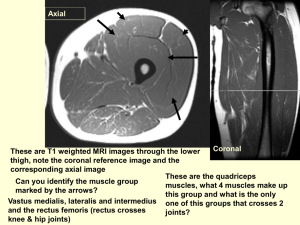
Frontal nerve is branch of which of following
advertisement

Frontal nerve is branch of which of following A. Trochlear nerve B. Vagus nerve C. Optic nerve D. Facial nerve E. Ophthalmic nerve ANSWER: E Bleeding from dural sinuses cant arrest because: A. High pressure in dural sinuses B. High speed of blood flow C. Many venous tributaries D. Negative pressure in dural sinuses E. They are not collasible ANSWER: E What is syntopy: A. Anatomical structures attitude to body parts B. Anatomical structures attitude to skeleton bones C. Anatomical structures attitude to organism regions D. Variants of organs blood supply E. Relationship between organs ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries is damage in case of temporal region injury: A. Anterior cerebral artery B. Medial cerebral artery C. Anterior meningeal artery D. Superficial temporal artery E. Medial meningeal artery ANSWER: E In which layer of calvarium hematoma has bump form: A. Skin B. Subaponeurotical tissue C. Subperiosteal tissue D. Diploe substance E. Subcutaneous tissue ANSWER: E Which of the following layers form scalping flap: A. External lamina of bone, diploe, periosteum B. Periosteum, subperiosteal tissue, bone C. Epicranial aponeurosis, subaponeurotical tissue D. Subcutaneous tissue, epicranial aponeurosis, subaponeurotical tissue E. Skin, subcutaneous tissue, epicranial aponeurosis ANSWER: E The epicranial aponeurosis locates between which of the following structures: A. Left and right temporal bones B. Frontal and occipital muscles C. Left and right temporal muscles D. Frontal and occipital bones E. Frontal and occipital bellies of frontooccipital muscle ANSWER: E The scalping flap consist of following layers A. Periosteum, subperiosteal tissue, bone B. Skin, subcutaneous tissue, epicranial aponeurosis, subaponeurotical tissue C. Subcutaneous tissue, epicranial aponeurosis, subaponeurotical tissue D. External lamina of bone, diploe, periosteum E. Skin, subcutaneous tissue, epicranial aponeurosis ANSWER: E Middle meningeal artery locates in A. Subperiostal tissue B. Subarachnoid space C. Subdural space D. Epidural and subdural space E. Epidural space ANSWER: E Magendies foramen connects which of the following structures A. 4-th venticle with subarachnoid space of spinal cord B. 2-nd ventricle with 3-rd C. 3-rd venticle with 4-th D. Later ventricles of cerebrum with 3-rd E. 4-th venticle with subarachnoid cavity ANSWER: E Which anatomical structures pass through the round foramen A. Maxillary and mandibular nerve B. Ophthalmic and mandibular nerve C. Ophthalmic and maxillary nerve D. Optic nerve, ophthalmic artery and vein E. Maxillary nerve ANSWER: E Which of the following structures can be damaged during antrotomy in case of posterior border breach: A. Facial nerve B. Cavernous sinus C. Maxillary nerve D. Rectal sinus E. Sigmoid sinus ANSWER: E Which of the following nerves pass through the cavernous sinus A. Optic nerve B. Maxillary nerve C. Accessory nerve D. Olfactory nerves E. Oculomotor nerve ANSWER: E In the area of the infraorbital foramen we can do anesthesia of? A. The first branch of the trigeminal nerve B. The third branch of the trigeminal nerve C. The first branch of the trigeminal nerve D. The facial nerve E. Second branch of the trigeminal nerve ANSWER: E Diploe locates A. under internal laminae of skull bone B. Under the epicranial aponeurosis C. Under the temporal muscle D. Between laminas of the temporal aponeurosis E. Between external and internal laminae of skull bone ANSWER: E Which of the following vessels locates in subaponeurotical tissue of frontoparietooccipital region: A. Occipital artery B. Temporal superficial artery C. Temporal superficial artery and vein D. Posterior auricular artery E. No vessels ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries furnish circulation of occipital region: A. Left and right occipital arteries B. Posterior cerebral artery C. Temporal and occipital arteries D. Left and right vertebral arteries E. Left and right occipital arteries, posterior auricular arteries ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries is source of occipital artery: A. Internal carotid artery B. Medial temporal artery C. Auricular arteries D. Vertebral arteries E. External carotid artery ANSWER: E Where locates the auriculotemporal