Review Jeopardy
advertisement
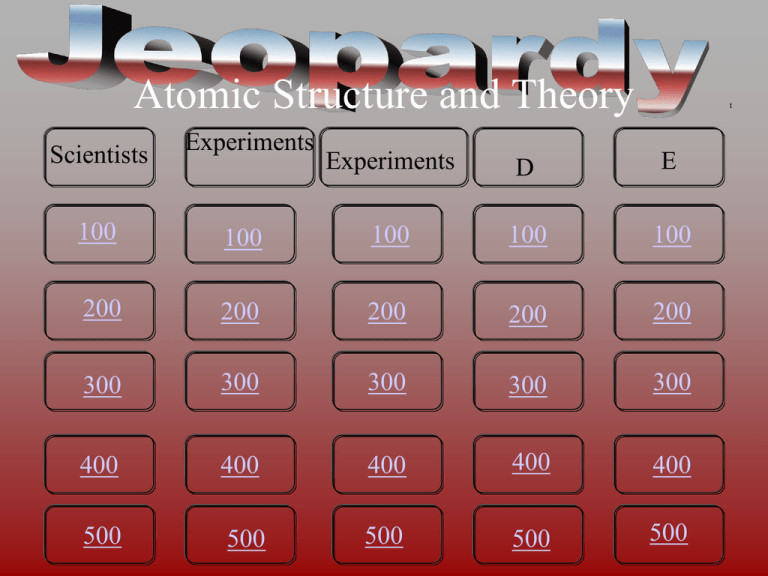
Atomic Structure and Theory Scientists Experiments 100 t Experiments D E 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 I-100 Thought of the atom as “plum-pudding” . Answer I-200 Thought of the atom as a “planetary” model . Answer I-300 This scientist first discovered the nucleus. . Answer I-400 Thought of the “billiard ball” model for the atom . Answer I-500 Provided a mathematical relationship describing the 3D space that an electron can occupy . Answer II-100 First modern scientist that said that matter is composed of indestructible and indivisible atoms . Answer II-200 isotopes are atoms of one kind of element that contain different numbers this subatomic particle . Answer II-300 When you have the same element, it is guaranteed that you have the same of this (these) subatomic particles. . Answer II-400 This law states that the total mass of a chemical reaction must remain the same. . Answer II-500 • Which of these parts of Dalton's Atomic theory were proven incorrect? • a.) Atoms of different elements differ in their physical and chemical properties • b.) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds • c.) All matter is made of indivisible and indestructible atoms. • d.) Chemical reactions consist of the combination, separation, or rearrangement of atoms • e.) All atoms of a given element are identical in their . properties. chemical and physical Answer III-100 what the Au foil experiment showed about the volume of an atom . Answer III-200 the charge carried by alpha particles and the charge carried by the nucleus . Answer III-300 particles that make up most of the mass of the atom and where they are found . Answer III-400 a subatomic particle that was discovered by J.J. Thompson in the late 1800's . Answer III-500 Describe why the spectral glasses gave out different colored lines . Answer IV-100 the element with 32 electrons and 73 neutrons . Answer IV-200 the mass number of the most likely most abundant isotope of chlorine, Cl . Answer IV-300 the number of electrons in a copper atom with a postive two charge . Answer IV-400 all atoms of the same element have the same…; give name and particle name . Answer IV-500 the isotope by which all other isotopes’ masses are measure; the standard mass . Answer V-100 the two characteristics of isotopes of one kind of element that are needed to determine the average atomic mass of the element . Answer V-200 the number on the periodic table that represents the AAM . Answer V-300 235 70 Q 2 Based on the following symbol, how many protons, neutrons and electrons does it have 235 70 . Q 2 Answer V-400 How many protons, neutrons and electrons is in a N-15 isotope with a negative 3 charge . Answer V-500 Why are the AAM’s not whole numbers? . Answer I-100 A • JJThomson Game board I-200 A • Bohr Game board I-300 A • Rutherford Game board I-400 A • Dalton Game board I-500 A • Schrodinger Game board II-100 A • Dalton’s Atomic Theory Game board II-200 A • Neutron Game board II-300 A • Protons Game board II-400 A • Law of Conservation of Mass Game board II-500 A • The third and 5th one Game board III-100 A • it is mostly empty space Game board III-200 A • positive Game board III-300 A • neutrons and protons; the nucleus Game board III-400 A • electron Game board III-500 A • The electricity gives the gas energy and promotes the electron to a higher energy level. When it goes back to a lower energy level it gives off the energy as the form of light which we see as different wavelengths/colors. Game board IV-100 A • germanium Game board IV-200 A • 35 Game board IV-300 A • 27 Game board IV-400 A • atomic number; protons Game board IV-500 A • carbon-12 Game board V-100 A • mass of each isotope and the relative percent abundance of each isotope Game board V-200 A • the one with the decimal! Game board V-300 A • 70 Protons, 165 Neutrons, 68 electrons Game board V-400 A • 7 protons, 8 neutrons, 10 electrons Game board V-500 A • the AAM is based on the weighted average of all isotopes of the element Game board