Learning Curves - Jps
advertisement
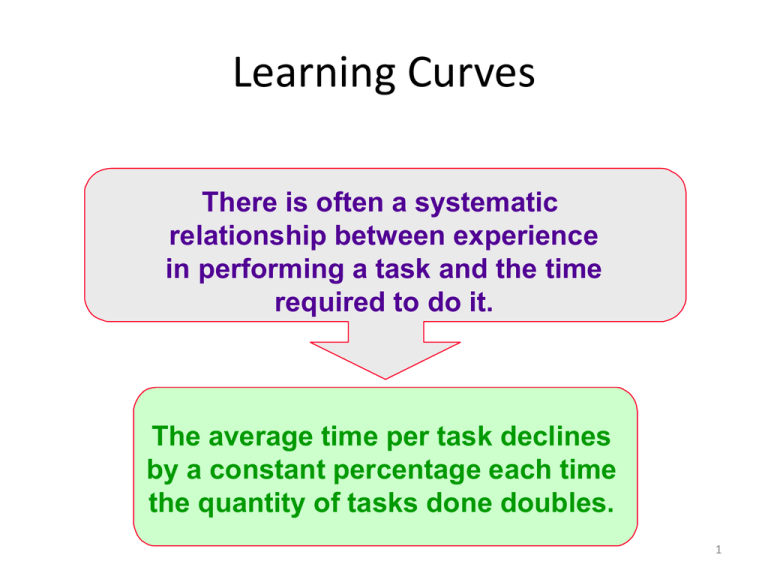
Learning Curves There is often a systematic relationship between experience in performing a task and the time required to do it. The average time per task declines by a constant percentage each time the quantity of tasks done doubles. 1 Types of Learning Curves Cumulative Average-Time Learning Model – • cumulative average time per unit declines by a constant percentage each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles Incremental Unit-Time Learning Model – • incremental time needed to produce the last unit declines by a constant percentage each time the cumulative quantity of units produced doubles 2 Effect of Learning on Cost Behavior Berry Co. makes products requiring labor that follows an 80 percent learning rate. If the first unit of such a product requires 10 hours, what is the average time for 16 units of this product? An 80 percent learning rate: the average time required to make 2 units is 80 percent of the time for 1 unit and the average time for 4 units is 80 percent of the time for 2 units, etc. 3 Cumulative Average-Time Learning Model Number of Units 1 2 4 8 16 Average Labor Time per Unit 1 × 10 = 10 .80 × 10 = 8 .80 × 8 = 6.4 .80 × 6.4 = 5.12 .80 × 5.12 = 4.096 Total Time: Average x Units 1 × 10 = 10 2 × 8 = 16 4 × 6.4 = 25.6 8 × 5.12 = 40.96 16 × 4.096 = 65.536 The graphic presentation of the learning phenomenon is called the learning curve. 4 Learning Curve Average Labor Time per Unit Learning effects are large initially. Learning effects become smaller, eventually reaching expected final time. Cumulative Production Output 5 Average Labor Time per Unit This is used to help determine investment required. This is used to estimate ongoing results. Cumulative Production Output 6 Learning Curve Formula Cumulativeaveragelabor timeper unit DLH to produce unit 1 Cumulativeno.of units produced learning factor ln learningrate% in decimalform Learningfactor ln 2 7 Question for Discussion 2 Time to produce the first unit = 100 minutes Learning factor = ln(0.80)/ln2 = -0.32193 • • What is the cumulative average time to produce .1 5 units? What is the total time to produce 5 units? .2 What is the time it took to produce the 5th unit? .3 8 Incremental Unit-Time Learning Model Using the example of Berry Co. and using the incremental unit-time learning model Number of Units 1 2 3 4 5 Individual Unit Time for X-th Unit 1 × 10 = 10 0.80 × 10 = 8 7.02 0.80 × 8 = 6.40 5.96 Cum. Cumulative Ave. Time Total Time Per Unit 10 10 10 + 8 = 18 9 18 + 7.02 = 25.02 8.34 25.02 + 6.40 = 31.42 7.86 31.42 + 5.96 = 37.38 7.48 9