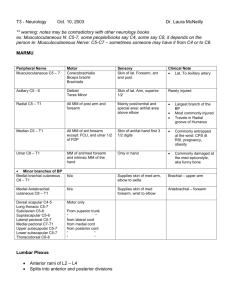
Single choice questions
advertisement

CONTENTS LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM .................................................................................................................................... 1 SINGLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ................................................................................................................................. 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................................................. 8 ANSWER QUESTIONS ......................................................................................................................................... 10 UPPER LIMB ..................................................................................................................................................... 11 SINGLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 11 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ........................................................................................................................... 18 ANSWER QUESTIONS ......................................................................................................................................... 20 THE LOWER LIMB .......................................................................................................................................... 21 SINGLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 21 MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS .......................................................................................................................... 23 ANSWER QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................................. 25 HEAD AND NECK ............................................................................................................................................. 26 SINGLE CHOICE QUESTIONS .............................................................................................................................. 26 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ........................................................................................................................... 33 ANSWER QUESTIONS ......................................................................................................................................... 35 THORAX ............................................................................................................................................................. 36 SINGLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 36 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ........................................................................................................................... 42 ANSWER QUESTIONS ......................................................................................................................................... 45 ABDOMEN ......................................................................................................................................................... 46 SINGLE CHOICE QUESTIONS .............................................................................................................................. 46 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS .......................................................................................................................... 49 ANSWER QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................................. 55 PELVIC AND PERINEUM ............................................................................................................................... 56 SINGLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 56 MULTI-CHOICE QUESTIONS ................................................................................................................................ 64 ANSWER QUESTIONS .................................................................................................................................. 67 Locomotor system Single choice questions 1.Which bone does belong to the long bone? A. sternum B. costal bone C. humerus D. parietal bone E. scapula 1 2.Which bone does belong to the short bone? A.occipital bone B.temporal bone C.cuboid bone D.fibula E.ischium 3.Which bone does belong to the flat bone? A. tibia B. patella C. sphenoid bone D. zygomatic bone E. costal bone 4.Which bone does belong to the irregular bone? A. vertebrae B. phalanges of fingers C. sternum D. radius E. ulna 5. Concerning the cervical vertebrae, the right description is: A. all cervical vertebrae have vertebral body and articular process B. the first cervical vertebra has no transverse foramen C. the end of the spinous process of the cervical vertebrae bifurcated entirely D. the articular facets are relatively horizontal E. the