M_7thGr_1st_6wks_GPS_1011
advertisement
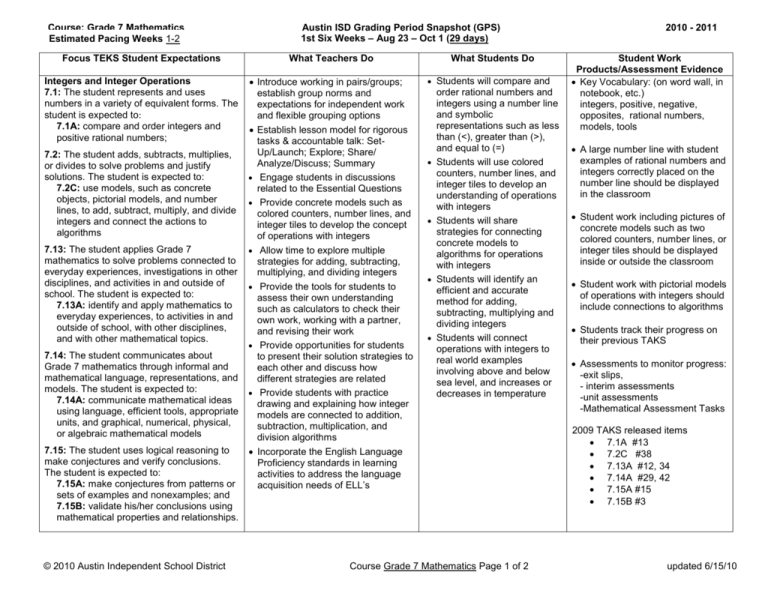
Course: Grade 7 Mathematics Estimated Pacing Weeks 1-2 Focus TEKS Student Expectations Integers and Integer Operations 7.1: The student represents and uses numbers in a variety of equivalent forms. The student is expected to: 7.1A: compare and order integers and positive rational numbers; 7.2: The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, or divides to solve problems and justify solutions. The student is expected to: 7.2C: use models, such as concrete objects, pictorial models, and number lines, to add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers and connect the actions to algorithms 7.13: The student applies Grade 7 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school. The student is expected to: 7.13A: identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics. 7.14: The student communicates about Grade 7 mathematics through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models. The student is expected to: 7.14A: communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models 7.15: The student uses logical reasoning to make conjectures and verify conclusions. The student is expected to: 7.15A: make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and nonexamples; and 7.15B: validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships. © 2010 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) 1st Six Weeks – Aug 23 – Oct 1 (29 days) What Teachers Do Introduce working in pairs/groups; establish group norms and expectations for independent work and flexible grouping options Establish lesson model for rigorous tasks & accountable talk: SetUp/Launch; Explore; Share/ Analyze/Discuss; Summary Engage students in discussions related to the Essential Questions Provide concrete models such as colored counters, number lines, and integer tiles to develop the concept of operations with integers Allow time to explore multiple strategies for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers Provide the tools for students to assess their own understanding such as calculators to check their own work, working with a partner, and revising their work Provide opportunities for students to present their solution strategies to each other and discuss how different strategies are related Provide students with practice drawing and explaining how integer models are connected to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division algorithms What Students Do Students will compare and order rational numbers and integers using a number line and symbolic representations such as less than (<), greater than (>), and equal to (=) Students will use colored counters, number lines, and integer tiles to develop an understanding of operations with integers Students will share strategies for connecting concrete models to algorithms for operations with integers Students will identify an efficient and accurate method for adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing integers Students will connect operations with integers to real world examples involving above and below sea level, and increases or decreases in temperature Incorporate the English Language Proficiency standards in learning activities to address the language acquisition needs of ELL’s Course Grade 7 Mathematics Page 1 of 2 2010 - 2011 Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence Key Vocabulary: (on word wall, in notebook, etc.) integers, positive, negative, opposites, rational numbers, models, tools A large number line with student examples of rational numbers and integers correctly placed on the number line should be displayed in the classroom Student work including pictures of concrete models such as two colored counters, number lines, or integer tiles should be displayed inside or outside the classroom Student work with pictorial models of operations with integers should include connections to algorithms Students track their progress on their previous TAKS Assessments to monitor progress: -exit slips, - interim assessments -unit assessments -Mathematical Assessment Tasks 2009 TAKS released items 7.1A #13 7.2C #38 7.13A #12, 34 7.14A #29, 42 7.15A #15 7.15B #3 updated 6/15/10 Course: Grade 7 Mathematics Estimated Pacing Weeks 3-6 Focus TEKS Student Expectations Numerical Representations: 7.1: The student represents and uses numbers in a variety of equivalent forms. The student is expected to: 7.1C: represent squares and square roots using geometric models. 