Chapter 3--Activity Cost Behavior
advertisement

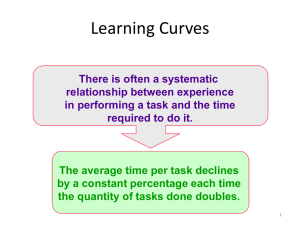
CHAPTER 3 Activity Cost Behavior LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Define and describe fixed, variable, and mixed costs. 2. Explain the use of the resources and activities and their relationship to cost behavior. 3. Separate mixed costs into their fixed and variable components using the high-low method, the scatterplot method, and the method of least squares. 4. Evaluate the reliability of the cost formula. 5. Explain how multiple regression can be used to assess cost behavior. 6. Define the learning curve, and discuss its impact on cost behavior. 7. Discuss the use of managerial judgment in determining cost behavior. CHAPTER SUMMARY This chapter introduces cost behavior as the way in which a cost changes in relation to changes in activity output. The resource usage model helps one better understand the cost behavior. It emphasizes that the committed resources may have excess capacity because they are frequently fixed. There are three methods of separating mixed costs presented in the chapter with their strengths and weaknesses. The method of least squares produces the line that best fits the data points and is therefore recommended over the high-low and scatterplot methods. The leastsquares method has the advantage of offering methods to assess the reliability of cost equations. The learning curve is discussed to better describe a nonlinear relationship between labor hours and output. The chapter concludes by describing how managers use their judgment alone or in conjunction with the cost behavior analytical methods. CHAPTER REVIEW Knowledge of cost behavior allows you to assess changes in costs that result from changes in activities. Cost accountants use this knowledge to assess the effects of decisions that change activities. I. Basics of Cost Behavior Learning Objective #1 A. Cost behavior is the way a cost changes in relation to changes in the levels of activity usage. B. The types of cost behavior include variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. 39 40 Chapter 3 Summary of Variable and Fixed Cost Behavior Cost In Total Per Unit Variable Total variable cost changes as activity level changes. Variable cost per unit remains the same over wide ranges of activity. Fixed Total fixed cost remains the same even when the activity level changes. Fixed cost per unit goes down as activity level goes up. Review textbook Exhibit 3-1, which graphically illustrates fixed cost behavior. Review textbook Exhibit 3-2, which graphically illustrates variable cost behavior. Mixed costs are costs that have both a fixed and a variable component. Review textbook Exhibit 3-5, which graphically illustrates mixed cost behavior. C. Linearity Assumption A linear cost function is used to approximate the underlying cost function within a relevant range because it is less time consuming and less expensive to estimate. A relevant range is the range of activity for which the assumed cost relationship is valid. Review textbook Exhibit 3-4, which graphically illustrates linear cost function approximation within the relevant range. D. Time Horizon 1. The longer the time period, the more likely that a cost will be a variable cost. In the long run, all costs are variable. 2. The short run is a period of time in which at least one cost is fixed. 3. Two factors determine what is long run and what is short run: Management judgment Types of decisions that management faces (short-term and long-term decisions) 4. Understanding of the nature of long-run and short-run cost behavior provides insights to activities and the resources needed to enable an activity to be performed. II. Resources, Activities, and Cost Behavior A. Learning Objective #2 Introduction 1. Resources are the economic elements that are consumed in performing activities. 2. When a firm acquires the resources needed to perform an activity, it is obtaining activity capacity. Activity capacity is the ability to perform activities. a. Practical capacity is the level at which the activity is performed efficiently. b. Unused capacity occurs when the activity capacity acquired is not used. Unused capacity = Activity capacity – Capacity used Activity Cost Behavior B. 41 Flexible Resources Flexible resources are acquired from outside sources with no long-term commitments. They are supplied as used and needed. 1. There is no unused capacity for this category of resources (Resource supplied = Resource usage). 2. Flexible resources are generally treated as a variable cost. C. Committed Resources Committed resources are acquired by the use of either an explicit or implicit contract to obtain a given quantity of resource. They are supplied in advance of usage, regardless of whether the resources acquired are fully used or not. Acquisition of committed resources include: 1. Committed fixed expenses are the costs incurred to provide long-term activity capacity. They are not subject to change in the short run. Examples: Acquiring multiperiod service capacities by hiring employees. Purchasing a long-lived asset or entering a long-term contract (buildings and equipment, either purchased or leased). 2. Discretionary fixed expenses are the costs incurred for the acquisition of shortterm activity capacity. They are independent of actual activity usage, but the levels of usage can be changed quickly. Example: Salaries of employees, because workers may not be laid off if there is a shortterm drop in production. D. Implications for Control and Decision Making 1. Operational control information systems encourage managers to pay more attention to controlling resource usage and spending and to eliminate excess capacity. 2. Managers need to calculate and evaluate the changes in supply and demand of resources resulting from different decisions. E. Step-Cost Behavior A step-cost function displays a constant level of cost for a range of activity output and then jumps to a higher level of cost at some point, where it remains for a similar range of activity. 