Business Research Methods Course Material
advertisement

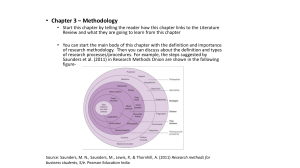
Business Research Methods Course Title: Business Research Methods Text Book: Research Methodology: A step-By-Step Guide For Beginners by Ranjit Kumar Must Read Books: Business Research Methods by William G. Zikmund 7. ed Reference Books: Greener, S. (2008) Business Research Methods, Ventus Publishing. FREE download: http://bookboon.com/uk/student/management/introduc tion-to-research-methods Saunders, M., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A. (2007). Research Methods for Business Students, (4th ed.), Prentice Hall - Financial Times. What is Research? “The systematic investigation into and study of materials, sources, etc., in order to establish facts and reach new conclusions” Oxford English dictionary “A process of finding out information and investigating the unknown to solve a problem” Maylor and Blackmon (2005) “Something that people undertake in order to find out things in a systematic way, thereby increasing their knowledge” Saunders et al (2007, p.5) Business Research Business Research Defined Business research is defined as the systematic and objective process of generating information for aid in making business decisions. So what's not Research? Research isn’t information gathering: Gathering information from resources such as books or magazines isn’t research. No contribution to new knowledge. Research isn’t the transportation of facts: Merely transporting facts from one resource to another doesn’t constitute research. No contribution to new knowledge although this might make existing knowledge more accessible. Research Characteristics Originates with a question or problem. Requires clear articulation of a goal. Follows a specific plan or procedure. Often divides main problem into sub problems. Guided by specific problem, question, or hypothesis. Accepts certain critical assumptions. Requires collection and interpretation of data. Types of Business Research Types of Research From the view point of Application Pure Research Applied Research Objectives Type of Information Sought Exploratory Research Quantitative Research Discriptive Research Qualitative Research Correlation Research Explanatory Research Application View Point Basic Research Attempts to expand the limits of knowledge. Not directly involved in the solution to a pragmatic problem. To test theory or to discover more about a concept. Basic Research Example Is executive success correlated with high need for achievement? Are members of highly cohesive work groups more satisfied than members of less cohesive work groups? Do consumers experience cognitive dissonance in lowinvolvement situations? Applied Research Conducted when a decision must be made about a specific real-life problem. Applied Research Examples Should McDonalds add Italian pasta dinners to its menu? Business research told McDonald’s it should not? Should Procter & Gamble add a high-priced home teeth bleaching kit to its product line? Summarizing Applied And Basic Research Applied research is research undertaken to solve practical problems rather than to acquire knowledge for knowledge sake. Basic research is experimental and theoretical work undertaken to acquire new knowledge without looking for long-term benefits other than the advancement of knowledge. Kind of Research Key Characteristics Basic research Focuses on generating fundamental knowledge Applied research Focuses on real-world questions and applications