Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions

CHAPTER TWENTY-THREE
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN?
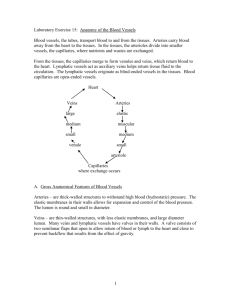
1. An anastomosis occurs where two or more arteries (or veins) merge to supply the same body region. Anastomoses provide alternate blood supply routes to body tissues or organs.
2. Unlike elastic arteries, the elastin in muscular arteries is confined to two circumscribed rings: the internal elastic lamina that separates the tunica intima
3. from the tunica media, and the external elastic lamina that separates the tunica media from the tunica externa.
Continuous capillaries are the most common type of capillary. The endothelial cells form a complete continuous lining and are connected by tight junctions.
These capillaries are found in muscle, skin, the thymus, the lungs, and the CNS.
Fenestrated capillaries have holes (or fenestrations) within each endothelial cell, but the basement membrane of the endothelial cells is continuous. Fenestrated capillaries are seen in tissues where a great deal of fluid transport between blood and tissues occurs, such as the intestinal villi, ciliary process of the eye, most endocrine glands, and the kidney. Sinusoids (discontinuous capillaries) have larger gaps than fenestrated capillaries, and a discontinuous or absent basement membrane. Sinusoids are found in bone marrow, the anterior pituitary, parathyroid glands, suprarenal glands, the spleen, and the liver.
4. Valves assist in the movement of blood because they only open one way, so blood is pushed through them but cannot flow back. This prevents both pooling of the blood in the limbs and backflow of blood in the veins. In addition to the venous valves, many deep veins pass between skeletal muscle groups. As the skeletal muscles contract, they help pump the blood toward the heart.
5.
Blood pressure is the force per unit area that blood places on a blood vessel wall.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury
(mm Hg). Systolic blood pressure is the pressure in the blood vessels during systole (ventricular contraction). Diastolic blood pressure occurs during diastole
(ventricular relaxation). Systolic pressure is typically greater than diastolic pressure due to the greater force from ventricular contraction. Blood pressure readings are expressed in a ratio format, where the numerator (upper number) is the systolic pressure and the denominator (lower number) is the diastolic pressure.
6.
The three main branches that arise from the aortic arch are the brachiocephalic trunk, the left common carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery. The brachiocephalic trunk further divides into the right common carotid artery
(supplies arterial blood to the right side of the head and neck) and the right subclavian artery (supplies the right upper limb and some thoracic structures).
The left common carotid artery supplies the left side of the head and neck. The left subclavian artery supplies the right upper limb and some thoracic structures.
7. The internal carotid artery forms multiple branches after it enters the skull, such as the anterior and middle cerebral arteries. The vertebral arteries emerge from the subclavian arteries and travel through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae before entering the skull through the foramen magnum, where they merge to form the basilar artery. The basilar artery subdivides into the posterior cerebral arteries that supply the posterior portion of the cerebrum. The cerebral arterial circle (circle of Willis) is an important anastomosis of arteries around the sella turcica. The circle is formed from posterior cerebral arteries and posterior communicating arteries (branches of the posterior cerebral arteries), internal carotid arteries, anterior cerebral arteries, and anterior communicating arteries
(connect the two anterior cerebral arteries). This arterial circle equalizes blood pressure in the brain and can provide collateral channels should one vessel become blocked.
8. The hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins are on the left side of the vertebrae and drain the left-side veins. The azygos vein drains the right-side veins and also receives blood from the hemiazygos veins, esophageal veins, bronchial veins, and pericardial veins. The azygos vein merges with the superior vena cava.
9. The celiac trunk gives off three branches: the left gastric artery, the splenic artery, and the common hepatic artery.
10. The paired arterial branches that emerge from the lateral sides of the descending abdominal aorta include: (1) the middle suprarenal artery, which supplies each adrenal gland; (2) the renal artery, which supplies each kidney; (3) the gonadal artery, which supplies each gonad (testes in males, ovaries in females); and (4) lumbar arteries, which supply the inferior abdominal wall.
11. The hepatic portal system consists of a network of veins that drain the gastrointestinal tract and shunt the blood to the liver for processing. The hepatic portal vein is the large vein that receives blood from the gastrointestinal organs.
The three main branches that merge to form this vein include the inferior mesenteric vein, the splenic vein, and the superior mesenteric vein.
12. The uterine artery, which supplies the uterus and vagina, is only found in females.
13. On the dorsum of the hand, a dorsal venous arch of veins drains into the basilic vein and the cephalic vein. In the cubital region, an obliquely positioned median cubital vein connects the cephalic and basilic veins. The basilic vein eventually helps form the axillary vein. The cephalic vein drains into the axillary vein.
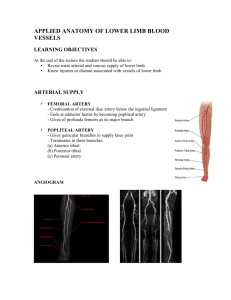
14. The main arterial supply for the lower limb comes from the external iliac artery (a branch of the common iliac artery). The external iliac artery travels inferior to the inguinal ligament, where it is renamed the femoral artery. The femoral artery gives off several branches, including the deep femoral artery. The femoral artery is renamed the popliteal artery when it enters the popliteal fossa. The popliteal artery divides into an anterior tibial artery and a posterior tibial artery. The posterior tibial artery gives off a fibular artery. The posterior tibial artery branches into medial and lateral plantar arteries. The anterior tibial artery crosses over the anterior surface of the ankle, where it is renamed the dorsalis pedis artery. The dorsalis pedis artery and a branch of the lateral plantar artery unite to form the plantar arch of the foot. Digital arteries come from the plantar arch.
15. Pulmonary veins carry blood high in oxygen, and drain into the left atrium of the heart.
16. Oxygenated blood leaves the left ventricle and enters the ascending aorta before entering the aortic arch and then the descending thoracic aorta.
17. As adults get older, the heart and blood vessels become less resilient. Many of the elastic arteries are less able to withstand the forces from the pulsating blood.
Systolic blood pressure may increase with age, exacerbating this problem.
18. The right vitelline vein gives rise to most of the hepatic portal system.
19. The cardinal system of veins consists of a series of paired veins. The anterior cardinal veins develop into the veins of the head and neck and veins superior to the heart.
20. Each umbilical artery becomes a medial umbilical ligament after a baby is born.