tracking_calculating - Hertfordshire Grid for Learning
advertisement

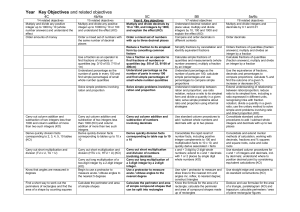
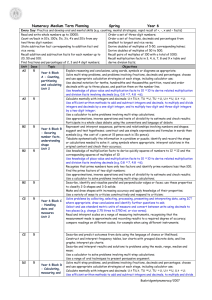
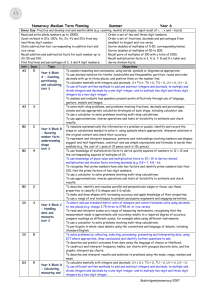
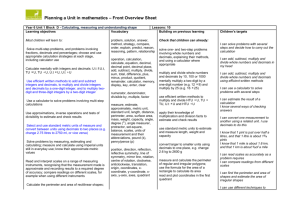
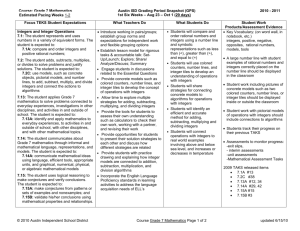
Tracking Maths Objectives by Year – Calculating – Year 6 to 9 Year 6 Calculate mentally with integers and decimals: U.t ± U.t, TU × U, TU ÷ U, U.t × U, U.t ÷ U Progression into Year 7 Consolidate and extend mental methods of calculation to include decimals, fractions and percentages Year 7 Extend mental methods of calculation to include decimals, fractions and percentages Year 8 Year 9 Exceptional Performance Add, subtract, multiply and divide integers Generate terms of a sequence using term-to-term and position-to-term definitions of the sequence, on paper and using ICT; write an expression to describe the nth term of an arithmetic sequence Use efficient written methods to add and subtract integers and decimals, to multiply and divide integers and decimals by a one-digit integer, and to multiply two-digit and threedigit integers by a two-digit integer Use standard column procedures to add and subtract integers and decimals, and to multiply two-digit and three-digit integers by a one-digit or twodigit integer; extend division to dividing three-digit integers by a twodigit integer Multiply and divide three-digit by two-digit whole numbers; extend to multiplying and dividing decimals with one or two places by single-digit whole numbers Use standard column procedures for multiplication and division of integers and decimals, including by decimals such as 0.6 or 0.06; understand where to position the decimal point by considering equivalent calculations Relate fractions to multiplication and division (e.g. 6 ÷ 2 = 1/2 of 6 = 6 × 1/2); express a quotient as a fraction or decimal (e.g. 67 ÷ 5 = 13.4 or 132/5); find fractions and percentages of wholenumber quantities (e.g. 5/8 of 96, 65% of £260) Calculate percentage increases or decreases and fractions of quantities and measurements (integer answers) Break a complex calculation into simpler steps, choosing and using appropriate and efficient operations and methods Use the equivalence of fractions, decimals and percentages to compare proportions; calculate percentages and find the outcome of a given percentage increase or decrease Use a calculator to solve problems involving multi-step calculations Use bracket keys and the memory of a calculator to carry out calculations with more than one step; use the square root key Check a result by considering whether it is of the right order of magnitude Know and use the index laws for multiplication and division of positive integer powers Understand and use proportionality and calculate the result of any proportional change using multiplicative methods Tracking Maths Objectives by Year – Calculating – Year 6 to 9 Understand how the commutative, associative and distributive laws, and the relationships between operations, including inverse operations, can be used to calculate more efficiently; use the order of operations, including brackets Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables Substitute integers into simple formulae Know and use the order of operations and understand that algebraic operations follow the same conventions and order as arithmetic operations Simplify or transform linear expressions by collecting like terms; multiply a single term over a bracket Change the subject of a formula Construct and solve linear equations with integer coefficients, using an appropriate method Square a linear expression and expand the product of two linear expressions of the form x + n; establish identities Solve a pair of simultaneous linear equations by eliminating one variable; link a graphical representation of an equation or a pair of equations to the algebraic solution Examine critically the results of a statistical enquiry and justify choice of statistical representation in written presentations Identify possible sources of bias in a statistical enquiry and plan how to minimise it