1. Step-variable costs are costs that follow a step-cost behavior with narrow steps (resources must be purchased in small chunks). Step-variable costs can be approximated with a strictly variable cost assumption. 2. Step-fixed costs are costs that follow a step-cost behavior with wide steps (resources are acquired at large quantities). Many so-called fixed costs are best described by a step-cost function because they are fixed over the normal operating range of a firm (relevant range). Many committed resources, such as engineers’ salaries, follow a step-cost function. 42 Chapter 3 3. A contemporary cost management system informs users of the relationship between resources supplied and resources used as follows: Activity availability = Activity output + Unused capacity Activity rate is the average unit cost obtained by dividing the resource expenditure by the activity’s practical capacity. The activity rate is used to calculate the cost of the activity used (resource usage) and the cost of unused activity as follows: Cost of activity used = Activity rate × Actual activity output Cost of unused activity = Activity rate × Unused activity Thus, Cost of activity supplied = Cost of activity used + Cost of unused activity Note that a traditional cost management system typically provides information only about the cost of the resources supplied. F. Activities and Mixed Cost Behavior 1. Mixed costs have a fixed and a variable component. 2. The accounting records often reveal the total cost of an activity and a measure of activity output. Thus, it is necessary to separate the total costs into their fixed and variable components. III. Methods for Separating Mixed Costs into Fixed and Variable Components A. Introduction Learning Objective #3 1. The expression of the mixed cost as a linear equation is: Y = F + VX Total activity cost (Y ) is the dependent variable because its value depends on the value of another variable. Measure of activity output (X ) is the independent variable because it measures activity output and explains changes in the activity cost. There may be more than one independent variable. The choice of an independent variable is related to its economic plausibility. The intercept parameter corresponds to fixed activity cost (F ) or total fixed cost. Graphically, the intercept parameter is the point at which the mixed cost line intercepts the cost (vertical) axis. The slope parameter corresponds to the variable cost per unit of activity (V ). Graphically, this represents the slope of the mixed cost line. 2. There are three widely used methods of separating mixed costs into their fixed and variable components: the high-low method, the scatterplot method, and the method of least squares. B. The High-Low Method The high-low method uses two points to determine the equation of the cost line. 1. Two activity points, the highest and the lowest, and their corresponding costs are used to determine the cost formula. 2. The parameters for the cost formula (F and V ) are computed using the following equations: 43 Activity Cost Behavior Variable cost per unit of activity = Change in cost / Change in activity V = (Y2 – Y1) / (X2 – X1) Fixed activity cost = Total cost – Total variable cost F = Y2 – VX2 or F = Y1 – VX1 3. Advantages of the high-low method: Objectivity—Any two people using a particular set of data will come up with the same answer. Quick estimation—Only two points of data are needed. 4. Disadvantage of the high-low method: The high and low points may not be representative of the cost-activity relationship. C. The Scatterplot Method In the scatterplot method, data points are plotted so that the relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variable can be seen. 1. A scattergraph is a visual portrait of the relationship between cost and activity. Total activity cost (material-handling cost) is the vertical axis. The activity driver or output measure (number of moves) is the horizontal axis. Review textbook Exhibit 3-8, which shows an example of plotting a scattergraph. 2. A scattergraph allows the users to: Determine whether a relationship between the dependent variable and the independent variable exists. Assess the validity of the assumed linear relationship. Identify outliers (i.e., points that do not fit the general pattern of behavior). 3. Comparison of the high-low method and the scatterplot method: a. The main advantage of the high-low method is that it directs the manager as to which two points to select to compute the linear cost formula. Thus, the highlow method removes subjectivity from the estimation process. b. The advantage of the scatterplot method over the high-low method is that it allows the users to inspect the data visually. Review textbook Exhibit 3-9, which illustrates cost behavior situations not appropriate for the high-low method. Using a scattergraph to inspect data visually would be more advantageous. D. The Method of Least Squares The method of least squares produces a best-fitting line that is closer to the data points than any other line. 44 Chapter 3 1. Mathematically, closer is defined as the line with the smallest sum of the squared deviations. Deviation is defined as the difference between the predicted and actual cost. 2. The method of least squares uses the sum of squared deviations to identify the best-fitting line because: Squaring the deviations eliminates the canceling effect of positive and negative deviations. Squaring the deviations also assesses a larger “penalty” to data points that have a large deviation. Many small deviations are better than a few large deviations. Since the measure of closeness is the sum of the squared deviation of points from the line, the smaller the measure, the better the line fits the data points. E. Using the Regression Programs 1. Spreadsheet packages such as Microsoft Excel, Lotus 1-2-3, and Quattro Pro1 have regression routines that will perform the least squares computations. For example, in Excel pull down the “Tools” menu and choose “Add-in” to activate the “Data Analysis Toolpack.” Reopen the “Tools” menu to choose “Data Analysis” and then click on “Regression.” Specify the dependent variable data range in the Y window and the independent variable data range in the X window within the Regression dialog box. Review textbook Exhibit 3-12, which shows regression output produced by Excel. 