ABSITE Review Part 2
advertisement

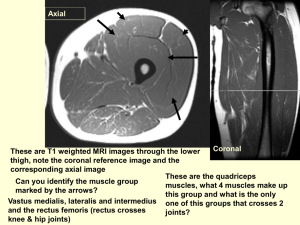
ABSITE: THE NITTY, GRITTY STUFF PART 2 KRUKENBERG TUMOR? Colon or stomach cancer metastasis to ovary Histology? Signet rings NAME THE GENETIC MUTATION FAP APC gene Medullary thyroid cancer RET proto-oncogene BOWEN’S DISEASE Intra-epithelial squamous cell carcinoma of the anus Treatment: Wide local excision ESOPHAGEAL MANOMETRY Normal 15-25mmHg Normal LES tone? 4cm length? ESOPHAGEAL MANOMETRY No peritalsis, high LES pressure, fails to relax Next step in management? Barium swallow Dilated esophagus that ends in a bird’s beak Management? Heller myotomy WHAT IS THIS DISEASE PROCESS Achalasia Decreased ganglion cells in Auerbach’s plexus DURING ESOPHAGECTOMY … Decide to use the stomach to replace the esophagus… What is the blood supply to the stomach Right gastroepiploic artery HEAD AND NECK #1 benign tumor of the parotid gland Pleomorphic adenoma Treatment? Superficial parotidectomy (spare facial nerve) BEEP, BEEP, BEEP … 6-5566 (GROAN) Patient who has RUQ tenderness, febrile and hypotensive On exam… jaundice, solmnolent Next step in management? Resuscitation, abx, emergent drainage of CBD ERCP with sphincterotomy GI unavailable common bile duct exploration NERVE INJURY A 17yo is stabbed in the axilla. He is noted to have loss of function of the ulnar nerve. If nonoperative therapy is used for treatment of this nerve injury, at what rate is the nerve expected to regenerate? A) 1mm/wk B) 1mm/mo C) 1mm/day D) 10mm/mo E) 1cm/wk HEMATOMAS Epidural hematoma Characteristics on CT? Lens shape History Lucid interval Arterial or venous injury Arterial – middle meningeal Tempoparietal skull fracture HEMATOMAS Subdural hematoma Characteristics on CT? Crescent shape, conforms to brain Arterial or venous injury venous CONN’S SYNDROME Characteristics? HTN, low K, high Na 80% adenoma (surgical resection) 20% bilateral hyperplasia (medical treatment) Hyperaldosteronism CLINIC ANYONE? Patient complaining of an “ugly” scar Exam: raised and extends outside of wound margin Keloid Difference between keloid & hypertrophic scar? Hypertrophic scar does not extend beyond margins Treatment? Steroid injection WOUND HEALING Patient is now 5 days post-op….and needs to go back to the OR for retained sponge Wound healing… quicker, slower, or no change Quicker All the cells are in place already Macrophages, fibroblasts BEEP, BEEP, BEEP…..6-5804 Patient Next s/p open chole with temp 400 step in management? Look at wound….drainage, color, cx to the lab Gram stain = G+ rods, no WBCs What are you worried about? Clostridium Treatment: Debridement Abx: PCN THE CELL CYCLE The G1 G0, P53 The most RNA synthesis G1 The most variable period most radioresistent S Repair enzymes RESPIRATORY QUOTIENT Fat 0.7 Carbs 1.0 Mixed fuel 0.85 Brain RQ = 1 GLUTAMINE Which is not true? A) Essential for small bowel mucosa B) Essential for replicating cells (macrophages) C) Source for purines and pyrimidines D) Is an essential amino acid NUTRITION 70 y/o patient with obstructed esophageal cancer was admitted with severe malnutrition. TPN was started. 48 hr later, patient developed respiratory distress and was confused. CT chest: no pulmonary embolism. The most likely nutritional abnormality is A) hypokalemia B) hyperglycemia C) hypophosphotemia D) hyponatremia NUTRITION 35 y/o multiple trauma patient (not septic) is intubated in the SICU. Which of the following is most helpful to decrease protein catabolism in the first 72hr A) adequate analgesia & sedation B) early use of TPN C) daily administration of 120gm glucose D) early enteral nutrition WHY 120GM OF GLUCOSE D5= 50gm/L Run IVF @ 100cc/h 120gm glucose Needed Still for the brain in catabolic state (low RQ) Rising RQ signs of recovery, anabolic state, start TPN or enteral nutrition CODE 99 During CPR for cardiac arrest, which of the following is the earliest indication of a better outcome A) rising DBP B) rising SBP C) return of sinus rhythm D) return of end tidal CO2 E) decrease in base deficit Starting a lap chole, a 35 y/o patient became severely hypotensive, lost end tidal CO2, airway pressure is normal. The most appropriate next step is A) insertion of chest tube B) increase minute ventilatin C) trendelenburg position D) fiberoptic bronchoscopy SVO2 All are true, except A) is increased by paralysis and decreased by shivering B) the lowest value is at the coronary sinus C) is decreased in VSD D) can be directly measured from a swan ganz catheter IABP Contraindications to an intra-aortic balloon pump Aortic regurgitation Severe peripheral vascular disease Aortic aneurysm (presence of synthetic thoracic aortic graft) IABP Mechanism of action Increases coronary perfusion by increasing diastolic blood flow Decreases afterload Decreases myocardial O2 consumption When does it inflate? When does it deflate? HARD SIGNS OF ARTERIAL INJURY IN TRAUMA Active hemorrhage Pulsatile hematoma Lack of distal pulses Thrill or bruit Acute