first cervical vertebra is called axis 6. Thoracic vertebrae: A. have transverse foramen B. the end of the transverse process bifurcated C. the articular facets are relatively sagittal D. have costal fovea on the vertebral body laterally E. have no transverse costal fovea 7. Concerning the lumbar vertebrae, the right description is: A. the body are small have costal fovea on the vertebral body laterally . have transverse foramen D. the articular facets are relatively sagittal E. the spinous processes point obliquely downward 8. Sacrum: A. is made up of four fused vertebrae B. the base of it is downward C. the auricular surface is on the anterior surface D. the anterior sacral foramina is not communicating with sacral canal E. have four pairs of posterior sacral foramina 9. A. is made of manubrium and xiphoid connects the fourth costal cartilage laterally D .the body has the jugular notch E. lies opposite the lower border of T4 posteriorly 2 10. Concerning the ribs, the right description is: A. the ribs are eleven in number on each side B. 1st~8th Ribs are called true ribs C. 8th~11th Ribs are called false ribs D. the anterior end is called costal angle E. the posterior end of rib enlarged to form the costal head 11. The following bones for the proximal row of carpal bones except the: A. lunate B. pisiform C. scaphoid D. trapezium E. triquetral 12.The bone which have the diaphysis and epiphysis is A. short bone B. flat bone C. long bone D. irregular bone E. sesamoid bone 13. The structure which can act haemopoiesis is A. yellow marrow B. spongy bone C. periosteum D. red marrow E. compact bone 14. The structure lies on the posterior aspect of shaft of humerus is: A. deltoid tuberosity B. groove for radial nerve C. bicipital groove D. olecranon fossa E. capitulum 15. Inferior angle of scapula marks the level of A. the 2th rib B. the 7th rib C. the spine of the 2nd thoracic vertebra D. the spine of the 7th thoracic vertebra E. the spine of the 10th thoracic vertebra 16. The structure lies on the posterior aspect of scapula is: A. subscapular fossa B. coracoid process C. suprascapular notch D. spine of scapula E. glenoid cavity 18. Ulnar: A. the upper end is called the head of ulna B. lies the lateral side of the forearm C. the olecranon and coronoid process are on its upper end 3 D.interosseous border E. the trochlear notch is on the body of ulnar 19.Hip bone: A. the obturator foramen is formed by pubis and ischium B. inferior to the anterior inferior iliac spine is the greater sciatic notch C. the external surface of the ala of ilium is called iliac fossa D. the anterior superior iliac spine can not be palpated E. consists of ilium and ischium 20.Femur: A. the intertrochanteric line is on the posterior surface of two trochanters B. the intertrochanteric crest is on the anterior surface of two trochanters C. the adductor tubercle is inferior to the medial epicondyle D. the linea aspera is on the anterior surface of the body of femur E. the lower end of the femur has the medial and lateral epicondyles 21.Tibia: A. B. the medial border of the body is termed as interosseous border C. the lower end of the tibia has a prominence which is called lateral malleolus D. the tibial tuberosity is on the anterior aspect of the upper end of the tibia E. fibular notch is medial to the lower end of the tibia 22.Fibula: A. B. its lower end is called the fibular head C. its lower end of the fibula forms the lateral malleolus D. the lateral border of the body is termed as interosseous border E. the lateral malleolus can not be palpated 23. Which is the accessory structure of synovial joint? A. articular surface, articular disc, ligament B. ligament ,articular capsule, articular surface C. ligament, articular cavity, articular disc D. articular cavity ,synovial fold, synovial bursa E. articular labrum, ligament, synovial fold 24. Concerning the intervertebral disc, the right description is: A. 22 in number in adults B. is a symphysis between vertebral arches C. is composed of anulus fibrous and nucleus pulposus D.the nucleus pulposus protrude anterorlaterally easily E. the anulus fibrosus is an inner soft, highly elastic structure 25. Which ligaments associate with the lamina of vertebral arch adjacently?A. anterior longitudinal ligament B. posterior longitudinal ligament C. ligamenta flava D. interspinal ligament E. supraspinal ligament 26. Temporomandibular joint: A. is formed by mandibular fossa and head of mandibleB. has intracapsular ligment 4 C. the extracapsular ligament is the medial ligament D. has the articular disc E. the temporomandibular joint is dislocated (脱位)only backward 27.Sternoclavicular joint: A. is the only joint between the upper limb and the trunk B. is formed by the sternal end of the clavicle and the clavicular notch of sternum C. its capsule is thin and loose D. has not the articular disc E. it can elevate and depress only 28. Concerning the shoulder