2. Use the coefficients of the intercept and the X variable reported at the bottom of the regression output to construct the cost formula. IV. Reliability of Cost Formulas Learning Objective #4 Regression output is useful to assess the reliability of the estimated cost formula because it provides the results of hypothesis testing of cost parameters, goodness of fit, and confidence intervals. These tests help the manager determine whether there is a strong association between an activity cost and an activity driver. Strong test results provide evidence to the manager about the correctness of the driver selection. A. Hypothesis Test of Parameters The hypothesis test of cost parameters indicates whether the parameters are different from zero. 1. The t statistic is used to test the hypothesis that the cost parameters are statistically different from zero. 2. The reported P-value shows the level of statistical significance achieved by the t statistic. If the reported P-value is less than the specified degree of confidence (for example, 0.05), the independent variable is a significant explanatory variable. 1 Excel is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. Lotus and 1-2-3 are registered trademarks of the Lotus Development Corporation. Quattro Pro is a registered trademark of Novell, Inc. Any further reference to Excel, Lotus 1-2-3, or Quattro Pro refers to this footnote. 45 Activity Cost Behavior If the reported P-value is greater than the specified degree of confidence (for example, 0.05), the independent variable is not a significant explanatory variable. B. Goodness of Fit Measures Goodness of fit measures the degree of association between cost and activity output. Measures of goodness of fit include the coefficient of determination and the coefficient of correlation. 1. The coefficient of determination measures the percentage of variability in the dependent variable that is explained by the independent variable. The coefficient of determination is labeled as R Square (R2) in regression output. R2 always ranges between 0 and 1.00. The higher the percentage of cost variability explained, the better the fit. 2. The coefficient of correlation is the square root of the coefficient of determination. It provides information on the direction of the relationship between cost and activity, because the value of the coefficient of correlation can range between –1 and +1. When a positive correlation exists, as activity increases, costs also increase. When a negative correlation exists, as activity increases, costs decrease. Review textbook Exhibit 3-13, which illustrates various correlations and the associated correlation coefficients. C. Confidence Intervals A confidence interval provides a range of values for the actual cost with a prespecified degree of confidence. 1. The confidence interval of the predicted costs is used to measure the discrepancy between the actual cost and the predicted cost using the least-squares cost equation. The predicted cost can be expected to be different from the actual cost because: The cost equation may have omitted a relevant activity driver. A sample was used to estimate the relationship. 2. The standard error (Se) in the regression statistics and a t statistic is required to construct the confidence interval for the predicted cost. Confidence interval = Predicted cost ± t × Standard error where Standard error is the measure of dispersion found in the data. t statistic is a specified degree of confidence that describes the likelihood that the prediction interval will contain the actual costs. The value of the t statistic depends on the following: Degree of freedom = n – p where n = Number of data points used to calculate the cost formula p = Number of parameters in the cost equation Confidence level 46 Chapter 3 Review textbook Exhibit 3-14, which provides a table of selected t values. 3. Implications of the confidence interval include the following: The wider the confidence interval, the less useful the cost equation. The width of the confidence interval can be reduced by using more data points. With a larger sample, both the standard error and the t statistic will decrease. V. Multiple Regression Learning Objective #5 Multiple regression uses least squares to fit an equation involving two or more explanatory variables. The hypothesis test of the parameters now is a test of whether or not the independent variable should be included in the equation. The “adjusted R Square” is used as the goodness of fit measure. The t statistic for each regression coefficient is calculated, and the achieved level of statistical significance (the reported p value) is tested in the same way as those in simple regression. Calculate the confidence interval in the same way as those in simple regression. Review textbook Exhibit 3-15, which shows a sample multiple regression analysis output. VI. The Learning Curve and Nonlinear Cost Behavior Learning Objective #6 The learning curve describes the mathematical or graphic representation of how the labor hours worked per unit decrease as the volume produced increases in a nonlinear fashion. The learning rate, expressed as a percent, gives the percentage of time needed to make the next unit, based on the time it took to make the previous unit. The use of the learning curve concept helps management to be more accurate in budgeting and performance evaluation for processes in which learning occurs. The learning curve can be applied to the service industry and to the manufacturing industry using the following models: A. Cumulative Average-Time Learning Curve The cumulative