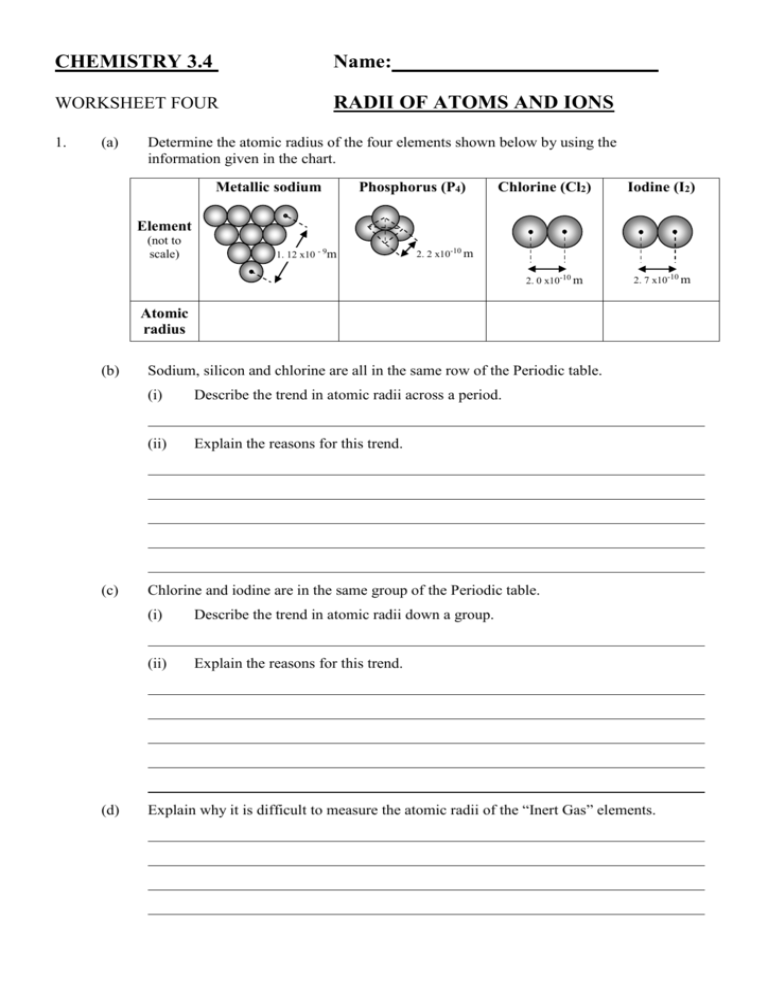
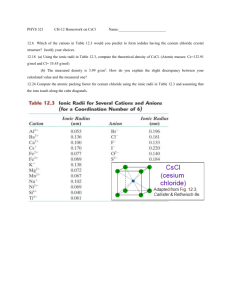
CHEMISTRY 3.4 Name: WORKSHEET FOUR RADII OF ATOMS AND IONS 1. (a) Determine the atomic radius of the four elements shown below by using the information given in the chart. Metallic sodium Phosphorus (P4) Chlorine (Cl2) Iodine (I2) Element (not to scale) 1. 12 x10 - 9m 2. 2 x10-10 m 2. 0 x10-10 m 2. 7 x10-10 m Atomic radius (b) (c) (d) Sodium, silicon and chlorine are all in the same row of the Periodic table. (i) Describe the trend in atomic radii across a period. (ii) Explain the reasons for this trend. Chlorine and iodine are in the same group of the Periodic table. (i) Describe the trend in atomic radii down a group. (ii) Explain the reasons for this trend. Explain why it is difficult to measure the atomic radii of the “Inert Gas” elements. 2. The atomic and ionic radii of several elements are given below in pm (1 pm = 1x10-12 m). Element Li / Li+ Be /Be2+ N / N3- O / O2- F / F- Na /Na+ K / K+ Atomic radii 152 112 75 73 72 186 227 Ionic radii 90 59 132 124 117 116 152 Using the information in the table, answer the following questions. 3. (a) For an element, its positive ion is than its neutral atom. (b) For an element, its negative ion is than its neutral atom. (c) (d) Within a group, the size of the ions with the same charge down the group. Explain your answer to (a). (e) Explain your answer to (b). (f) The following are isoelectronic: P3-, S2-, Cl-, Ar, K+, Ca2+. Compare and discuss the expected values of their radii. as you go In each of the following groups of atoms and ions, circle the one with the smallest radius. (a) B, Al, Ga (b) Cs, Cs+ (c) P3-, S2-, Cl- (d) Li+, N3-, O2- (e) F, Cl, Br, I. (f) S, S2- (g) Cl, Cl- (h) Mg, Mg2+ (i) Na+, Mg2+, Al3+