Atomic Structure Worksheet: Protons, Neutrons, Electrons
advertisement
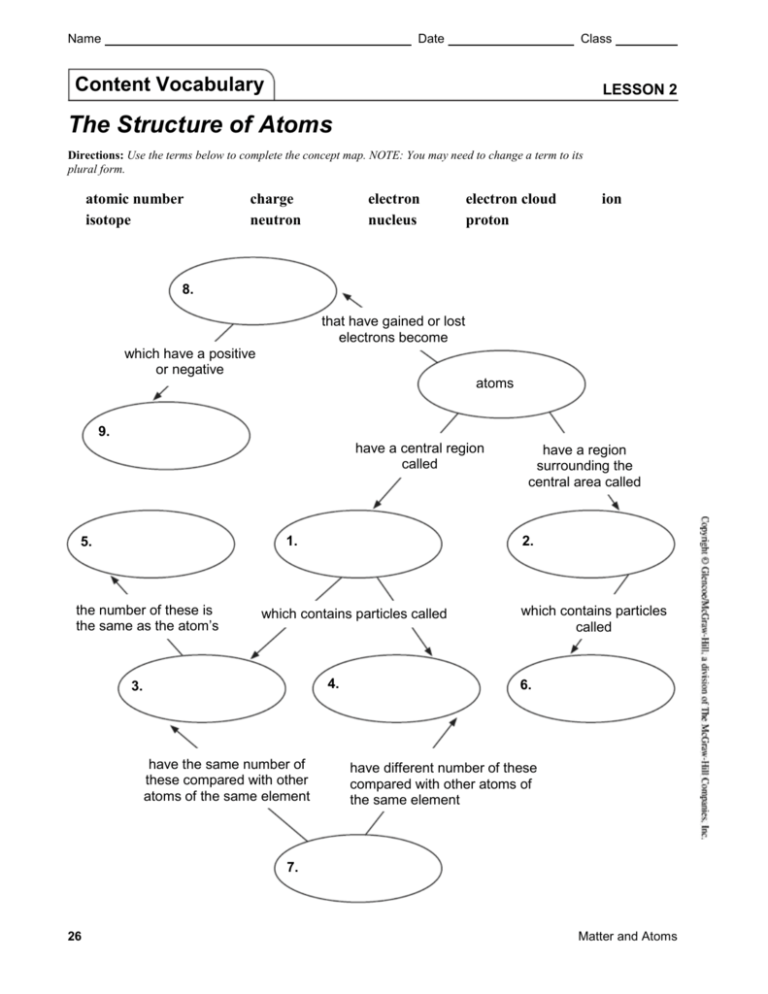
Name Date Class Content Vocabulary LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Directions: Use the terms below to complete the concept map. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. atomic number isotope charge neutron electron nucleus electron cloud proton ion 8. that have gained or lost electrons become which have a positive or negative atoms 9. have a central region called 1. 5. the number of these is the same as the atom’s 2. which contains particles called 4. 3. have the same number of these compared with other atoms of the same element have a region surrounding the central area called which contains particles called 6. have different number of these compared with other atoms of the same element 7. 26 Matter and Atoms Name Date Class Lesson Outline LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms A. The Parts of an Atom 1. Every kind of element is made up of its own kind of . 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small ; the particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. of each of these 3. The region at the center of an atom that contains most of the mass of the atom is called the . a. A positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n) . b. An uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n) . 4. A negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus is called a(n) a. . are much smaller in size than and neutrons, and they move very quickly. b. The region surrounding an atom’s nucleus where one or more electrons are most likely to be found is called a(n) . c. An electron cloud is mostly made up of not a cloud of d. The electrons closest to the electrons farthest from the space; it is . have the least energy; the have the most energy. B. The Size of Atoms 1. All the substances around you, including your body and the air you breathe are made up of millions and millions of . 2. If you could enlarge an atom to be 1 million times larger than its natural size, it would be the size of a(n) same degree would be the size of Matter and Atoms ; this object enlarged to the . 27 Name Date Class Lesson Outline continued C. Differences in Atoms 1. Every atom has a(n) charged nucleus surrounded by a(n) charged electron cloud; however, atoms can have different numbers of , neutrons, and electrons. 2. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element is called the . a. Each has a different atomic number. b. The number of in the nucleus of the atom determines the identity of the atom. 3. One of two or more atoms of an element having the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons is called a(n) . 4. A neutral atom has the same number of as in its nucleus in its electron cloud. a. A neutral atom can gain one or more atom a(n) more charge. , giving the charge; a neutral atom can lose one or , giving the atom a(n) b. An atom that has a charge because it has gained or lost electrons is called a(n) . c. Ions have same number of and are the same element they were before gaining or losing electrons. D. Atoms and Matter 1. All atoms of the same element have the same number of . 2. For each element, the number of and the number of can vary. 3. The properties of an element and the ways its combine are determined mainly by the number and the arrangement of the in its atoms. 28 Matter and Atoms Name Date Class Content Practice A LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Directions: On the line before each definition, write the letter of the term that matches it correctly. Each term is used only once. 1. positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom 2. region surrounding an atom’s nucleus where one or more electrons are often found 3. negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus 4. one or more atoms of an element having the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons A. atomic number B. electron C. electron cloud D. ion E. isotope F. nucleus G. neutron H. proton 5. region at the center of an atom that contains most of the mass of an atom 6. an atom that has a charge because it has gained or lost electrons 7. the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element 8. uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom 30 Matter and Atoms Name Date Class Content Practice B LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that correctly completes each sentence. 