average-time learning curve model states that the cumulative average time per unit decreases by a constant learning rate each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles. Review textbook Exhibit 3-16, which gives the data for a cumulative average-time learning curve with an 80 percent learning rate and 100 direct labor hours for the first unit. Note that the bold rows give the cumulative average time and cumulative total time according to the doubling formula. Activity Cost Behavior 47 Calculate the amounts for units that are not doubles of the original amount using the following formula: Y = pXq Where: Y = Cumulative average time per unit X = Cumulative number of units produced p = Time in labor hours required to produce the first unit q = Rate of learning = ln (percent learning) / ln 2 Review textbook Exhibit 3-17, which shows the graph of both the cumulative average time per unit and the cumulative total hours required. B. Incremental Unit-Time Learning Curve The incremental unit-time learning curve model describes that the incremental time per unit decreases by a constant learning rate each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles. Review textbook Exhibit 3-18, which gives data for an incremental unit-time learning curve with an 80 percent learning rate and 100 direct labor hours for the first time. Calculate the amounts for units that are not doubles of the original amount using the following formula: m = pXq Where: m = Time needed to produce the last unit X = Cumulative number of units produced p = Time in labor hours required to produce the first unit q = Rate of learning = ln (percent learning) / ln 2 C. The difference between the cumulative average-time learning curve model and the incremental unit-time learning curve model is in the underlying assumptions of the two models. 1. The cumulative average-time learning curve model assumes that the decrease in learning applies to all the units in between the original observation and the doubled observation, not just to the incremental unit. 2. The incremental unit-time learning curve model assumes that the decrease in learning applies only to the incremental unit, not to all the units in between the original observation and the doubled observation. 3. In general, the incremental unit-time learning curve model does not decrease as rapidly as the cumulative average-time learning curve model. 48 VII. Chapter 3 Managerial Judgment Learning Objective #7 Managers may use their experience and past observations of cost relationships to determine fixed and variable costs. This is the most widely used method in practice; its appeal is simplicity. Managers may use their experience and judgment to refine the statistical estimates. For example, experienced managers might “eyeball” the data and throw out several points as outliers, excluding them from the computations. 49 Activity Cost Behavior KEY TERMS TEST SET #1 From the list that follows, select the term that best completes each statement and write it in the space provided. activity capacity activity rate committed fixed expenses cost behavior cost of resource usage cumulative average-time learning curve model discretionary fixed expenses fixed costs flexible resources learning curve long run mixed costs practical capacity relevant range resources supplied in advance of usage short run step-cost function step-fixed cost step-variable cost unused capacity variable costs 1. If the cost remains constant over wide ranges of activity usage, it is a(n) ________ _____________________; if the ranges are relatively narrow, it is a(n) ________ _____________________. 2. The ability to perform activities is called ______________________________. 3. The __________________________________________ states that the cumulative average time per unit decreases by a constant learning rate each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles. 4. The efficient level of activity performance is the ______________________________. 5. The period of time in which all costs are variable is the __________________; the period of time in which at least one cost is fixed is the __________________. 6. The activity rate multiplied by actual activity usage is the formula for _____________ _______________________. 7. The ______________________ is the average unit cost. 8. Costs incurred for the acquisition of short-term _____________________________________________. capacity or services are 9. _______________________ is the way in which a cost changes in relation to changes in activity usage. 10. The difference between the acquired activity capacity and the actual activity usage is the ______________________________. 11. Costs incurred for the acquisition of long-term activity capacity are _____________________ ________________________. 50 Chapter 3 12. When the cost function is defined for ranges of activity usage, it is a(n) _______________ ______________. 13. ______________________________ are resources acquired from outside sources with no requirement of any long-term commitment, while ___________________________________ ____________________________ are acquired through either an explicit or implicit contract to obtain a given quantity of resource, whether fully used or not. 14. _________________________ vary in total in direct proportion to changes in an activity driver. 15. _________________________ have both a fixed and a variable component. 16. _________________________ are in total constant within the relevant range as the level of the activity driver varies. 17. The assumed cost relationship is valid only for the __________________________. 