joint, the right description is: A.its capsule is strong and thickthe head of the humerus takes part in forming the joint C. biaxial joint the glenoid cavity of the scapula is deep tendon of short head of biceps brachii passes though the cavity 29. Elbow joint: A. is formed by the humerus and radius only B. is formed by the humerus and ulna only C. the capsule is strongly thickened D. radial collateral ligament attached to medial epicondyle E. annular ligament of radius attached to anterior and posterior margins of radial notch of ulnaproximal row of carpal bones, radius and ulnaB. its capsule is tense movements include flexion and extension, adduction and abduction only.E. is a biaxial synovial joint 31. Concerning the hip joint, the right description is: A. is formed by the head of femur and the acetabulum.B. is biaxial joint C. the iliofemoral ligament can confine .the anteflexion of the thigh excessively. D. the fracture of femoral neck must be the intracapsular type. E. the ischiofemoral ligament block the acetabular notch. 31.The knee joint: A. is made up of the lower end of femur and the upper end of tibia only. B. the tibial collateral ligament is attached to the medial meniscus compactly . C. the fibular collateral ligament is attached to the lateral meniscus compactly . D. the medial meniscus is smaller and assume “O” shape.. E. the lateral meniscus is larger and assume“C”shape. 32. Which joint has the articular disc ? A.shoulder joint B.sternoclavicular joint C.elbow joint D.hip joint E.talocrural joint 33.Which joint has the articular labrum A. temporomandibular joint B. elbow joint C. shoulder joint D. radiocarpal joint E. talocrural joint 34.Talocrural joint: 5 A. is made up of lower ends of tibia and fibula, trochlea of talus B. extension and flexion is the only movements of this joint. C. is thickened on the anterior surface of the articular capsule with ligaments D. the lateral ligament is called deltoid ligament. E. this joint is also called talocalcaneal joint. 35. Which muscle can evert the ankle joint? A. peroneus longus B. the tibialis anterior C. the tibialis posterior D. the soleus E. flexor digitorom brevis 36. Which muscle can depress the mandible? A. epicranius B. masseter C. temporalis D. medial pterygoid E. lateral pterygoid 37. Sternocleidomastoid: A. arises from the manubrium only B. lies in the deep part of the neck C. left sternocleidomastoid contract,the head inclines to the right. D. right sternocleidomastoid contract,the head inclines to the right. E. inserts into the styloid process of temporal bone. 38.Which muscle can elevate and to draw back the mandible? A.masseter B.temporalis C.medial pterygoid D.lateral pterygoid E.epicranius 39.The scalenus: A. the scalene fissure is formed by scalenus anterior and scalenus medius only. B. the scalenus anterior insert in the second rib. C. the scalenus medius insert on the first rib. D. the scalenus arise from the body of the cervical vertebrae E. the scalenus is not related to the respiratory movement. 40 .The trapezius: A. is a superficial muscle lying on the anterior surface of the neck.. B. is long thin muscle. C. arises from the spines of several thoracic vertebrae. D. inserts on the clavicle only. E. left trapezius contract, the neck inclines to the left. 41.The latissimus dorsi: A. covers the upper part of the chest. B. insert on the crest of greater tubercle of humerus. C. arises from the spines of all thoracic vertebrae. D. can extend, adduct and medially rotate humerus at shoulder joint. 6 E. long thoracic nerve supply it. 42.Which muscle pull the scapula forward and hold the scapula against the chest wall? A. transverses thoracis B. intercostales interni C. intercostales externi D. intercostales intimi E. serratus anterior. 43. Which muscle doesn’t belong to the muscles of shoulder? A. deltoid B. supraspinatus C. infraspinatus D. teres minor E brachialis 44. Which muscle can abduct the shoulder joint? A. deltoid B. infraspinatus C. teres minor D. teres major E. subscapularis 45. Biceps brachii: A. lies in the posterior part of the arm. B. the short head arises from the supraglenoid tubercle. C. the long head arises from the coracoid process. D. it can flexes elbow joint . E. it inserts on tuberosity of the ulna. 46. Triceps brachii: A. the long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of scapula. B. the lateral head arises from the posterior surface of the humerus below the groove for radial n. C. the medial head arises from the posterior surface of the humerus above the groove for radial n.. D. can flexes elbow joint E. inserts on the tuberosity of radius. 