nerve: A. In the epidural space of temporal region B. In the interaponeurotical tissue of temporal region C. In the subaponeurotical tissue of temporal region D. In the subperiosteal tissue of temporal region E. In the subcutaneous tissue of temporal region ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries is source of supratrochlear artery: A. Ethmoidal artery B. Anterior cerebral artery C. Anterior meningeal artery D. Medial cerebral artery E. Ophthalmic artery ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries is source of deep temporal artery: A. Temporal superficial artery B. Facial artery C. External carotid artery D. Internal carotid artery E. Maxillary artery ANSWER: E Tendinous septa locate in which of the following calvarium fat tissues: A. Subperiosteal B. Subaponeurotical C. Interaponeurotical D. All cellular spaces E. Subcutaneous ANSWER: E A skull fracture involving the right foramen spinosum would probably cause: A. Extradural bleeding from the internal carotid artery B. Loss of taste over the posterior 1/3 of the tongue on the right side C. Extradural bleeding from emissary sphenoid vein D. Right facial paralysis E. Extradural bleeding from the middle meningeal artery ANSWER: E Which of the following structures passes through the jugular foramen? A. Cranial nerve V3 B. Ophthalmic artery and the central retinal vein C. Cranial nerve XII D. Vertebral arteries and the brain stem E. Cranial nerves IX ANSWER: E Which of the following nerves pass through the cavernous sinus A. Olfactory nerves B. Optic nerve C. Mandibular nerve D. Accessory nerve E. Abducent nerve ANSWER: E Venous return from temporal superficial vein realize in: A. Angular vein B. Facial vein C. Maxillary vein D. Parietal vein E. Retromandibular vein ANSWER: E When permanent arrest of bleeding from skull bones is correct: A. Coagulation B. Hemostatic sponge C. Hot physiologic saline D. Vessels ligation by catgut E. Rodding ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries is source of zygomaticoorbital artery: A. Ophthalmic artery B. Temporal superficial artery C. Facial artery D. Internal carotid artery E. Maxillary artery ANSWER: E How realize the permanent arrest of bleeding from meningeal arteries: A. By the catgut ligation B. By the rubbing of wax C. By the using of hot physiologic saline D. By the electrocoagulation E. By the clipping ANSWER: E Penetretive skull wound is: A. Damage of skull bone B. Damage of internal lamina of skull bones C. Damage of dura mater and arachnoid of brain D. Damage of all meninges E. Damage of dura mater of brain ANSWER: E Frontal nerve is branch of which of following: A. Facial nerve B. Abducent nerve C. Trochlear nerve D. Optic nerve E. Ophthalmic nerve ANSWER: E Greater occipital nerve is branch of which of the following nerve: A. Vagus nerve B. Third spinal nerve C. First spinal nerve D. Cervical plexus E. Second spinal nerve ANSWER: E Which of the following statements about the scalp is not true? A. Loose areolar tissue occupies the subaponeurotic space B. The prolific arterial blood supply of the scalp is in the dense subcutaneous tissue C. All of the above statements are true. D. The subaponeurotic layer is sometimes referred to as the danger space of the scalp E. The scalp is innervated by the infraorbital nerve ANSWER: E Lymphatic outflow from the parietal region of calvarium realize to which of the following lymph nodes: A. Parotid lymph nodes B. Deep parotid lymph nodes C. Facial lymph nodes D. Occipital lymph nodes E. Retroauricular lymph nodes ANSWER: E In sponge substance of skull bone locates which of the following structures: A. Venous sinuses B. Emissary veins C. Cranial nerves D. Deep arteries of calvarium E. Diploidic veins ANSWER: E Cecal foramen locates in: A. Near optic chiasm. B. Middle cranial fossa C. Posterior cranial fossa D. Sphenoid bone E. Anterior cranial fossa ANSWER: E Pacchionian granulations is formations of which of the following structures: A. Dura mater of brain B. Pericranium C. Pia mater of brain D. Venous sinuses E. Arachnoid of brain ANSWER: E Which anatomical structure pass through the spinous foramen: A. Ethmoidal artery B. Anterior meningeal artery C. Middle cerebral artery D. Posterior meningeal artery E. Middle meningeal artery ANSWER: E Indicate brain structures, which form venous sinuses: A. Pericranium B. Epidural