1. The nucleus of an atom contains (protons/electrons) and neutrons. 2. The nucleus has a (positive charge/negative charge) and the (least mass/most mass) of the atom. 3. An electron is a (positively charged/negatively charged) particle located outside the nucleus. 4. The modern model of an atom is called the (electron-cloud/nucleus-orbit) model. 5. Electrons that are close to the nucleus have (more energy/less energy) than electrons that are farther from the nucleus. 6. The atomic number is the number of (protons/neutrons) in the nucleus of an atom of an element. 7. Isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of (electrons/neutrons). 8. An ion has a charge because it has gained or lost (protons/electrons). 9. A (positive/negative) ion has more protons than electrons. 10. Adding a(n) (proton/electron) to a neutral atom produces a new element. Matter and Atoms 31 Name Date School to Home Class LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Directions: Use your textbook to respond to each statement. 1. All atoms have the same basic structure. The nucleus is the center region of the atom. Describe the nucleus by identifying the particles that are inside of it, its overall charge, and its mass compared to the mass of an atom. 2. Electrons are one of the components of atoms. They are found in a region of the atom called the electron cloud. Describe electrons by identifying their charge and their relative mass compared to the atom as a whole. 3. Elements are arranged in the periodic table in order of their atomic numbers. Identify what can be learned about an atom of an element if its atomic number is known. 4. Although every atom of an element has the same number of protons, the atoms of an element can vary in other ways. Identify how atoms can vary and what these types of atoms are called. 5. Atoms of an element can gain or lose electrons. An atom that has gained or lost electrons is called an ion. Describe how gaining an electron changes the overall charge on an atom. Matter and Atoms 35 Name Date Key Concept Builder Class LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Key Concept Where are protons, neutrons, and electrons located in an atom? Directions: Label this diagram by writing the correct term on each line. 1. 2. 3. Directions: Answer each question or respond to each statement on the lines provided. 4. Which particle in an atom has a positive charge? 5. Which particle in an atom has no charge? 6. Which particle in an atom has a negative charge? 7. Where is most of the mass of an atom found? 8. Describe the structure of the atom in the diagram above. How many of each type of particle does the atom have? 36 Matter and Atoms Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Key Concept How is the atomic number related to the number of protons in an atom? Directions: On each line, write the term or phrase that correctly completes each sentence. 1. The is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element. 2. You can identify an element if you know its atomic number or 3. In the periodic table, the atomic number of an element is the above its symbol. Directions: Complete the chart with the correct numbers on the lines provided. Element Atomic Number magnesium carbon oxygen Matter and Atoms 12 Number of Protons Number of Electrons 4. 6. 5. 6 8 7. 6 8. 37 Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 2 The Structure of Atoms Key Concept What effect does changing the number of particles in an atom have on the atom’s identity? Directions: Complete the chart with the correct terms or numbers from the word bank on the lines provided. Some terms or numbers may be used more than once or not at all. isotope 5 negative ion 6 7 new element 9 8 positive ion 10 12 11 Possible Changes in Atoms Neutron Atom Change carbon 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons add one proton carbon 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons add one neutron carbon 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons carbon 6 protons 6 neutrons 6 electrons 38 add one electron lose one electron Results 1. 2. protons 3. 4. neutrons electrons 5. 