18. The ____________ describes the mathematical or graphic representation of how the labor hours worked per unit decrease as the volume produced increases in a nonlinear fashion. SET #2 From the list that follows, select the term that best completes each statement and write it in the space provided. activity output coefficient of correlation coefficient of determination committed resources confidence interval dependent variable deviation flexible resources goodness of fit high-low method hypothesis test of cost parameters independent variable intercept parameter incremental unit-time learning curve learning rate method of least squares multiple regression nonunit-level drivers scattergraph scatterplot method slope parameter unit-level drivers 1. __________________ is the difference between the predicted value and the actual cost. 2. The ________________________________________ is a measure of the relationship between two variables, including the direction of the relationship. 3. The plot of cost versus activity is a(n) _____________________. 4. The __________________________________ is used to predict the _________________ _____________. 5. The ______________________________________________ is the percentage of total variability in the dependent variable that is explained by the independent variable. Activity Cost Behavior 51 6. The ___________________________ is the degree of association between cost and activity. 7. Two methods that fit a line to data using only two points are the _________________ _____________ and the _______________________________. 8. A(n) ________________________________ provides a range of predicted values rather than a single point estimate. 9. The fixed cost is estimated by the ________________________________, while the variable cost per unit of activity usage is estimated by the ________________________________. 10. The statistical method of finding the equation of the line that best fits the set of data is the _______________________________________. If two or more variables are used, it is called _______________________________. 11. The _________________________________model states that the incremental time per unit decreases by a constant learning rate each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles. 12. The percentage of time needed to make the next unit, based on the time it took to make the previous unit, is called ____________. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZ Complete each of the following statements by circling the letter of the best answer. 1. The amount of activity capacity used in producing the organization’s output is: a. practical capacity. b. resource spending. c. resource usage. d. unused capacity. e. none of the above. 2. Which of the following costs remain constant in total when the level of the activity driver varies? a. conversion costs b. direct costs c. fixed costs d. mixed costs e. variable costs 52 Chapter 3 3. Committed fixed expenses are costs: a. incurred that provide long-term activity capacity. b. that can easily be changed. c. incurred that provide short-term activity capacity. d. that are allocated from another organizational unit. 4. Discretionary fixed expenses are costs: a. incurred that provide long-term activity capacity. b. that are supplied as used and needed. c. that cannot be changed. d. incurred that provide short-term activity capacity. e. that are allocated from another organizational unit. 5. Which of the following is true about resources supplied in advance of usage? a. There is no unused activity capacity for this category of resources. b. The organization is free to buy only the quantity of resources needed. c. These resources may take the form of either committed fixed expenses or discretionary fixed expenses. d. Normally a long-term commitment is not required. e. All of the above are true. 6. Which of the following is the best definition of a step-fixed cost? a. It is a cost that is constant in total over the relevant range. b. It is a cost that varies in total in direct proportion to changes in activity. c. It is a cost that follows a step-cost behavior with narrow steps. d. It is a cost that follows a step-cost behavior with wide steps. e. It is a cost that measures activity usage in steps—first, the fixed cost of resources used; then, the fixed cost of unused capacity. 7. The variable whose value is based on the value of another variable is the: a. activity variable. b. dependent variable. c. independent variable. d. intercept parameter. e. slope parameter. 8. The item that corresponds to the variable cost per unit of activity is the: a. activity variable. b. dependent variable. c. independent variable. d. intercept parameter. e. slope parameter. 53 Activity Cost Behavior 9. Which of the following best describes the difference between the high-low method and the scatterplot method? a. The high-low method uses all of the activity points; the scatterplot method uses only two points. b. The high-low method uses the high activity point and the low activity point; the scatterplot method allows the user to select two points that better represent the relationship between activity and costs. c. The high-low method uses the coefficient of correlation; the scatterplot method uses the coefficient of determination. d. The high-low method uses costs from the accounting records; the scatterplot method uses costs from the operating records. e. None of the above accurately describe the difference between the high-low method and the scatterplot method. 10. Which of the following is not an advantage of using the least squares method rather than the high-low method? a. The equation line is the best-fitting line to the data points. b. All of the data points, rather than just two points, are used. c. A measure of the goodness of fit is available. d. Measures of the reliability of the resulting line are available. e. All of the above are advantages of the least squares method. 