47.Which muscle can flex the hip and knee joint? A. quadriceps femoris B. sartorius C. adductor longus D. pectineus E. adductor magnus 48. Which muscle does belong to the anterior group of the muscles of leg? A. extensor digitorum longus B. peroneus longus C. peroneus brevis D. flxor digitorum longus E. popliteus 49.Which muscle can invert the foot? A. peroneus longus B. popliteus 7 C. tibialis posterior D. flexor hallucis longus E. flexor digitorum longus 50.Concerning triceps surae, the right description is: A. the gastrocnemius lies deeply to the soleus. B. the tendo calcaneus inserts on the calcaneus bone. C. it can extend the ankle joint. D. the gastrocnemius arises from the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula E. the soleus arises from the medial and lateral condyles of the femur. Multiple choice questions 1. Concerning the structure of bone, the right description includ: A. the bones substance include compact and spongy bone. B .the whole of the bone is covered by periosteum C. the bone marrow include red and yellow marrow D .the red marrow can make blood cells E. the yellow marrow can make blood cells 2. The srtuctures in the middle cranial fossa are? A. foramen cecum B. foramen rotundum C. foramen ovale D. foramen spinosum E. trigeminal impression 3. The structures in the posterior cranial fossa are? A. hypoglossal canal B. internal acoustic pore C. tuberculum sellae D. internal occipital protuberance E. crista galli 4.The structures on the lateral wall of the bony nasal cavity are? A. B. superior nasal concha C. middle nasal concha D. inferior nasal concha E. superior nasal meatus 5.Which paranasal sinuses open into middle nasal meatus? A .frontal sinus B. sphenoidal sinus C. posterior groups of ethmoidal sinuses D.anterior and middle groups of ethmoidal sinuses E. maxillary sinus 6.B. the scapular notch is on the superior border 7th opposite to the 2nd rib 7.The proximal row of the carpal bones are?A. trapezoid bone B. scaphoid bone C. lunate bone 8 D. pisiform bone E. hamate bone 8. Concerning the phalanges, the right description includ: A. 12 in number B. two for the thumb and three for each of other digitis C. each one is consisting of base, shaft and head D. the distal end of the distal phalanges is called tuberosity of distal phalanx E. are long bones 9. which bones are anterior to the navicular bone? A. talus B. calcaneus C. medial cuneiform bone D. intermediate cuneiform bone E. lateral cuneiform bone 10. The essential structures of a synovial joint? A. articular surface B. articular capsule C. ligament D. articular cavity E. articular disc 11. Concerning the pelvis, the right description includ: A. the pelvis is formed by the two hip bones , sacrum and coccyx. B. the greater pelvis is the portion situated superior to the terminal line. C. the lesser pelvis is the portion situated below the terminal line. D. the superior pelvic aperture is formed by the terminal line. E. the pubic arch is formed by the two sides conjoined rami of the pubis and ischium 12.Which muscles do belong to the masticatory muscles? A. buccinator B. masseter C. temporalis D. medial pterygoid E. lateral pterygoid 13.Pectoralis major: A. arises from the medial half of the clavicle B. arises from the sternum and 1~6 costal cartilages. C. inserts on the crest of greater tubercle of humerus. D. can flex, adduct and rotate the arm medially. E. lies deep to the serratus anterior. 14.Which muscles do help inspiration? A. erector spinae B. levator scapulae C. pectoralis minor D. intercostales externi E. intercostales interni 15. Concerning the diaphragm, the right description includ: A. it forms the floor of thorax and the roof of abdominal cavities. 9 B. the central aponeurotic portion of it is called the central tendon C. the aortic hiatus lies at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra. D. the esophageal lies at the level of the 9th vertebra . E. the vena cava foramen lies at the level of the 8th vertebra . 16. Which muscles do belong to the anterolateral group of muscles of abdomen? A. obliquus externus abdominis B. obliquus internus abdominis C. transversus abdominis D. rectus abdominis E. quadratus lumborom 17. Which aponeurosis form the anterior layer of sheath of rectus abdominis (above the arcuate line)? A. the aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis B. the posterior layer of the aponeurosis of obliquus internus abdominis C. the aponeurosis of transversus abdominis D. the aponeurosis of rectus abdominis E. the anterior layer of the aponeurosis of obliquus internus abdominis. 18.Which muscles do belong to the anterior group of the muscles of forearm? A. brachioradialis B. pronator teres C. flexor digitorum superficialis D. flexor pollicis longus E. flexor pollicis brevis 19.Which muscles do belong to the posterior group of the muscles of forearm? A. abductor digiti minimi. B. extensor carpi radialis longus C. extensor carpi radialis brevis D. extensor digitorum E. supinator 20. Which muscles do belong to the posterior group of the muscles of hip? A. gluteus maximus B. gluteus medius C. piriformis D. obturator internus E. quadratus femoris 21.The articulations of wrist join consist of A. distal end of radius B. scaphoid bone C. triquetral bone D. pisiform bone E. trapezium bone Answer questions 1. Briefly describe the classification of bones 2. Briefly describe the general structure of bone 3. Write out the composition of the bones of upper limb. 4.Briefly describe the bone markings of scapula, humerus, ulna and radius. 