7.2: The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, or divides to solve problems and justify solutions. The student is expected to: 7.2E: simplify numerical expressions involving order of operations and exponents. Representing, Multiplying, and Dividing Fractions and Decimals: 7.1: The student represents and uses numbers in a variety of equivalent forms. The student is expected to: 7.1A: previously stated 7.1B: convert between fractions, decimals, whole numbers, and percents mentally, on paper, or with a calculator. 7.2: The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, or divides to solve problems and justify solutions. The student is expected to: 7.2A: represent multiplication and division situations involving fractions and decimals with models, including concrete objects, pictures, words, and numbers. 7.2B: use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve problems involving fractions and decimals. 7.2F: select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections. 7.2G: determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem. 7.13: The student applies Grade 7 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school. 7.13B, C, D: develop and use a problemsolving model and a variety of strategies using mathematical tools. © 2010 Austin Independent School District Austin ISD Grading Period Snapshot (GPS) 1st Six Weeks – Aug 23 – Oct 1 (29 days) What Teachers Do Continue to provide opportunities for working in pairs/groups; establish group norms and expectations for independent work and flexible grouping options. What Students Do Students will connect Communicate clear expectations for quality work products Engage students in discussions related to the Essential Questions Provide concrete and pictorial models for understanding square numbers and their roots Display and reinforce a strategy for remembering and applying the order of operations to simplify expressions Provide concrete models and manipulatives for representing and ordering fractions and decimals Provide opportunities for students to convert between fractions, decimals, and percents Provide scaffolding activities such as concrete and pictorial models for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions and decimals Incorporate the English Language Proficiency standards in learning activities to address the language acquisition needs of ELL’s models of squares and square roots to numerical representations Students will simplify numerical expressions using the order of operations Students will relate models of equivalent forms of rational numbers to the numerical representations Students will create equivalent forms of rational numbers given any one representation (fractions, decimals, and percents) Students will use manipulatives and pictorial models of fractions and decimals to represent multiplication and division problems Students will add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions and decimals in problem situations Students will justify solutions to rational number problems verbally and in writing Students will determine if answers to rational number problems are reasonable Differentiate instruction for struggling learners using mathematical manipulatives and flexible grouping strategies Course Grade 7 Mathematics Page 2 of 2 2010 - 2011 Student Work Products/Assessment Evidence Key Vocabulary: (on word wall, in notebook, etc.) square numbers, square roots, area of a square, order of operations, parentheses, exponents, factors, product, grouping, sharing, dividend, divisor, quotient Posters created by students with the area of the squares and square roots (side length) labeled Student work with pictorial models of fractions and decimals for ordering, representing equivalent forms, and adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing Student work posters with strategies for remembering and applying the order of operations Assessments to monitor progress: -exit slips, - interim assessments -unit assessments -Mathematical Assessment Tasks -white boards or write and wipe worksheets 2009 TAKS released items 7.1C #7 7.2E #26 7.1B #2 7.2A #43 7.2B #10 7.2F #46 7.2G #30 7.13B #6, 48 7.13C #31 updated 6/15/10