Make an equation from a table
advertisement

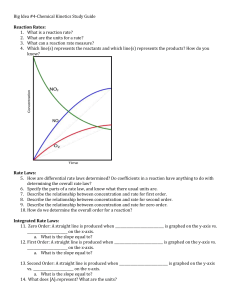
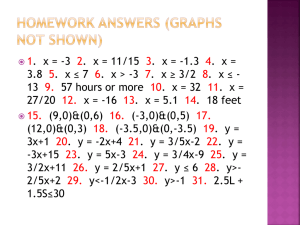
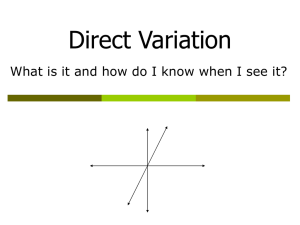
Make an equation from a table x 0 1 2 3 4 y 1 3 5 7 9 Y = mx + b 1. Find the rate of change. a. When x goes up by one, figure out what y is (or the change in y divided by the change in x) 2. The rate of change is the coefficient of x (m in the equation above) 3. Find the y-intercept a. When x is 0, figure out what y is 4. The y-intercept is the b in the equation above. Make a table from an equation x 0 1 2 3 4 1. 2. 3. 4. y 2 4 6 8 10 Y = 2x + 2 Make a t-table. Number x from 0 to (about) 4 Plug the values of x into the equation. Write the answer to the equation in the corresponding y- column. a. Example: If x = 3, then 2 (3) + 2 = 8 Make a graph from an equation 1. First, make a t-table 2. Plot the points on the graph (x, y) a. Example (from above table): the coordinate points to plot are (0, 2), (1, 4), (2, 6), (3, 8) (4. 10) b. Tip: The first number is always graphed on the x-axis (independent variable) and the second number on the y-axis (dependent variable). Y = mx + b Y = the dependent variable What we are trying to solve for Graphed on the y-axis M = the coefficient of x The constant rate of change X = the independent variable You multiply the coefficient by this Graphed on the x-axis +b = the y-intercept In a table, when x is 0, this is y In a graph, this is where the line crosses the y-axis