10 5. Write out the composition of the bones of lower limb. 6. Briefly describe the bone markings of the hip bone, femur, tibia and fibula. 7. Briefly describe the classification, shape, and structures of ribs. 8. Briefly describe the shape and structures of sternum. 9. Briefly describe the shape and structures of cervical, thoracic, and lumber vertebrae. 10. Briefly describe the shape and structures of sacrum 11. Briefly describe apertures of thoracic cage. 12. Briefly describe joints of the vertebral bodies and physiological curves of vertebral column. 13. Write out the essential structures of the synovial joint. 14. Briefly describe the composition, structural features and movement of the shoulder joint, elbow joint and wrist joint. 15. Briefly describe the composition, structural features and movement of the hip joint, knee joint and ankle joint. 16. Briefly describe the composition of the arches of foot. 17. Briefly describe the important structure of internal surface of base of skull. Upper limb Single choice questions The basilic vein Arises from the lateral side of dorsal venous rete of hand. B. runs along the medial of biceps brachii . C.accompanies the ulnar artery D.drains into the azygos vein E.receives the superficial veins of the hand and lateral side of the forearm. The nerve which supplies the pronator quadratus. is ulnar nerve radial nerve C. median nerve D.axillary nerve E. musculocutaneous nerve The teres major inserts to lesser tubercle B. crest of the lesser tubercle C.base of the intertubercular groove D.crest of the greater tubercle E.greater tubercle The nerve distributing to the adductor pollicis is musculocutaneous N. median N. ulnar N. D.radial N. E.axillary N. The nerve which controls the m. of anterior group of the arm is: 11 ulnar n. radial n. median n. axillary n. E. musculocutaneous n. Which muscle can abduct the shoulder joint?(C) latissimus dorsi pectoralis major C. deltoid D. teres major E. trapezius 7. Which nerve injured can lead to “clawhand”(爪形手)? A. musculocutaneous nerve B. median nerve C. ulnar nerve D. axillary nerve E. radial nerve 8. Concerning the basilic vein, which is true? A. begins at the ulnar side of the dorsal venous network of hand B. begins at the radial part of the dorsal venous network of hand C. ascends along the lateral part of the arm D. pass through the groove between the pectoralis major and deltoid E. end in the subclavian vein 9. Which nerve injured can lead to “Ape-like”hand (猿掌)? A. musculocutaneous nerve and median nerve B. median nerve and ulnar nerve C.ulnar nerve and axillary nerve D.axillary nerve and radial nerve E.radial nerve 10. Which nerve injured can lead to “wristdrop”? A. musculocutaneous nerve B. median nerve C. ulnar nerve D. axillary nerve E. radial nerve 11. Which structures is not in the cubital fossa? A. brachial artery B. median nerve C. tendon of biceps brachii D. ulnar nerve E. brachial v. 12. Which nerve passes through the quadrilateral foramen? A. musculocutanous nerve B. median nerve C. ulnar nerve D. radial nerve 12 E. axillary nerve 13.The radial nerve supplies A. all of the flexor muscles of upper limb B. the extenser muscles of arm only C. all of the extensor muscles of upper limb D.the extensor muscles of forearm only E.the muscles of the hand 14. The axillary artery A. begins from the medial border of the ist rib B. gives off the internal thoracic artery C. ends at the lower border of the teres minor D.its branches distribute to the pectoralis major m. Only E.gives off the anterior intercostal artery 15. The nerves which distribute the posterior group muscles of the forearm is A. the radial nerve B.the axillary nerve C.the musculocutaneous nerve D.ulnar nerve E.median nerve 16. The cephalic vein arises from the medial side of dorsal venous rete of hand accompany the radial artery drain into the brachial v. receives the superficial veins of the hand and the medial side of the forearm E. runs along the lateral side of the biceps brachi. 17. Regarding the nerves of the upper limb, which is false A. The median nerve is easily damaged as it crosses the wrist. B. The medan nerve supplies all the muscles of the thenar eminence except the adductor pollicis. C. The median and ulnar nerves give off no branches in the axilla. D. The median and radial nerves supply flexor digitorum profundus muscles. E. The ulnar nerve is motor to all the interosseus muscles of the hand. 18. Concerning the muscles of the upper limb, which is false? A. The supinator muscles forms the floor of the cubital fossa. B. The median nerve passes between the two heads of pronator teres as it leaves the cubital fossa. C. The median nerve passes to the hand through the carpal canal D. The ulnar nerve enters the forearm superficial to the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris. The deltoid muscle is supplied by the axillary nerve. 