11. Which of the following is true about the coefficient of determination R 2? a. R 2 is the probability that the actual value will be included in the confidence interval. b. An R 2 of 95% means that 95% of the data points fall on the equation line. c. A negative R 2 means that as activity increases, costs will decrease. d. R 2 measures the percentage of the total variability of the costs that is explained by the equation line. e. None of the above are true. 12. Why is managerial judgment so critical in determining cost behavior? a. All statistical methods are notoriously unreliable. b. Statistical methods are highly accurate in depicting the past, but they cannot foresee the future. c. The fixed and variable cost breakdowns are recorded in the accounting records; management just needs to know the appropriate accounts to search. d. The managers can use their experience to refine the statistical estimates. e. Managerial judgment is not critical; statistical methods can capture all of the manager’s expertise without any bias. 13. XYZ Corporation has reported activity costs. When 10,000 units are produced, the average cost is $23 per unit. When the activity is only 6,000 units, the average cost is $30 per unit. What are the fixed and variable costs? Fixed a. $105,000.00 b. 12.50 c. 19.50 d. (8,400.00) e. 180,000.00 Variable $ 12.50 105,000.00 (1.75) 0.08 7.00 54 Chapter 3 14. Almost Company had setup costs totaling $265,000 when 2,750 setups were performed. When 3,500 setups were performed, setup costs totaled $310,000. Determine the fixed and variable cost breakdown for setup costs. Fixed Variable a. $ (1,666.67) b. 475,000.00 c. 100,000.00 d. 12,000.00 e. (12,000.00) $ 16.67 (60.00) 60.00 92.00 92.00 15. Colfax, Inc., had packaging costs of $150,000 when 12,500 packages were shipped. Packaging costs were $190,000 when 17,500 packages were shipped. The variable costs were: a. $8.00. b. $10.86. c. $11.33. d. $12.00. e. none of the above. 16. Acme Company has just completed a least squares regression analysis of its material-handling costs. The cost analyst has provided you with the following summary, with apologies that the original computer output was not available: Parameter Intercept ................................... Number of moves ..................... Estimate Standard Error of Parameter 347.86 3.731 61.758 0.2387 Summary regression statistics are provided as follows: R Square (R 2) .......................... 0.876 Standard Error (Se)................... 53.51 Observations ............................ 22 What is a 95 percent confidence interval for an estimated 150 moves of material (use t = 2.086)? a. 97.56 ± 46.87 b. 351.59 ± 150.00 c. 794.98 ± 45.89 d. 907.51 ± 111.62 e. 907.51 ± 128.83 Activity Cost Behavior 55 PRACTICE TEST EXERCISE 1 Fisk Engineering is an independent testing laboratory with contracts to perform standardized quality testing for local manufacturers. Fisk employs four engineers who are responsible for all phases of the testing. Each engineer is paid an average salary of $40,000 and is capable of conducting 3,200 tests per year. The facility was recently constructed for $450,000 and is being depreciated on a straight-line basis over 20 years. Testing equipment is leased for $6,000 per year on a fiveyear lease. Consumable supplies are expected to average $175,000 per year at full capacity. During 20XX, there were 11,000 tests performed. Required: 1. Classify the resources into one of the following: (1) long-term resources supplied in advance, (2) short-term resources supplied in advance, or (3) resources supplied as needed. 2. Calculate the activity rate, breaking it down into fixed and variable components. 3. Calculate the total activity available, breaking it down into activity usage and unused activity. 56 Chapter 3 EXERCISE 2 Antz Industries has provided you with the following data for its materials storeroom: Month January ..................... February.................... March ........................ April ........................... May ........................... June .......................... July............................ August ....................... September ................ October ..................... November ................. December ................. Number of Shipments Storeroom Costs 175 225 275 175 200 225 300 325 275 200 150 175 $3,000 3,600 4,300 3,800 2,700 3,200 4,250 4,400 4,100 3,150 2,650 2,750 Required: 1. Determine the cost behavior using the high-low method. 2. Prepare a scattergraph of the data points, using cost as the vertical axis and number of shipments as the horizontal axis. Do any of the points seem to be outliers? 57 Activity Cost Behavior EXERCISE 2 (Continued) 3. Determine the cost behavior using the scatterplot method. How do these results compare with the high-low method? EXERCISE 3 The Saints Company wants to develop an estimate of its supplies costs. George Saint, the controller, has collected what he believes to be the relevant data for the past 12 months. It is Mr. Saint’s professional opinion that the supplies cost should be closely related to the volume of the product produced; thus, he has provided you with the following information: Month Units Produced January ..................... February ................... March ....................... April .......................... May........................... June.......................... July ........................... August ...................... September ................ October..................... November ................. December ................. Cost of Supplies 100 80 70 50 60 80 70 80 100 70 60 50 $3,550 2,980 2,970 2,410 2,530 3,180 2,830 2,820 3,220 2,950 2,560 2,420 REGRESSION SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.9324129 R Square 0.8693939 Adjusted R Square 0.8563333 Standard Error 132.26091 Observations 12 ANOVA Regression Residual Total Intercept Units Produced df 1 10 11 SS 1164437.19 174929.4766 1339366.667 MS 1164437 17492.9 F 66.56609354 Coefficients 1445.8953 19.619835 Standard Error 178.4756267 2.404743773 t Stat 8.10136 8.1588 P-value 1.05437E-05 9.9085E-06 Significance F 9.909E-06 Lower 95% 1048.2268 14.261731 Upper 95% 1843.5639 24.977939 58 Chapter 3 EXERCISE 3 (Continued) Required: 1. Prepare a cost formula for the supplies cost using the regression output. 2. Determine the coefficient of determination. 3. Determine the coefficient of correlation. 