Homework, Chapter 8: 3, 9, 13, 21
advertisement

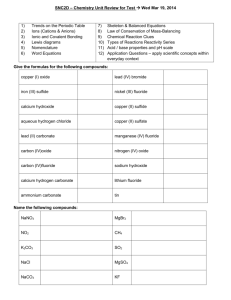
Homework, Chapter 8: 3, 9, 13, 21 3. Balance each of the following equations and classify it: a) 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O combination; b) 3 C + Fe2O3 2 Fe + 3 CO decomposition; c) H2SO4 + 2 NaOH 2 H2O + Na2SO4 double displacement; d) Al2(CO3)3 Al2O3 + 3 CO2 decomposition; e) 2 NH4I + Cl2 2 NH4Cl + I2 single displacement. 9. Change these word equations into formula equations and balance them: a) water hydrogen + oxygen 2 H2O 2 H2 + O2 b) acetic acid + potassium hydroxide potassium acetate + water. CH3COOH + KOH CH3COOK + H2O c) phosphorus + iodine phosphorus triiodide 2 P + 3 I2 2 PI3 d) aluminum + copper(II) sulfate copper + aluminum sulfate 2 Al + 3 CuSO4 3 Cu + Al2(SO4)3. e) ammonium sulfate + barium chloride ammonium chloride + barium sulfate (NH4)2SO4 + BaCl2 2 NH4Cl + BaSO4. f) sulfur tetrafluoride + water sulfur dioxide + hydrogen fluoride SF4 + 2 H2O SO2 + 4 HF g) chromium(III) carbonate chromium(III) oxide + carbon dioxide. Cr2(CO3)3 Cr2O3 + 3 CO2 13. Use the activity series to predict which of the following reactions will occur. Complete and balance the equations. When no reaction will occur, write “no reaction” as the product. Ag(s) + H2SO4(aq) no reaction Cl2(g) + 2 NaBr(aq) 2 NaCl(aq) + Br2(l) Mg(s) + ZnCl2(aq) MgCl2(aq)+ Zn(s) Pb(s) + AgNO3(aq) PbNO3(aq) + Ag(s) 21. Write balanced equations for each of these reactions including the heat term: a) Lime, CaO, is converted to slaked lime, Ca(OH)2 by reaction with water. The reaction liberate 65.3 kJ of heat for each mole of lime reacted. CaO + H2O Ca(OH)2 + 65.3 kJ b) The industrial production of aluminum metal from aluminum oxide is an endothermic electrolytic process requiring 1630 kJ per mole of Al2O3. Oxygen is also a product. 2 Al2O3 + 1630 kJ 4 Al + 3 O2 Chpt. 6 (p.122): 3, 6, 8, 15, 17, 25, 29 3. Write formulas for the following cations (don’t forget to indicate charges): sodium: Na+; magnesium” Mg2+; aluminum Al3+; copper(II): Cu2+; iron(II): Fe2+; iron(III): Fe3+; lead(II): Pb2+; silver: Ag+; cobalt(II): Co2+; barium: Ba2+; hydrogen: H+; mercury(II): Hg2+; tin(II): Sn2+; chromium(III): Cr3+; tin(IV): Sn4+; manganese(II): Mn2+; bismuth(III): Bi3+. 6. Write the systematic names for the following: a) slaked lime (Ca(OH)2): calcium(II) hydroxide; b) saltpeter (NaNO3): sodium nitrate; c) brimstone (S): sulfur; d) baking soda (NaHCO3): sodium hydrogen carbonate; e) pyrite (FeS2): iron(IV) sulfide; f) potash (K2CO3): potassium carbonate. 8. Complete the table, filling each box with the proper formula. NH4+ Ca2+ Fe3+ Ag+ Cu2+ SO42(NH4)2SO4 CaSO4 Fe2(SO4)3 Ag2SO4 CuSO4 15. Name these compounds by the Stock (IUPAC) System: 17. OHNH4OH Ca(OH)2 Fe(OH)3 AgOH Cu(OH)2 AsO43(NH4)3AsO4 Ca3(AsO4)2 FeAsO4 Ag3AsO4 Cu3(AsO4)2 C2H3O2NH4C2H3O2 Ca(C2H3O2)2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 AgC2H3O2 Cu(C2H3O2)2 CrO42(NH4)2CrO4 CaCrO4 Fe2(CrO4)3 Ag2CrO4 CuCrO4 a) CuCl2: copper(II) chloride; b) CuBr: copper(I) bromide; c) Fe(NO3)2: iron(II) nitrate; d) FeCl3: iron(III) chloride; e) SnF2: tin(II) fluoride; f) HgCO3: mercury(II) carbonate. Write formulas for these acids: a) hydrochloric acid: HCl; b) chloric acid: HClO3; c) nitric acid: HNO3; d) carbonic acid: H2CO3; e) sulfurous acid: H2SO3; f) phosphoric acid: H3PO4. 25. Write the chemical formula for these substances: a) baking soda: NaHCO3; b) lime: Ca(OH)2; c) Epsom salts: MgSO4; d) muriatic acid: HCl; e) vinegar: HC2H3O2; f) potash: K2CO3; g) lye: NaOH. 29. Write formulas for all possible compounds formed between the calcium ion and the anions shown in Question 28: a) CaSO4; b) Ca3(PO4)2; c) Ca(NO3)2; d) Ca(ClO3)2; e) Ca(OH)2 f) CaCO3.