space C. Pia mater encephali D. Arachnoid encephali E. Dura mater encephali ANSWER: E Inferior sagittal sinus locates on: A. Upper edge of falx of cerebrum B. Edge of internal occipital tuberosity C. Sulcus of transverse sinus of occipital bone D. Edge of Turkish saddle E. Lower edge of falx of cerebrum ANSWER: E Rectal sinus locates on: A. Edge of falx of cerebellum B. Upper edge of falx of cerebrum C. Edge of Turkish saddle D. Sulcus of transverse sinus of occipital bone E. Connective place of falx and tentorium of cerebellum ANSWER: E How realize the arrest of bleeding from cerebral vessels: A. By the catgut ligation B. By the rubbing of wax C. By the using of hot physiologic saline D. By the electrocoagulation E. By the clipping ANSWER: E Subcutaneous emphysema is possible in case of damage of which of the following structures: A. Turkish saddle B. Sigmoid sinus C. Cavernous sinus D. Superior sagittal sinus E. Frontal sinus ANSWER: E Which of the following anatomical structures produces the liquor: A. Pacchionian granulations B. Lateral ventricles of cerebrum C. Subarachnoid space D. Third ventricle of cerebrum E. Vascular plexuces ANSWER: E Indicate the reason of convergent strabismus: A. Damage of facial nerve B. Damage of optic nerve C. Ophthalmic vein thrombosis D. Damage of ophthalmic artery E. Cavernous sinus thrombosis ANSWER: E Which of the following anatomical structures pass through the great occipital foramen: A. Temporal superficial artery B. Occipital artery C. frontal artery D. Great occipital nerve E. Left vertebral artery ANSWER: E Liquor passes from 4-th ventricle of cerebrum to subarachnoid space through which of the following foramen: A. Interventricular Monros foramen B. Lushkas foramen C. Cerebral Silviis aqueduct D. Rolands foramen E. Magendies foramen ANSWER: E Inflammatory process in case of purulent parotitis spreads to: A. Internal ear B. Middle cranial fossa C. Temporopterygoid space D. Subcutaneous tissue of temporal region E. External acoustic meatus ANSWER: E Which of the following structures pass through the parotid gland: A. Facial vein B. External jugular vein C. Temporal superficial vein D. Internal jugular vein E. Retromandibular vein ANSWER: E The nerve of the pterygoid canal is formed by the: A. Greater and lesser petrosal nerves B. Greater petrosal nerve alone. C. Greater, lesser and deep petrosal nerves D. Lesser and deep petrosal nerves E. Greater and deep petrosal nerves ANSWER: E Complication in case of purulent parotitis: A. Damage of proper parotid fascia B. Pus spread to the temporopterygoid space C. Dysphagy D. Neuritis of vagus nerve E. Paresis of muscles of facial expression on damaged side ANSWER: E Interfascial cellular space of temporopterygoid space locates in which of the following head regions: A. Temporal region B. Oral cavity. C. Buccal region D. Occipital region E. Deep facial region ANSWER: E During swallowing one of the following muscles raises the soft palate A. Inferior constrictor B. Palatopharyngeus C. Superior constrictor D. Palatoglossus E. Levator veli palatine ANSWER: E A lesion that compresses the neural contents within the right jugular foramen might result in: A. Loss of pain from anterior two-thirds of the tongue B. Inability to protrude tongue C. Sensory loss from skin overlying the zygomatic bone D. Inability to turn chin upward and to the left E. Inability to elevate soft palate ANSWER: E Which of the following anatomical structures pass through the great occipital foramen: A. Occipital artery and vein B. Spinal cord C. Occipital artery D. Occipital vein E. Medulla oblongata ANSWER: E Which of the following nerves is usually the first extracranial branch of the facial nerve? A. Cervical branch B. Marginal mandibular branch C. Buccal branch D. Zygomatic branch E. Posterior auricular ANSWER: E Which of the following nerves realizes the innervetion of dura mater of brain: A. Facial nerve B. Olfactory nerve C. Hypoglossal nerve D. Optic nerve E. Accessory nerve ANSWER: E The anterior ethmoidal sinuses drain into the A. Lacrimal sac B. Superior meatus of the nose C. Inferior meatus of the nose D. Sphenoid sinus E. Middle meatus of the nose ANSWER: E The deep portion of the parotid fascia forms which of the following? A. Buccopharyngeal fascia B. Spenomandibular ligament C. Pterygomandibular raphe D. Carotid sheath