4. Prepare a 95 percent confidence interval for supplies cost when 90 units are produced (using t statistic = 2.228). 59 Activity Cost Behavior EXERCISE 4 The Yuma Company has accumulated the following information in its quest to determine the cost behavior of the Receiving Department. Gail Nelson, the manager of Yuma, feels that tons of material received, the dollar value of receipts, the number of purchase orders, and the number of incoming shipments could all reasonably influence the Receiving Department costs. Receiving Department Costs Tons of Material Received Dollar Value of Receipts $67,100 75,200 92,200 88,600 87,700 80,200 98,000 67,600 68,500 78,500 71,700 80,300 78,000 80,000 93,800 47,300 68,200 93,500 79,200 96,800 49,500 73,700 40,700 46,200 63,800 50,600 48,400 55,000 69,300 53,900 $138,600 157,000 158,400 139,900 144,000 134,100 162,000 117,000 152,100 143,100 117,000 148,500 127,800 136,800 153,000 Number of POs 90 89 96 105 91 110 128 85 88 90 87 108 103 98 125 Number of Incoming Shipments 103 117 139 148 120 138 156 114 117 133 130 136 115 126 168 Required: 1. Prepare a cost formula for the Receiving Department costs. How many activity drivers are used? Are they all different from zero? 60 Chapter 3 EXERCISE 4 (Continued) Use this space to continue your answer. 2. How well does your model explain the variability in the costs? 3. Prepare an estimate of costs for a month when 75,000 tons valued at $125,000 are received, 90 purchase orders are handled, and 125 shipments are received. 4. Prepare a 95 percent confidence interval for the point estimate you prepared in Requirement 3. 61 Activity Cost Behavior EXERCISE 5 Titan Corp. manufactures high-tech equipment for space shuttles. It has completed manufacturing the first unit of the new TN-3 machine design. Management believes that the 100 labor hours required to complete this unit are reasonable and is prepared to go forward with the manufacture of additional units. An 80 percent cumulative average-time learning curve model for direct labor hours is assumed to be valid. Data on costs are as follows: Direct materials $750 per unit Direct labor $15 per direct labor hour Variable manufacturing overhead $40 per direct labor hour Required: 1. Set up a table with columns for cumulative number of units, cumulative average time per unit in hours, cumulative total time in hours, and individual unit time for the nth unit in hours. Complete the table for 1, 2, 4, and 8 units. 2. What is the total variable cost of producing 1, 2, 4, and 8 units? What is the variable cost per unit for 1, 2, 4, and 8 units? 62 Chapter 3 “CAN YOU?” CHECKLIST Can you explain the relationship among activities, resource usage, and cost behavior? Can you explain how resource spending, resource usage, and unused capacity are interrelated? Can you describe how resources supplied affect cost behavior? Can you describe the different patterns of step-cost behavior? Can you explain how the concept of the relevant range affects the estimation of these costs? Can you determine cost behavior using either the high-low method or the scatterplot method? Can you explain the difference between these two methods? Can you explain how the method of least squares defines closest and best-fitting line? Can you use the least squares method to develop a cost formula? Can you determine whether or not the resulting cost formula is reliable? Can you use the cumulative average-time learning curve model and the incremental unit-time learning curve model to produce more accurate estimates in budgeting and performance evaluation for processes in which learning occurs? Can you describe the role that managerial judgment plays in determining cost behavior? ANSWERS KEY TERMS TEST SET #1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. step-fixed cost, step-variable cost activity capacity cumulative average-time learning curve model practical capacity long run, short run cost of resource usage activity rate discretionary fixed expenses Cost behavior unused capacity 11. committed fixed expenses 12. step-cost function 13. Flexible resources, resources supplied in advance of usage 14. Variable costs 15. Mixed costs 16. Fixed costs 17. relevant range 18. learning curve SET #2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Deviation coefficient of correlation scattergraph independent variable, dependent variable coefficient of determination goodness of fit 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. high-low method, scatterplot method confidence interval intercept parameter, slope parameter method of least squares, multiple regression incremental unit-time learning curve learning rate 63 Activity Cost Behavior MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. c c a d c d b e b 10. 11. 12. 13. e d b a 14. c 15. a 16. d Variable = ($23 × 10,000 – $30 × 6,000) / (10,000 – 6,000) = $50,000 / 4,000 = $12.50 Fixed = $230,000 – ($12.50 × 10,000) = $105,000 Variable = ($310,000 – $265,000) / (3,500 – 2,750) = $45,000 / 750 = $60.00 Fixed = $310,000 – ($60 × 3,500) = $100,000 Variable = ($190,000 – $150,000) / (17,500 – 12,500) = $40,000 / 5,000 = $8.00 Y = 347.86 + (3.731 × 150) = 907.51 Y = 2.086 × 53.51 = 111.62 PRACTICE TEST EXERCISE 1 (Resources and Activities) 1. Engineers: Facility: Leased Equipment: Supplies: short-term resources supplied in advance long-term resources supplied in advance long-term resources supplied in advance resources supplied as needed 2. Activity rate: Fixed: [4 × $40,000 + ($450,000 / 20) + $6,000] / (4 × 3,200) = $188,500 / 12,800 = $14.7266 per test Variable: $175,000 / 12,800 = $13.6719 3. Activity available = Activity usage + Unused Activity 12,800 = 11,000 + 1,800 EXERCISE 2 (High-Low Method and Scatterplot Method) 1. Variable: ($4,400 – $2,650) / (325 – 150) = $1,750 / 175 = $10.00 per shipment Fixed: $4,400 – ($10 × 325) = $4,400 – $3,250 = $1,150 Storeroom Cost = $1,150 + $10 × number of shipments 2. In Excel, click on the Chart Wizard button and choose XY (Scatter) to produce a scattergraph as follows: Storeroom costs 5000 4000 3000 Series1 2000 1000 0 0 100 200 300 400 Number of shipments An analysis of the scattergraph indicates that further investigation on April data is needed. The storeroom costs in April do not fit the general pattern of behavior in the data and, thus, can be an outlier. 