Density and Buoyancy Worksheet: Middle School Science
advertisement

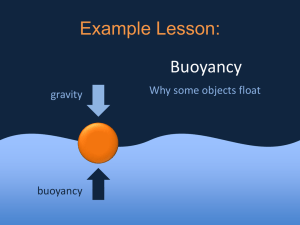
Unit 8 C: Fluids (Pg. 178 - 257) Chapter 8: Density and Buoyancy (pg. 206 - 225) Name: __________________________ Date: ___________________ 8. 1: Weight, Mass, and Volume (Pg. 208 - 209): Read Pages 208 - 209. Answer the following questions: 2. In your own words, describe the relationship between weight, mass, and volume. Use a diagram or a chart if this is helpful. (See the chart on PB Pg. 167 # 3) Weight is the gravitational pull on an object. Because the pull is greater on objects with greater mass, objects with greater mass have greater weight. Mass is the amount of matter in an object or substance. If you compare the volumes of two objects made of the same substance, the object with a greater volume will have the greater mass. 3. Describe three ways of determining the volume of an object (solid). a) regular: V = l x w x h b) irregular: Use the method of displacement c) irregular (too big objects): If the object is too large to fit in a graduated cylinder, you can place the object in a container filled with water, while collecting and then measuring the overflow. 8.3: Density (Pg. 212 – 213): Read Pages 212 - 213. Answer the following questions: 1. Explain the mathematical relationship between mass, volume, and density. The density of a substance is the ratio of the mass of a sample to its volume. 2. Use the particle theory to explain the difference in density between most solids, liquids, and gases. You may use sketches in your explanation. Solids: The particles closest, vibrate, strong FOA …etc (See the diagram on PB pg. 169 Fig. 1) 3. What units can be used to measure density? Since Density = Mass__ The units of density can include: g/mL, g/cm3, and kg/m3. Volume 4. 5. See PB pg. 172 # 3. See PB pg. 172 # 4. 6. An empty container has a mass of 65 g. When 85 mL of oil are placed in it, the total mass is 140 g. Calculate the density of the oil. See “Sample Problem” on TB pg 212. Mass of oil = mass (oil + container) – mass of container = 140 g – 65 g = 75 g Density = mass = _75 g = 0.88 g/mL Volume 88 mL Statement: The density of the oil is about 0.9 g/mL 7. Calculate the density of a diamond if the volume of the diamond is 0.50 cm3 and its mass is 1.75 g. Density = mass = _1.75 g = 3.5 g/cm3 Volume 0.50 cm3 Statement: The density of the diamond is 3.5 g/cm3 8.5: Buoyancy (Pg. 216 - 217: Read Pages 216 - 217. Answer the following questions. 1. Define buoyancy and add a visual to the explanation. Buoyancy is the upward force that a fluid exerts on an object. Illustrations should use arrows to indicate the upward buoyant force on a floating object. 2. What is the relationship between density and buoyancy for objects and substances? If the density of an object is less than the density of the surrounding fluid, the buoyant force of the liquid will cause the object to float. 3. Explain how a dense substance, such as metal, is able to float on a less dense substance, like water. Use an example from this section in your explanation. An object made of a dense metal, such as a ship, can float on a less-dense substance, such as water, if the shape of the object (with a large volume) gives it an overall density less than that of the less-dense substance. The displacement of water by a large boat results in a large buoyant force. The same amount of metal in a more compact shape, however, would displace a smaller amount of water, resulting in a smaller buoyant force. In this case, the piece of metal would sink. 4. Why does a ship float at different levels depending on the type of water it sails in? The density of the water changes, depending on its composition. The ship always floats at a level so that the weight of the displaced water equals the weight of the ship 8.6: Density and Buoyancy in Action (Pg. 219 – 221): Read Pages 219 – 221. Answer the following questions. 3. Is the density of oil helpful or harmful when dealing with oil spills? Explain. The density of oil is both harmful and helpful in cleaning up oil spills. Because oil is less dense than water, oil floats on water. At the surface of the water, the oil is more harmful to plants and animals by contaminating their food, making it difficult for them to breathe, and disrupting the insulating effects of their fur or feathers. However, because the oil floats on water, it is more accessible during cleanup of the spill. 4. a) Explain how ballast tanks work. You may use a diagram in your explanation. (See PB Pg 182, Fig. 5) A ballast tank can be filled with air or water to change the overall density of a submarine, allowing it to rise or sink in the water. Forcing air into the ballast tanks pushes water out, making the submarine less dense, allowing it to rise. Replacing air with sea water increases the submarine’s density, causing it to sink. b) How is a fish swim bladder similar to a submarine ballast tank? Like a submarine, a fish can change its buoyancy. Filling the swim bladder with oxygen allows the fish to float higher in the water. Decreasing the amount of oxygen in the swim bladder allows the fish to drop lower in the water without using energy to dive and stay at a greater depth. Chapter 8 - Review (pages 224 - 225) Name: __________________________ Date: ___________________ What Do You Remember? 