19. Where does the axillary artery become the brachial artery? A. lower border of pectoralis major. B. Lower border of teres mojor. C.Upper border of pectoralis minor. D.Lateral border of 2nd rib E.Upper border of subscapularis. 20. The medial wall of axilla is bounded by A. pectoralis major,pectoralis minor B. intertubercular sulcus of the humerus,the two heads of biceps and the coracobrachialis. 13 C. Trilateral foramen and quadrilateral foramen. D.Lateral wall of chest and serratus anterior. E. Humerus and triceps brachii. 21. Which nerve arises from the lateral cord of brachial plexus A. musculocutaneous nerve B. ulnar nerve C. medial pectoral nerve D. radial nerve E. thoracodorsal nerve 22. Concerning the musculocutaneous nerve, which is true A. arises from medial cord of brachial plexus B. innervates triceps brachii C. supplies posterior group of muscles of arm D. perforates the coracobrachialis E. acompanies with deep brachial vessels 23. Which doesn’t belong to the posterior wall of axilla A. subscapularis B. deltoid m. C. latissimus dorsi D. teres major E. scapula 24. Which muscle is not included in the wall of axilla A. pectoralis major B. latissimus dorsi C. brachialis D. intercostal muscles E. biceps brachii 25. Which part doesn’t belong to the apex of axilla A. medial 1/3 part of clavicle B. upper border of scapula C. head of humerus D. the 1st rib E. nerves and vessles of upper limb pass the apex of axilla 26. The nerve which distributes to the deltoid muscle is A. ulnar nerve B. radial nerve C. median nerve D. pudendal nerve E. axillary nerve 27. The deep brach of radial nerve perforates A. flexor carpi radialis B. pronator quadratus C. supintator D. trilateral foramen E. quadrilateral foramen 28. Radial nerve and deep brachial vessels pass through 14 A. Radial carpal canal B. ulnar carpal canal C. carpal canal D. humeromuscular tunnel E. inguinal canal 29. Which structure accompany with radial nerve passing through humeromuscular tunnel A. nutrient vessels of humerus B. deep brachial artery C. radial artery D. ulnar artery E. brachial artery 30. Fracture of medial epicondyle of humerus can damage A. radial nerve B. brachial artery C. ulnar nerve D. median nerve E. musculocutaneous nerve 31.Regarding the nerve of the upper limb, Which is false A. The axillary nerve is easily damaged when the fracture of surgical neck of humerus B. The median nerve supplies all the thenar muscles C., The median and ulnar nerves give off no branches in the axilla D. The median and ulnar nerves supply flexor digitorum profundus muscles E. The ulnar nerve is motor to all the interossei muscles of the hand 32. The triceps brachii is mainly supplied by A. axillary artery B. posterior circumflex humeral artery C. deep brachial artery D. circumflex scapular artery E. anterior circumflex humeral artery 33. Deep palmar arch A. is formed by the anastomosis of the terminal part of the radial artery with deep branch of the ulnar atery B. is formed by the anastomosis of the terminal part of the ulnar artery with deep branch of the radial artery C. lies superficial to the tendons of flexor muscles D. lies superficial to the lumbricales E. gives off three common palmar digital ateries 34. Which artery doesn’t belong to the branches of axillary artery A. anterior circumflex humeral artery B. posterior circumflex humeral artery C. deep brachial artery D. subscapular artery E. lateral thoracic artery 35. Which nerve distributes to the skin of little finger A. median nerve B. radial nerve 15 C. ulnar nerve D. axillary nerve E. musculocutaneous nerve 36. Regarding the median nerve, which is true A. arises from brachial plexus with the lateral and medial root B. lies to the medial side of axillaty artery C. lies to the lateral side of brachial artery all through D. accompanies the deep brachial vessles along the arm E. lies to the lateral side of brachial artery in the cubital fossa 37. In the upper part of arm, brachial artery lies A. to posterior side of humerus B. to medial side of humerus C. to anterior and medial side of humerus D. to anterior side of humerus E. to lateral side of humerus 38. Regarding radial nerve, Which is true? A. arises from posterior cord of brachial plexus, and pierces coracobrachialis muscle B. arises from posterior cord of brachial plexus,and pierces biceps brachii C. arises from posterior cord of brachial plexus,and innervates biceps brachii D. arises from posterior cord of brachial plexus,and innervates deltoid muscle. E. Passes through humeromuscular tunnel, and divides into deep and superficial branches in forearm 39. Regarding axillary nerve, which is true A. arises from