64 Chapter 3 3. Any two points that appear reasonable could be used to calculate the cost formula. Individual results may be very similar to the high-low results, or they could be very different. EXERCISE 3 (Least Squares) 1. The estimated cost formula using the regression output can be expressed as follows: Supplies cost = $1,445.895 + $19.6198 × Units produced 2. The coefficient of determination (R Square) is 0.869. 3. r 0.869 0.932 Actual $3,550 2,980 2,970 2,410 2,530 3,180 2,830 2,820 3,220 2,950 2,560 2,420 Predicted $3,408 3,015 2,819 2,427 2,623 3,015 2,819 3,015 3,408 2,819 2,623 2,427 Deviation 142) (35) 151) (17) (93) 165) 11) (195) (188) 131) (63) (7) Sum ................ Deviation2 20,198 1,259 22,715 285 8,665 27,066 115 38,213 35,298 17,087 3,980 47 174,928 4. Confidence interval = Predicted value ± t × Standard error Confidence interval = 1,445.895 + (19.61983 × 90) ± 2.228 × 132.26 Confidence interval = 3,211.6797 ± 294.6752 Confidence interval = 2,917.0045 < Y < 3,506.3549 EXERCISE 4 (Multiple Regression) 1. The main objective is to decide how many independent variables should be included in the cost formula. To deter mine whether or not an independent variable should be included, perform the hypothesis test of the parameters. Any variable that is not significantly different from zero should be excluded. Thus, the multiple regression analysis will be performed in the following step-wise manner. First Pass: Include all four variables in the regression. SUMMARY OUTPUT: All FOUR VARIABLES Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.9927017 R Square 0.98545666 Adjusted R Square 0.97963933 Standard Error 1397.87556 Observations 15 ANOVA Regression Residual Total df 4 10 14 SS MS 1324068773 331017193 19540560.7 1954056.1 1343609333 F 169.4 Significance F 3.85634E-09 65 Activity Cost Behavior Intercept Tons of DM received Dollar value of receipts No. of purchase orders No. of incoming shipments Coefficients Standard Error 5058.15695 4090.100748 0.32367875 0.025601107 -0.00771516 0.033722885 349.727053 50.73502222 164.702734 38.54285933 t Stat 1.2366827 12.643154 -0.228781 6.8932078 4.273236 P-value 0.24446 1.8E-07 0.82365 4.2E-05 0.00163 Lower 95% -4055.15701 0.266635918 -0.08285444 236.6823593 78.82387702 Upper 95% 14171.4709 0.38072158 0.06742413 462.771747 250.581591 Based on the P-values, the results suggest that the tons of direct material received, number of purchase orders, and number of incoming shipments are significantly different from zero, because their P-values are less than the 5% degree of confidence. These variables seem to be good explanatory variables of the cost behavior of the Receiving Department. Adjusted R 2 = 0.9796, or 97.96% Standard Error = 1397.876 Second Pass: Drop the variable and redo the regression, since the P-value for the variable of “dollar value of receipts” is not significant. SUMMARY OUTPUT: THREE VARIABLES Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.99266336 R Square 0.98538054 Adjusted R Square 0.98139342 Standard Error 1336.30554 Observations 15 ANOVA Regression Residual Total Intercept Tons of DM received No. of purchase orders No. of incoming shipments df 3 11 14 SS MS 1323966496 441322165 19642837.45 1785712.5 1343609333 Coefficients Standard Error 4439.25537 2932.575239 0.3209441 0.021642175 346.374717 46.43353003 164.917318 36.83431142 Adjusted R 2 = 0.9814, or 98.14% t Stat 1.5137737 14.829568 7.4595818 4.4772744 F 247.141 Significance F 2.26457E-10 P-value 0.15827 1.3E-08 1.3E-05 0.00094 Lower 95% -2015.30248 0.27330997 244.1751551 83.84550461 Upper 95% 10893.8132 0.36857823 448.57428 245.989132 Standard Error = 1336.306 Since all P-values of explanatory variables are significant at a 5% confidence level, the three-variable model is adequate. The three-variable model also has a higher adjusted R 2 value (98.14%) than the four-variable model (97.96%). Thus, the estimated cost formula is as follows: Receiving Department costs = $4,439.255 + ($0.320944 × tons) + ($346.3747 × POs) + ($164.9173 × shipments) 2. The model chosen explains the variability in Receiving Department costs very well, because the adjusted R2 equals 98.14%. 3. Based on the estimated cost formula, an estimate of Receiving Department costs for a month when 75,000 tons are received, 90 purchase orders are handled, and 125 shipments are received will be as follows: Receiving Department costs = $4,439.255 + ($0.320944 × 75,000) + ($346.3747 × 90) + ($164.9173 × 125) Receiving Department costs = $80,298.44 66 Chapter 3 4. Confidence interval of the estimated Receiving Department costs = $80,298.44 ± t (95%, 11 degrees of freedom) × Se = $80,298.44 ± 2.201 × 1,336.306 Thus, $80,298.44 ± $2,941.21 That is, $77,357.23 < Estimated Receiving Department costs < $83,239.65 EXERCISE 5 (Learning Curve) 1. The table with columns for cumulative number of units, cumulative average time per unit in hours, cumulative total time in hours, and individual unit time for the nth unit in hours for 1, 2, 4, and 8 units is presented below. Cumulative Number of Units Cumulative Average Cumulative Total Individual Time for Time per Unit in Time: Labor nth Unit: Labor Hours Hours Hours (1) (2) (3) = (1) x (2) (4) 1 100 100 100 2 80 (0.8 x 100) 160 60 4 64 (0.8 x 80) 256 45.4 8 51.2 (0.8 x 64) 409.6 35.5 2. The calculation of total variable cost of producing 1, 2, 4, and 8 units and the variable cost per unit for 1, 2, 4, and 8 units is presented below. 1 unit 2 units 4 units 8 units 750 $ 1,500 $ 3,000 $ 6,000 Direct labor 1,500 2,400 3,840 6,144 Variable overhead 4,000 6,400 10,240 16,384 Total variable cost $ 6,250 $10,300 $ 17,080 $ 28,528 Direct materials Divided by units Unit variable cost $ 1 $ 6,250 2 $ 5,150 4 $ 4,270 8 $ 3,566