4. Use the particle theory to explain density. K/U The density of a material depends on the mass of the particles and how tightly those particles are packed in the material. Because particles of most substances in the solid state are packed more closely together than particles of the substance in the liquid state, solids generally have a greater density than liquids. Because particles of a liquid are packed closer than the particles of a gas, liquids have greater density than gases. Gases have relatively low densities because their particles can move freely. 5. What is meant by positive buoyancy, neutral buoyancy, and negative buoyancy? K An object has positive buoyancy if its weight is less than the buoyant force on it. The object will begin to float upward. An object has negative buoyancy if its weight is greater than the buoyant force on it. The object will begin to sink. An object has neutral buoyancy if its weight equals the buoyant force. The object neither rises nor sinks in the fluid. 6. What is meant by a characteristic property of matter? A characteristic property of matter is a property that is specific to a particular substance and can be used to distinguish one substance from another. 7. What are one advantage and one disadvantage of determining volume by the water displacement method? Advantage: The shape of the object does not matter and volume is easy to measure in this way. Disadvantage: It cannot be used to determine the volume of a very small object. 9. Why must hot air balloons carry a heat source with them? Hot air balloons must carry a heat source with them because they must warm the air inside the balloons in order to maintain their buoyancy. The air in the balloons naturally cools off over time, so for the balloons to stay aloft, the air must be heated periodically. K/U C 13. Use Table 1 in Section 8.3 to answer the following questions: (a) Which solids would fl oat on water? wood and ice (b) Which solids would sink in water but fl oat on mercury? Lead (c) If 0.5 m3 of an unknown substance has a mass of 0.65 kg, what is the substance likely to be? Density = mass = 0.65 kg = 1.3 kg/m3 Volume 0.5 m3 Statement: The density of the substance is 1.3 kg/m3, so it is likely to be air. What Do You Understand? 14. Imagine that you have travelled to a planet that is much smaller than Earth and has less gravitational pull. You have taken a block of metal with you. Compare the mass, weight, volume, and density of the object on Earth and on the smaller planet. K Because it is smaller than Earth, the planet would exert a smaller gravitational force on the block than Earth does. Because weight involves gravitational force, the weight of the block will be smaller on the other planet than on Earth. Mass, volume, and density, however, would remain the same. U T/I 15. (a) Does the swim bladder of a fish generally keep the fish positively, neutrally, or negatively buoyant? The swim bladder generally keeps a fish neutrally buoyant. (b) How does this compare to the use of ballast in a submarine? Explain your answer. The ballast in a submarine functions much like a swim bladder in a fish. Ballast tanks can take in air or water to keep the submarine neutrally buoyant. A 16. Two metal objects, A and B, each have a mass of 200 kg. Object A displaces 100 kg of water. Object B displaces 1000 kg of water. Which one is more likely to be a boat? Explain your reasoning. T Because their masses are the same, and because B displaces more water, the volume of B must be larger. So, B is more likely than A to be a boat. 17. You are the captain of a fully loaded ship sailing from warm tropical waters into the cold North Atlantic. As you sail north, will you need to dump some of your ballast water so that the ship can travel safely? Explain your answer. As the ship sails into colder waters, the density of the water will increase, and the ship will float higher in the water. The ship will not need to dump some of its ballast water because the denser water will provide a greater buoyant force. Solve a Problem. 20. If 30 mL of a fluid has a mass of 63 g, what is its density? Will it float or sink in water? Explain. Density = mass = _63 g = 2.1 g/mL Volume 30 mL Statement: The density of the fluid is about 2.1 g/mL. Because this is greater than the density of water, 1.0 g/mL, the fluid will sink in water. 21. You would like to raise a very delicate piece of sunken equipment to the surface, but you must do it slowly. In the flotation bags, you can use either air or diesel oil. Which would you use? Explain your reasoning. I would use diesel oil because the density of the oil is closer than the density of air to the density of water. Air will cause the flotation bags to rise quickly, but diesel oil will cause them to rise more slowly. 22. You are a manufacturer of carbon monoxide detectors. One of your employees suggests that the detectors should come with instructions to install them close to the floor. Another says that it does not matter. Use Table 1 in Section 8.3 and your knowledge of fluids to develop a response to your employees. The density of carbon monoxide is 1.45 kg/m3 (which is greater than the density of air), so it will sink in air. The first employee is correct; the detectors should be installed close to the floor where carbon monoxide would collect. Chapter 8: Density and Buoyancy – Practice Book