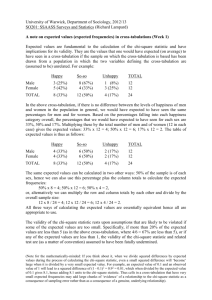
True/False 1. In an experiment involving matched pairs, a sample of
advertisement

True/False 1. In an experiment involving matched pairs, a sample of 14 pairs of observations is collected. The degree of freedom for the t statistic is 12. FALSE 2. In testing the difference between two means from two independent populations, the sample sizes do not have to be equal to be able to use the Z statistic. TRUE 3. In testing the difference between the means of two independent populations, if neither population is normally distributed, then the sampling distribution of the difference in means will be approximately normal provided that the sum of the sample sizes obtained from the two populations is at least 30. TRUE 4. If the limits of the confidence interval of the difference between the means of two normally distributed populations were 0.5 and 2.5 at the 95% confidence level, then we can conclude that we are 95% certain that there is a significant difference between the two population means. FALSE 5. When comparing two population means based on independent random samples, the pooled estimate of the variance is used if both population standard deviations are known. FALSE 6. The chi-square distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is always skewed to the right. TRUE 7. In a contingency table, when all the expected frequencies equal the observed frequencies the calculated X2 statistic equals 1. FALSE 8. In a contingency table, if all of the expected frequencies equal the observed frequencies, then we can conclude that there is a perfect dependence between rows and columns. TRUE 9. In performing a chi-square test of independence, as the difference between the respective observed and expected frequencies decrease, the probability of concluding that the row variable is independent of the column variable increases. TRUE 10. When we carry out a chi-square test of independence, the expected frequencies are based on the alternative hypothesis. FALSE 11. The standard error of the estimate (standard error) is the estimated standard deviation of the distribution of the independent variable (X). FALSE 12. In a simple linear regression model, the coefficient of determination not only indicates the strength of the relationship between independent and dependent variable, but also shows whether the relationship is positive or negative. FALSE 13. When using simple regression analysis, even if there is a strong correlation between the independent and dependent variable we cannot conclude that an increase in the value of the independent variable is associated with an increase in the value of the dependent variable. TRUE 14. The error term is the difference between an individual value of the dependent variable and the corresponding mean value of the dependent variable. FALSE