E. Stylomandibular ligament ANSWER: E The medial pterygoid muscle assists which of the following muscles in protrusion of the mandible? A. Mylohyoid B. Sphenomeniscus C. Geniohyoid D. Temporalis E. Lateral pterygoid ANSWER: E The motor root of the trigeminal nerve supplies all of the following muscles except the: A. Masseter B. Tensor veli palatini C. Mylohyoid D. Anterior belly of the digastric E. Buccinator ANSWER: E The pterygoid plexus receives tributaries from the: A. Sphenopalatine vein B. Deep temporal vein C. Middle meningeal vein D. Inferior alveolar vein E. All of these. ANSWER: E Tributaries of the internal jugular vein include the: A. Common facial vein B. Inferior petrosal sinus C. Middle meningeal vein D. Inferior alveolar vein E. All of these ANSWER: E Each of the following muscle is attached to the mastoid process except the: A. sternocleidomastoid muscle B. Splenius capitis muscle C. Digastric muscle D. Longus capitis muscle E. Longus cervicis muscle ANSWER: E Which of the following branches does not arise from the facial artery? A. Labial B. Tonsillar C. Submental D. Submandibular E. Stylomastoid ANSWER: E Where is place for cervical vago-sympathetic block after O. Vyshnevskyy? A. Between sternocleidomastoid muscles B. In the corner between clavicle and external edge of sternocleidomastoid muscle C. Jugular notch D. 3 cm above the mid-clavicle E. Intersection of the posterior edge of sternocleidomastoid with external jugular vein ANSWER: E Blood supplying of the cervical part of esophagus is realized by: A. Thyrocervical trunk B. Costocervical trunk C. Superior thyroid artery D. Inferior laryngeal artery E. Inferior thyroid artery ANSWER: E Which of the following anatomical structures takes part in forming of dangerous area, that located on posterior surface of lateral lobes of thyroid gland? A. Vagus nerve B. Superior laryngeal nerve C. Inferior laryngeal artery D. Superior laryngeal artery E. Recurrent laryngeal nerve ANSWER: E The medial wall of the pterygopalatine fossa is formed by which of the following bones? A. Lateral pterygoid plate B. Medial pterygoid plate C. Maxilla D. Palatine and maxilla E. Greater wing of sphenoid ANSWER: E Each of the following structures empties or opens into the middle nasal meatus except the: A. Middle ethmoidal air cells B. Maxillary sinus C. Frontal sinus D. Anterior ethmoidal air cells E. Sphenoid sinus ANSWER: E In which of the following bones are the foramen rotundum, ovale, and spinosum located? A. Frontal B. Ethmoid C. Maxillary D. Temporal E. Sphenoid ANSWER: E The primary action of the muscle that originates mostly from the medial aspect of the lateral pterygoid plate is to: A. Retrude (retract) the mandible B. Elevate the soft palate C. Protrude (protract) the mandible D. Tense the soft palate E. Elevate the mandible ANSWER: E After entering the submandibular triangle, the lingual artery passes immediately deep to which of the following muscles? A. Genioglossus B. Anterior belly of the digastric C. Mylohyoid D. Styloglossus E. Hyoglossus ANSWER: E Which of the following structures lies parallel and immediately deep to the carotid sheath in the neck? A. Superior ramus of the ansa cervicalis B. Trachea C. Vagus nerveS D. Internal jugular vein E. Sympathetic trunk ANSWER: E Which of the following veins normally is a tributary to the subclavian vein A. Inferior thyroid B. Lingual C. Facial D. Maxillary E. External jugular ANSWER: E Branches of which of the following nerves takes part in forming of nervous plexus of thyroid gland: A. Glossopharyngeal nerve B. Accesory nerve C. None of these D. Vagus nerve E. Superior laryngeal nerve ANSWER: E Rima glottidis A. Gap between B. Gap between C. In front of D. Gap between E. Gap between behind ANSWER: E is: the vocal folds in front and thyroid cartilages behind the vocal folds and epiglottis vocal folds the vocal folds the vocal folds in front and vocal processes arytenoid cartilages The subclavian vein joins the internal jugular vein to form the brachiocephalic vein at which of these structures? A. Behind the coracoclavicular joint B. Behind the acromioclavicular joint C. In front of sternal end of the clavicle D. In front of the coracohumeral ligament E. Behind the sternal end of the clavicle ANSWER: E An aneurysm (sac-like dilatation) on the ascending aorta also involves the anterior sinus. Which