ischemia Go to the OR SOFT SIGNS OF ARTERIAL INJURY Proximity History of hemorrhage Minor hemorrhage Small hematoma Associated nerve injury Further evaluation needed KTI LEVEL 1 … ETA 30 MINUTES 7 yo is involved in a bicycle accident & brought to the ER with LUQ pain. CT reveals a spleen with multiple fractures & hemoperitoneum. What are the indications for splenectomy A) persistent vomiting & anorexia B) increasing hemoperitoneum on CT C) transfusions exceeding 50% of the blood volume D) 2 episodes of hypotension responding to transfusions A known alcoholic with a history of several hospitalizations for acute pancreatitis presents with persistent hematemesis. EGD reveals gastric varices. Appropriate treatment is A) sengstaken-blakemore tube B) TIPs C) portocaval decompression operation D) splenectomy Splenectomy is indicated for ITP in which of the following conditions A) subarachnoid hemorrhage B) children under 15 yo C) following a good response to prednisone D) after a non-response to IgG A 40 yo alcoholic patient underwent an exploratory operation for acute abdomen & at surgery was found to have leaking pseudocst in the tail of the pancreas. A tube drainage was performed. The patient is now 2 weeks post-op & has a persistent pancreatic fistula of 200cc/day. Medical management has failed to reduce the drainage. The procedure of choice A) drainage of the fistulous tract into jejunum B) resection of the tail of the pancreas C) ERCP followed by pancreaticojejunostomy D) continued medical management Which of the following statements regarding the anatomy of the liver is correct A) the falciform ligament provides the landmark between the right & left lobes B) sub-segments of the liver are readily identified by external landmarks C) the vena cava serves as the posterior landmark for the division between the right & lefts lobes D) the gallbladder is the landmark between the medial & lateral segments of the right lobe of the liver The anterior scalene muscle A) separates the brachial plexus & the brachial artery B) is posterior to the subclavian vein C) lies anterior to the subclavian vein D) inserts on the clavicle In advanced peripheral vascular disease, findings of dry gangrene are noted at the mid calf level. Arterial occlusion is most likely at which level A) popliteal artery B) common femoral artery C) superficial femoral artery D) external iliac artery Postpartum ovarian vein thrombophlebitis A) is resistant to treatment with heparin B) may be clinically confused with appendicitis C) requires antibiotic treatment & surgical resection D) requires laparoscopy or laparotomy for definitive diagnosis An aldosterone tumor is suspected in a hypertensive patient. A saline load challenge will exhibit A) elevated urinary K levels B) low urinary aldosterone levels C) hyperkalemia D) metabolic acidosis An elderly female presents with extreme somnolence, hypoactive reflexes & a distended abdomen. The serum calcium is 14mg/dl. Appropriate treatment is A) immediate parathyroidectomy B) mithramycin C) saline & lasix D) cortisone Detection of the BRCA-1 gene in a woman with breast cancer places her at highest risk for A) an ovarian cancer B) a 2nd breast cancer C) uterine cancer D) colon cancer The histological breast lesion associated with the highest risk of developing breast cancer is A) fibrocystic disease B) sclerosing adenosis C) atypical hyperplasia D) intraductal papilloma The optimal rate of glucose administration for a patient on TPN A) 1-2gm/kg/hr B) 5-6gm/kg/hr C) 8-10gm/kg/hr D) 15-20gm/kghr The predominate cause of weight loss in cancer patients is A) inadequate nutritional weight loss B) GI obstruction C) incomplete metabolism of glucose D) cachexon-induced anorexia Following resection of the terminal small bowel for crohn’s disease, which of the vitamins will be deficient A) thiamine B) vitamin c C) riboflavin D) vitamin e The pre-transplant crossmatch involves A) recipient lymphocytes & donor plasma B) recipient plasma & donor lympocytes C) recipient macrophages & donor globulins D) recipient globulins & donor macrophages Adherence of leukocytes to the endothelium is due to A) integrins B) P-selectin C) L-selectin D) E-selectin The fluoroquinolones A) are primarily effective in gram + bacteremia B) have low concentrations in bile C) chronic liver disease dramatically affects pharmacokinetics D) are greater than 50% excreted unchanged in the urine The source of free oxygen radicals in reperfusion injury is A) superoxide B) hydrogen peroxide C) hydroxy radicals D) xanthine oxidase Marfan’s syndrome is associated with all of the following except A) aortic valve insufficiencys B) incomplete collagen formation C) abnormal bleeding D) decreased bone mass The changes associated with a mucous producing villous adenoma of the sigmoid A) metabolic acidosis B) hypokalemia C) urine pH 8.0 D) serum HCO3 of 15 Complications of hypothermia include A) convulsion B) tachycardia C) diuresis D) hypercoagulation