Financial Management
advertisement
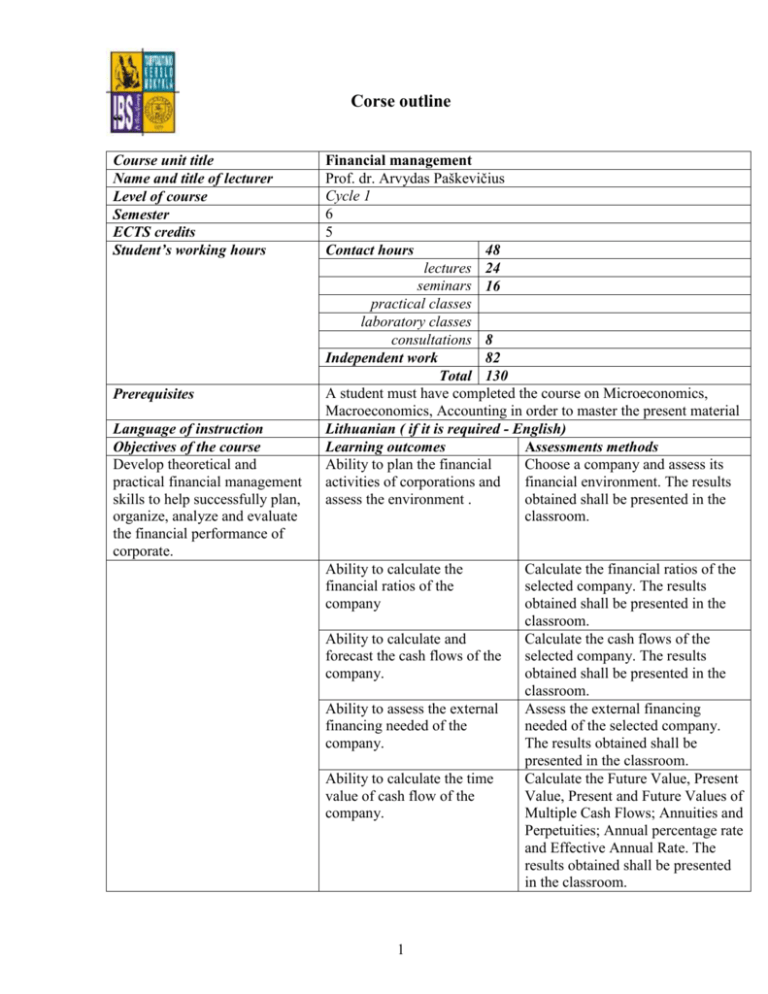
Corse outline “ Course unit title Name and title of lecturer Level of course Semester ECTS credits Student’s working hours Prerequisites Language of instruction Objectives of the course Develop theoretical and practical financial management skills to help successfully plan, organize, analyze and evaluate the financial performance of corporate. Financial management Prof. dr. Arvydas Paškevičius Cycle 1 6 5 Contact hours 48 lectures 24 seminars 16 practical classes laboratory classes consultations 8 Independent work 82 Total 130 A student must have completed the course on Microeconomics, Macroeconomics, Accounting in order to master the present material Lithuanian ( if it is required - English) Learning outcomes Assessments methods Ability to plan the financial Choose a company and assess its activities of corporations and financial environment. The results assess the environment . obtained shall be presented in the classroom. Ability to calculate the financial ratios of the company Ability to calculate and forecast the cash flows of the company. Ability to assess the external financing needed of the company. Ability to calculate the time value of cash flow of the company. 1 Calculate the financial ratios of the selected company. The results obtained shall be presented in the classroom. Calculate the cash flows of the selected company. The results obtained shall be presented in the classroom. Assess the external financing needed of the selected company. The results obtained shall be presented in the classroom. Calculate the Future Value, Present Value, Present and Future Values of Multiple Cash Flows; Annuities and Perpetuities; Annual percentage rate and Effective Annual Rate. The results obtained shall be presented in the classroom. Ability to calculate the Bond and Common Stock values using the discounted cash flow method. Teaching methods Course unit content Calculate the Bond and Common Stock values of selected company. The results obtained shall be presented in the classroom. During the lectures students shall be presented and explained the theoretical material. At home and during the seminars (practical classes) by solving problems-tasks and analyzing specific cases the students will take in the theoretical material and acquire practical skills. The course introduces fundamentals of financial management of a company. The following issues are presented: Corporate Finance and the Financial Manager; The Balance Sheet and Corporate Financial Decisions; The Corporate Form of Business Organization; The Goal of Financial Management; The Balance Sheet; The Income Statement; Cash flow from Assets; Cash flow to Bondholders and Stockholders; Cash Flow and Financial Statements; Standardized Financial Statements; Short-term and long-term Solvency measures; Asset management and profitability measures; Market Value and measures and Du Pont Identity; Long-term Financial planning and Growth; Financial Planning Models; The Percentage of Sales Approach; External Financing and Growth; Future Value and Compounding; Present Value and Discounting; Present and Future Values of Multiple Cash Flows; Annuities and Perpetuities; Annual percentage rate and Effective Annual Rate; Bonds and Bond Valuation; Common Stock Valuation; Net Present value; The Payback Rule; The Discounted Payback Rule; The Average Accounting Return; The Internal Rate of Return; The Profitability Index Subject title Contact hours 1. Introduction to the “Financial management of corporation“ 2 2. Financial Statements and Cash Flow 4 3. Working with Financial Statement 6 4. Long-term Financial Planning and Growth 8 5. The Time Value of Money 4 6. Discounted Cash Flow Valuation 8 7. Interest Rates and Bond Valuation 8 8. Stock Valuation 8 Total. 48 Reading list (up to five sources) Publication year 2009 2010 Author and title of the publication s Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, Stephen A. Ross, Randolph W. Westerfield, Bradford D. Jordan, Brealey R.A., Myers S., Allen F. „Principles of Corporate Finance“ 2 Independent work hours 4 8 10 12 6 14 14 14 82 Publishing house McGraw-Hill McGrawHill Assessment requirements Assessment criteria Composition of the final accumulative grade: The subject description prepared by: Approved by the Department: Approved by the Study Programme Committee: Analysis and solutions of tasks and problems at seminars, attendance of lectures and practical classes, interim tests, examination. The grade assigned for problem solution at seminars is multiplied by 0.20. Colloquium tests shall be taken by electronic means at the Examination centre. Students are required to solve not less than 50% of all tasks presented in four tests. Where the grade for the colloquium is above 4, it is multiplied by 0.2 and shall be added to the final result. It is obligatory to pass all 4 tests. Students who during semester have passed all tests and have accumulated positive assessment may be absent exam. The final accumulative grade shall be composed of: Problem solutions at seminars – 20 % Grade from colloquium 1 – 20% Grade from colloquium 2 – 20% Grade from colloquium 3 – 20% Grade from colloquium 4 – 20% Prof. dr. Arvydas Paškevičius Name, date Chairman: signature, date 3