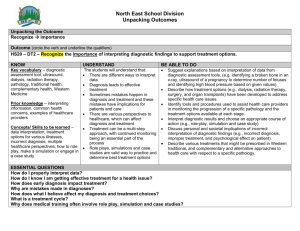
Is routine measurement of serum complement helpful
advertisement
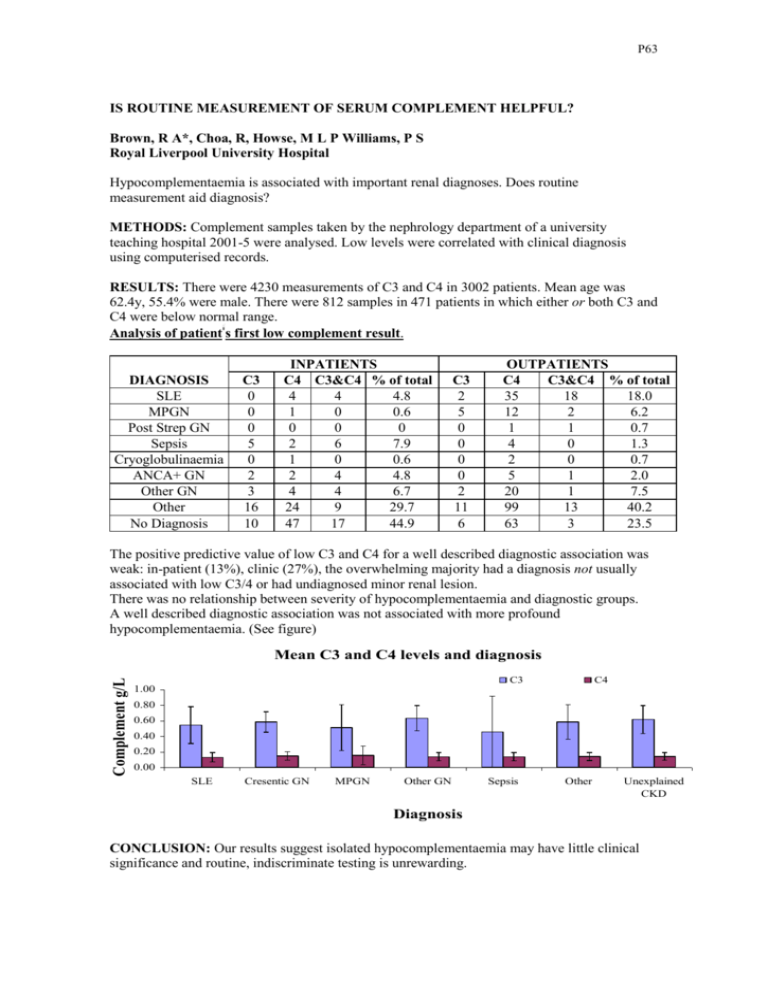
P63 IS ROUTINE MEASUREMENT OF SERUM COMPLEMENT HELPFUL? Brown, R A*, Choa, R, Howse, M L P Williams, P S Royal Liverpool University Hospital Hypocomplementaemia is associated with important renal diagnoses. Does routine measurement aid diagnosis? METHODS: Complement samples taken by the nephrology department of a university teaching hospital 2001-5 were analysed. Low levels were correlated with clinical diagnosis using computerised records. RESULTS: There were 4230 measurements of C3 and C4 in 3002 patients. Mean age was 62.4y, 55.4% were male. There were 812 samples in 471 patients in which either or both C3 and C4 were below normal range. Analysis of patient s first low complement result. DIAGNOSIS SLE MPGN Post Strep GN Sepsis Cryoglobulinaemia ANCA+ GN Other GN Other No Diagnosis C3 0 0 0 5 0 2 3 16 10 INPATIENTS C4 C3&C4 % of total 4 4 4.8 1 0 0.6 0 0 0 2 6 7.9 1 0 0.6 2 4 4.8 4 4 6.7 24 9 29.7 47 17 44.9 C3 2 5 0 0 0 0 2 11 6 OUTPATIENTS C4 C3&C4 % of total 35 18 18.0 12 2 6.2 1 1 0.7 4 0 1.3 2 0 0.7 5 1 2.0 20 1 7.5 99 13 40.2 63 3 23.5 The positive predictive value of low C3 and C4 for a well described diagnostic association was weak: in-patient (13%), clinic (27%), the overwhelming majority had a diagnosis not usually associated with low C3/4 or had undiagnosed minor renal lesion. There was no relationship between severity of hypocomplementaemia and diagnostic groups. A well described diagnostic association was not associated with more profound hypocomplementaemia. (See figure) Complement g/L Mean C3 and C4 levels and diagnosis C3 C4 1.00 0.80 0.60 0.40 0.20 0.00 SLE Cresentic GN MPGN Other GN Sepsis Other Unexplained CKD Diagnosis CONCLUSION: Our results suggest isolated hypocomplementaemia may have little clinical significance and routine, indiscriminate testing is unrewarding.