The nerve most commonly injured in a laparoscopic preperitoneal inguinal hernia repair is A) obturator B) genitofemoral C) ilioinguinal D) iliohypogastric A 30yo female attempts suicide with the ingestion of lye. Examination of the mouth & pharynx demonstrates erythema. Appropriate management is A) IVF, antibiotics & observations B) esophagoscopy to level of the 1st burn C) esophagoscopy to include the stomach D) laparotomy, gastrostomy & TPN A 68yo presents with signs of sepsis, substernal chest pain & air crepitus in the left neck. These symptoms & signs developed 16hr ago after forceful vomiting of a heavy meal. Treatment should include A) chest tube, IVF & antibiotics B) left thoracotomy & repair C) right thoracotomy & repair D) laparotomy & repair 12hr following esophagoscopy & biopsy of an obstructing esophageal cancer, the patient presents with fever & substernal chest pain. Esophagogram reveals perforation of the distal esophagus. Appropriate treatment is A) esophageal tube suction, IVF & antibiotics B) chest tube, esophageal suction, IVF & antibiotics C) closure of the perforation, chest tube, IVF & antibiotics D) esophagectomy & esophagogastrostomy A patient is placed on IVF & NPO following an uneventful laparotomy. 12hr later the patient develops palor, sweating, hypotension & abdominal pain. On exam the upper abdomen is distended & tympanic with a succussion splash. Appropriate action is A) increase IVF & transfuse pRBCs B) return to the OR C) insert NGT D) provide ventilatory support Splenectomy may be useful in the management of A) hairy cell leukemia B) malaria C) chromic myelogenous leukemia D) sickle cell disease A pulmonary function that would prohibit a successful pneumonectomy is A) FEV1 of 1000 B) pCO2 47 C) ability to climb 2 flights of stairs D) previous MI The most common complication of a popliteal aneurysm is A) thrombosis B) embolization C) rupture D) neurolysis The IMV A) drains the distal rectum B) passes lateral to the ligament of treitz C) joins the portal vein D) is medial to the aorta The right renal artery passes A) anterior to the vena cava B) anterior to the renal vein C) anterior to the renal pelvis D) anterior to the IMV The muscle anterior to the femoral artery in the Hunter’s canal is A) adductor minimus B) adductor magnus C) quadriceps femoris D) vastus medialis Which of the following group of drugs will provide effective treatment for hypertrophic subaortic stenosis A) inotropes B) Ca channel blockers C) ACE inhibitors D) loop diuretics The etiology of myasthenia gravis is A) insufficient Ach B) motor nerve axonal degeneration C) decreased number of Ach receptors D) overproduction of Ach esterase The earliest sign of uncal herniation is A) unilateral pupil dilatation B) deep coma C) contralateral decerebrate posturing D) bilateral decerebrate posturing A 30yo female with a history of dysmenorrhea & dyspareunia is found to have a tender 3cm smooth submucosal rectal mass. Appropriate treatment is A) danazol B) Flagyl C) LAR D) TAH-SBO Treatment of a malignant melanoma 2mm in depth is A) excision with 1cm margins B) excision with 2cm margins & sentinel node biopsy C) excision with 4cm margins & prophylatic node dissection D) excision with 1cm margins & interferon a Malignant pheochromocytoma is clearly identified by which of the following A) capsular invasion B) venous invasion C) invasion of adjacent structures D) histological examination The only certain sign of parathyroid malignancy is A) histologic features B) renal disease C) bone disease D) recurrence after resection The location of a lost upper parathyroid is likely to be found A) intrathyroid B) with the thymus C) adjacent to the inferior thyroid artery D) in the tracheoesophageal groove Proper treatment for a 3cm papillary thyroid cancer with tumor involving 4 lymph nodes is A) ipsilateral lobectomy with resection of involved lymph nodes B) total thyroidectomy C) total ipsilateral lobectomy, near total lobectomy on the contralateral side, & resect involved lymph nodes D) total thyroidectomy, central compartment node dissection & modified radical neck dissection Appropriate treatment for family members (without tumor) having a heterozygous RET proto-oncogene is A) observation B) total parathyroidectomy C) total thyroidectomy D) bilateral adrenalectomy Failure to identify gamma radiation or blue dye in a sentinel node biopsy procedure is due to A) no evidence of metastatic disease B) incorrect FNA diagnosis of cancer C) failure of dye & radiolabeled colloid to migrate D) absence of axillary lymph nodes The appropriate ultrasound probe for examination of a breast mass is A) 1.5-2.5 mHz B) 3-3.5 mHz C) 5-5.5 mHz D) 7.5-10 mHz Which of the following is the mediator that leads to relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi, is partially mediated by cholinergic stimuli, & has a diminished effect following vagotomy A) somatostatin B) glucagon C) cholecystokinin D) gastrin E) secretin