Density Notes
advertisement

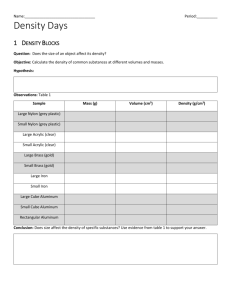
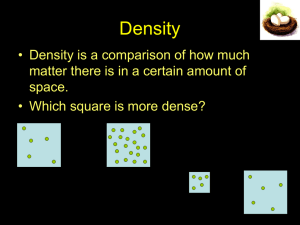
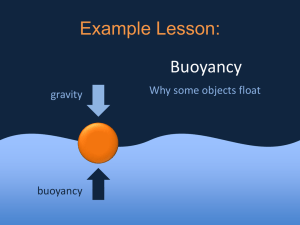
Chapter 4: Density and Buoyancy ______________________ Density: Investigation 4A What is density and how is it measured? ______________________ 1. Density. a. describes how much mass is in a given volume of a material ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ b. Solids, liquids and gases are matter, so they all have density. ______________________ c. The units used for density depends on whether the substance is solid or liquid. ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ - For liquids use units of grams per milliliter (g/mL) - For solids use density in units of g/cm3 Practice: Plastic’s density is greater that water’s density, but the bath toy floats. Why is this? _____________________________________________________________ ______________________ ______________________ _____________________________________________________________ d. Density is a property of material that is independent of quantity or shape. ______________________ e. density changes for different substances because: i. Atoms have different masses. ______________________ ______________________ ii. Atoms may be “packed” tightly or loosely. f. Liquids tend to be less dense than solids of the same material. i. Water is an exception to this rule. The density of solid water, ______________________ or ice, is less than the density of liquid water. Think: Why might this be important for sea life where lakes ______________________ ______________________ freeze in the winter? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ______________________ 2. Volume a. the amount of space an object takes up. ______________________ b. The volume of a rectangular solid is found by multiplying length times width times height. ______________________ width height ______________________ length ______________________ c. Use a graduated cylinder to measure the volume of a liquid. d. To measure the volume of an irregular shape, use a technique called ______________________ displacement. ______________________ i. put the object in water and measure the amount of water displaced (how much did the volume change?) ______________________ 3. Finding Volumes of Common Shapes ______________________ . ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Buoyancy: Investigation 4B sink or float Steel is more dense than water so why do steel boats float? ______________________ ______________________ 1. Weight a. Weight is a force, like any other pushing or pulling force, and is caused by Earth’s gravity. ______________________ ______________________ b. it is easy to confuse mass and weight, but they are not the same. c. Weight is the downward force of gravity acting on mass. ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 2. Buoyancy a. Buoyancy is a measure of the upward force a fluid exerts on ______________________ ______________________ an object that is submerged. b. The strength of the buoyant force on an object in water depends on the volume of the object that is underwater. ______________________ ______________________ More volume underwater Less volume underwater ______________________ ______________________ c. In the third century BC, a Greek mathematician named ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Archimedes realized that buoyant force is equal to the weight of fluid displaced by an object. d. A simple experiment can be done to measure the buoyant force on a rock with a spring scale. ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ e. Buoyancy explains why some objects sink and others float. Buoyant force is stronger than weight Object floats Weight is stronger than buoyant force Object sinks ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ 3. Practice Problem – Buoyancy a. What is the buoyant force on a rock with a volume of 1,000 cm3? 1. In air, the scale shows the rock’s weight as 29.4 newtons. 2. When the rock is completely submerged, the scale reads 19.6 newtons. ______________________ ______________________ 3. The difference is a force of 9.8 newtons. This is the buoyant force! 4. Density and buoyancy ______________________ ______________________ a. If you know an object’s density you can quickly predict whether it will sink or float. b. Average density determines whether objects sink or float. - An object with an average density GREATER than the density ______________________ of the liquid will sink. ______________________ ______________________ - An object with an average density LESS than the density of the liquid will float. c. steel boats can be made to float because their density is less than water ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ d. a loaded cargo ship will sit lower in the water than an unloaded ship nearby. - A full ship has more mass than an empty ship. ______________________ - A full ship must displace more water (sink deeper) to make the buoyant force large enough to balance the ship’s weight. ______________________ Summary – fill up ______________________ this section! ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________ ______________________ Density Essential Question What is density and how is it measured? 1. Density. a. describes how much ____________ is in a given volume of a material b. Solids, liquids and ____________ are matter, so they all have density. c. The ____________ used for density depends on whether the substance is solid or liquid. - For _______________ use units of grams per milliliter (g/mL) - For _______________ use density in units of g/cm3 Practice: Plastic’s density is greater that water’s density, but the bath toy floats. Why is this? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ d. Density is a property of material that is independent of quantity or _________________. e. density changes for different substances because: i. Atoms have different ___________________. ii. Atoms may be “packed” __________________ or loosely. f. Liquids tend to be ______________ dense than solids of the same material. i. _________________ is an exception to this rule. The density of solid water, or ice, is less than the density of liquid water. Think: Why might this be important for sea life where lakes freeze in the winter? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. Volume a. the amount of ___________________ an object takes up. b. The volume of a rectangular solid is found by multiplying length times width times ___________________. width height length c. Use a graduated cylinder to measure the volume of a ________________. d. To measure the volume of an ___________________ shape, use a technique called displacement. i. put the object in water and measure the amount of water ___________________________ (how much did the volume change?) 3. Finding Volumes of Common Shapes . Summary – no I, you, me us, etc. Tell a factual story of your notes. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Buoyancy: Essential Questions Will it sink or float? If steel is more dense than water, why do steel boats float? 1. Weight a. Weight is a ______________, like any other pushing or pulling force, and is caused by Earth’s _______________. b. it is easy to confuse mass and weight, but they are _______ the same. c. Weight is the downward force of gravity acting on mass. 2. Buoyancy a. Buoyancy is a measure of the _________________ force a fluid exerts on an object that is submerged. b. The ____________________ of the buoyant force on an object in water depends on the ________________ of the object that is underwater. Less volume underwater More volume underwater c. In the third century BC, a Greek mathematician named Archimedes realized that buoyant force is ________________ to the weight of fluid _____________________ by an object. d. A simple experiment can be done to measure the buoyant force on a rock with a spring scale. e. Buoyancy explains why some objects _______ and others _____________. Buoyant force is stronger than weight Object floats Weight is stronger than buoyant force Object sinks 3. Practice Problem – Buoyancy a. What is the buoyant force on a rock with a volume of 1,000 cm3? 1. In air, the scale shows the rock’s weight as _______________. 2. When the rock is completely ________________, the scale reads 19.6 newtons. 3. The difference is a force of 9.8 newtons. This is the ___________ force! 4. Density and buoyancy a. If you know an object’s __________________ you can quickly predict whether it will sink or float. b. Average density determines whether objects sink or ______________. - An object with an average density ___________________ than the density of the liquid will sink. - An object with an average density ______________ than the density of the liquid will float. c. steel boats can be made to float because their density is ___________ than water d. a ____________________ cargo ship will sit lower in the water than an unloaded ship nearby. - A full ship has more _________________ than an empty ship. - A full ship must _____________ more water (sink deeper) to make the buoyant force large enough to balance the ship’s weight. Summary – no I, you, me us, etc. Tell a factual story of your notes. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________