Neuro Objectives 6
advertisement

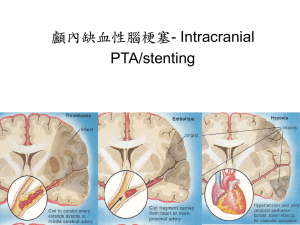
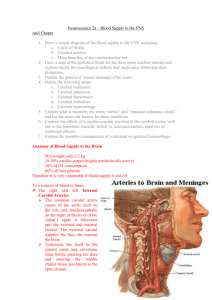
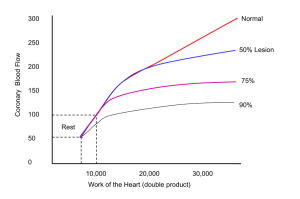
Neuro Objectives 6 1. Note: Spinal: o anterior spinal artery branches off the vertebral artery o posterior spinal artery branches off PICA Note: Choroidal: o anterior choroidal artery branches off the internal carotid artery o posterior medial and lateral choroidal arteries branch off the posterior cerebral artery Arterial Circulation: cerebral hemispheres: a. anterior cerebral artery (from internal carotid) a. goes to longitudinal fissure and supplies medial surfaces of frontal and parietal lobes as well as the orbital frontal lobe b. middle cerebral artery (from internal carotid) a. goes to the insula, then lateral sulcus to supply all lateral lobes c. posterior cerebral artery (from basilar artery) a. wraps around rostral midbrain and supplies inferior/medial surface of temporal lobe and the medial surface of the occipital lobe diencephalon: a. hypothalamus a. posterior communicating artery, internal carotid, anterior communicating artery b. thalamus a. posterior cerebral artery, posterior communicating artery, anterior choroidal artery brainstem: a. midbrain a. posterior cerebral artery, basilar artery, superior cerebellar artery b. pons a. basilar artery, AICA c. medulla a. ventricular arteries, PICA cerebellum: a. AICA (from vertebral arteries) a. supplies anterior portion of inferior cerebellum b. PICA (from basilar artery) a. supplies posterior portion of inferior cerebellum c. superior cerebellar artery (from basilar artery) a. supplies superior cerebellum Circle of Willis: The significance of the Circle of Willis is that it provides anastomoses with other major blood supplies and thus forms a route of collateral circulation for blood to get to major pathways (also drawn are branches of other arteries): (Anterior) (Posterior) 2. Three principal mechanisms that regulate blood flow: a. Autoregulation (arterioles are pressure sensitive and constrict/dilate in response to changes in blood pressure) – global b. Autonomic control (can shift autoregulation curve left or right) global c. Changes in metabolite concentrations (pH, [O2], [CO2], etc) – local 3. Venous return from brain: Two major types: a. superficial: superficial veins → superior sagittal sinus → confluence of sinuses b. deep: deep veins → internal cerebral veins (remember venous angle is found here when passing through intraventricular foramen) → great vein (of Galen) → straight sinus → confluence of sinuses From the confluence of the sinuses, blood travels into the transverse sinuses → sigmoid sinuses → internal jugular veins 4. Anatomical barriers between extracellular CNS spaces and extracellular spaces of body: a. Arachnoid barrier a. arachnoid cells form tight junctions and thus, form a diffusion barrier between extracellular and CNS space b. Choroid epithelium a. ependymal cells form tight junctions that causes a diffusion barrier between blood supply and ventricles c. Blood-brain barrier a. astrocytes “zip up” leaky capillaries by forming tight junctions (and thus, a diffusion barrier) between epithelial cells in intracerebral capillaries i. glucose can pass through via facilitated diffusion