6. protons 7. neutrons 8. electrons 9. 10. protons 11. neutrons 12. electrons 13. 14. protons 15. neutrons 16. electrons Matter and Atoms Lesson 2: The Structure of Atoms A. The Parts of an Atom 1. Every kind of element is made up of its own kind of atoms. 2. Atoms are composed of several basic types of very small particles; the number of each of these particles gives the different kinds of atoms their unique identity. 3. The region at the center of an atom that contains most of the mass of the atom is called the nucleus. a. A positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n) proton. b. An uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom is called a(n) neutron. 4. A negatively charged particle that occupies the space in an atom outside the nucleus is called a(n) electron. a. Electrons are much smaller in size than protons and neutrons, and they move very quickly. b. The region surrounding an atom’s nucleus, where one or more electrons are most likely to be found, is called a(n) electron cloud. c. An electron cloud is mostly made up of empty space; it is not a cloud of charge. d. The electrons closest to the nucleus have the least energy; the electrons farthest from the nucleus have the most energy. B. The Size of Atoms 1. All the substances around you, including your body and the air you breathe are made up of millions and millions of atoms. 2. If you could enlarge an atom to be 1 million times larger than its natural size, it would be the size of a(n) orange; this object enlarged to the same degree would be the size of Earth. C. Differences in Atoms 1. Every atom has a(n) positively charged nucleus surrounded by a(n) negatively charged electron cloud; however, atoms can have different numbers of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 2. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of an element is called the atomic number. a. Each element has a different atomic number. b. The number of protons in the nucleus of the atom determines the identity of the atom. 3. One of two or more atoms of an element having the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons is called a(n) isotope. 4. A neutral atom has the same number of protons in its nucleus as electrons in its electron cloud. a. A neutral atom can gain one or more electrons, giving the atom a(n) negative charge; a neutral atom can lose one or more electrons, giving the atom a(n) positive charge. b. An atom that has a charge because it has gained or lost electrons is called a(n) ion. c. Ions have same number of protons and are the same element they were before gaining or losing electrons. D. Atoms and Matter 1. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. 2. For each element, the number of electrons and the number of neutrons can vary. 3. The properties of an element and the ways its atoms combine are determined mainly by the number and the arrangement of the particles in its atoms. Content Vocabulary (page 26) 1. nucleus 2. electron cloud 3. protons 4. neutrons 5. atomic number 6. electrons 7. isotopes 8. ions 9. charge Content Practice A (page 30) 1. H 2. C 3. B 4. E 5. F 6. D 7. A 8. G Content Practice B (page 31) 1. protons 2. positive charge, most mass 3. negatively charged 4. electron-cloud 5. less energy 6. protons 7. neutrons 8. electrons 9. positive 10. proton School to Home (page 35) 1. The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. It has an overall neutral charge, and it contains most of the mass of the atom. 2. Electrons have a negative charge. They are very small; their mass is very tiny when compared to the mass of the atom as a whole. 3. An element’s atomic number tells the number of protons in each atom of the element. 4. Atoms can vary by the number of neutrons in their nucleus. These atoms are called isotopes. 5. Gaining an electron gives an atom an overall negative charge. Key Concept Builder (page 36) 1. proton 2. electron 3. neutron 4. proton 5. neutron 6. electron 7. in the nucleus 8. It has two protons, two neutrons, and two electrons. Key Concept Builder (page 37) 1. atomic number 2. the number of protons in its atoms 3. whole number 4. 12 5. 12 6. 6 7. 8 8. 8 Key Concept Builder (page 38) 1. new element 2. 7 3. 7 4. 7 5. isotope 6. 6 7. 7 8. 6 9. positive ion 10. 6 11. 6 12. 7 13. negative ion 14. 6 15. 6 16. 5