of the following is anatomically unlikely? A. Erosion into the pulmonary artery B. Involvement of the right coronary artery C. Rupture into the pericardium D. Extension forward to erode the sternum E. Pressure on the recurrent laryngeal nerve causing hoarseness ANSWER: E The esophageal hiatus transmits the esophagus and the: A. Superior phrenic artery B. Thoracic duct C. Lesser splanchnic nerve D. Greater splanchnic nerve E. Vagal nerve trunks ANSWER: E Branches of the internal thoracic artery furnish blood supply to the: A. breast B. pericardium C. diaphragm D. abdominal muscles E. all are correct ANSWER: E Ossification of the parts of the body of the sternum usually is complete by age (in years): A. 1 B. 3 C. 6 D. 15 E. 21 ANSWER: E The following statements concerning the main bronchi are correct except which? A. The right main bronchus is wider than the left main bronchus B. The right main bronchus is shorter than the left main bronchus C. The right main bronchus is m than the left main bronchus D. The left main bronchus passes to the left in front of the esophagus E. The left main bronchus gives off the superior lobar bronchus before entering the hilum of the lung. ANSWER: E The superficial layer of cervical fascia splits into two sheets to enclose which of the following muscles? A. Sternothyroid B. Anterior scalene C. Semispinals capitis D. Mylohyoid E. Trapezius ANSWER: E Which of the following fascial layers gives rise to the axillary sheath? A. Superficial layer of cervical fascia B. Pretracheal C. Carotid sheath D. Buccopharyngeal E. Prevertebral ANSWER: E The sternohyoid muscle is innervated by which of the following nerves? A. Hypoglossal B. Vagus C. Transverse cervical D. Supraclavicular E. Ansa cervicalis ANSWER: E The middle thyroid vein empties into which of the following veins? A. External jugular B. Anterior jugular C. Posterior jugular D. Vertebral E. Internal jugular ANSWER: E The superior deep cervical lymph nodes occupy which of the following cervical triangles? A. Submental B. Omoclavicular C. Submandibular D. Occipital E. Carotid ANSWER: E Which of the following ganglia is commonly located at the level of the cricoid cartilage? A. Superior ganglion of the vagus B. Inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal C. Otic D. Submandibular E. Middle cervical ANSWER: E The posterior belly of the digastric muscle is innervated by which of the following nerves? A. Trigeminal B. Hypoglossal C. Vagus D. Ansa subclavia E. Facial ANSWER: E Which of the following muscles of the larynx increases tension on the vocal folds? A. Transverse arytenoid B. Lateral cricoarytenoid C. Posterior cricoarytenoid D. Thyroarytenoid E. Cricothyroid ANSWER: E The trachea begins at the level of which of the following structures? A. Hyoid bone B. Thyroid cartilage C. Fourth cervical vertebra D. Second cervical vertebra E. Cricoid cartilage ANSWER: E The pharyngobasilar fascia contributes to which of the following layers of the pharyngeal wall? A. Mucous membrane B. Buccopharyngeal fascia C. Longitudinal muscle layer D. Circular muscle layer E. Submucosa ANSWER: E Which of the following nerves innervates the genioglossus muscle? A. Trigeminal B. Ansa cervicalis C. Glossopharyngeal D. Vagus E. Hypoglossal ANSWER: E The suboccipital triangle contains which of the following structures? A. Posterior auricular artery B. Lesser occipital nerve C. Spinal accessory nerve D. Occipital artery E. Vertebral artery ANSWER: E A tonsillar abscess may extend posteriorly through the pharyngeal wall into the: A. Pleural cavity B. Anterior triangle of the neck C. Suprasternal space D. Pharyngeal tonsil E. Retropharyngeal space ANSWER: E Which of the following structures locates in the antescalenus cellular space: A. Inferior thyroid artery B. Phrenical nerve C. Vagus nerve D. Brachial plexus E. Venous angle ANSWER: E Which of the following veins passes within the submandibular triangle: A. Internal jugular B. External jugular C. Mental D. Superior thyroid E. Facial ANSWER: E The esophagus is innervated by which of the following nerves: A. Phrenic B. Superior laryngeal C. Accessory D. Hypoglossal E. Reccurent laryngeal ANSWER: E Which of the following arteries realizes the arterial supply of the pharynx: A. Superior laryngeal B. Descending palatine C. Sublingual D. Ascending palatine E. Ascending pharyngeal ANSWER: E