lateral cord of brachial plexus, and accompanies with anterior circumflex humeral artery B. accompanies deep brachial artery, and passes humeromuscular tunnel C. accompanies posterior circumflex humeral artery, and passes through quadrilateral foramen D. accompanies anterior circumflex humeral artery,and passes through trilateral foramen E. innervates latissimus dorsi 40. Concerning musculocutaneous nerve, which is true? A. arises from medial cord of brachial plexus B. innervates triceps brachii C. innervates posterior group of muscles of arm D. perforates the coracobrachialis and control it E. accompanies deep brachial vessels 41. Regarding the radial nerve, which is true? A. It arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus. B. It lies to the medial side of the brachial artery. C. It has no branches in the arm . D. It is easily injured when the fracture of the surgical neck of humerus. E. It runs posteriorly with the deep brachial artery 42. Concerning biceps brachii, which is true? A. It lies deep to the lower half of the coracbrachialis. B. It is the chief extensor of the forearm. C. Its long head can also extend the shoulder joint D. The short head arise from the coracoid process 16 E. It flexes the wrist joint 43. Concerning triceps brachii, which is true A. Its long head arise from the supraglenoid tubercle. B. Its lateral head arise from the coracoid process. C. It flexes elbow joint. D. It supinates forearm. E. It is the chief extensor of the forearm. 44. The axillary artery is divided into three parts by A. the pectoralis major B. the pectoralis minor C. the subclavius D. the serratus anterior E. the teres minor 45. Which one does not belong to the branches of axillary artery A. the lateral thoracic artery B. the subscapular artery C. the anterior humeral circumflex artery D. the posterior humeral circumflex artery E. deep brachial artery. 46.Which one lies in relation to the lateral thoracic vessels? A. the pectoral lymph nodes B. the lateral lymph nodes C. the subscapular lymph nodes D. the central lymph nodes E. the apical lymph nodes 47. The lymph node along the distal part of the axillary vein is A. the pectoral lymph nodes B. the lateral lymph nodes C.the subscapular lymph nodes D.the central lymph nodes E. the apical lymph nodes 48.Which one is behind the third part of the axillary artery A. the radial nerve B. the medial root of the median nerve C. the lateral root of the median nerve D. the pectoralis major E. the musculocutaneous nerve 49. Which one does not pass through the carpal canal? A. the common flexor sheath B. the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis C. the tendons of the flexor digitorum profunds D. the median nerve E. the ulnar nerve 50. Concerning the carpal canal, which one is false A. it transmits the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis B. it transmits the tendons of the flexor digitorum profunds 17 C. it transmits the common flexor sheath D. it transmits the ulnar nerve E. it is formed by the flexor retinaculum and the groove of the carpal bones Multiple choice questions 1. Regarding the deltoid, the right description include(ACDE) A. It is the most powerful abductor of the arm B. Its anterior part is a strong flexor and lateral rotation of humerus C. It is inserted into the deltoid tuberosity of humerus D. It forms the rounded contour (轮廓) of the shoulder E. It protects and acts the shoulder joint 2. Concerning the biceps brachii, the right description include (CDE) A. Its short head arise from the supraglenoid tubercle B. Its long head arise from the coracoid process C. It flexes elbow joint D. It helps to flex the shoulder joint E. It supinates forearm 3. Concerning the triceps brachii, the right description include(AD) A. Its long head arise from the infraglenoid tuberosity of scapula B. Its lateral head arise from the posterior surface of the humerus below the groove for radial nerve C. Its medial head arise from the posterior surface of the humerus above the groove for radial nerve D. The strong tendon of it is inserted into the olecranon of ulna E. Its medial head can extend and adduct the shoulder joint 4. Regarding the pronator teres, the right description include(AD) A. It arises from the medial epicondyle of humerus and the deep fascia of forearm B. It only pronates forearm C. It only flexes elbow joint D. It belongs to the superficial layer of the anterior group of the muscles of forearm E. It flexes the thumb 5. Which ones have the function of opposition(对掌)(BCD) A. Abductor pollicis brevis B. Flexor pollicis brevis C. Opponens pollicis D. Opponens digiti minimi E. Lumbricales 6. Regarding the brachial artery, the right descriptions include(BCDE) A. It is the continuation of the subclavian artery B. Begins at the inferior border of the teres major C. Runs downwards on the medial side of the biceps brachii D. Its pulsation can be felt E. The deep brachial artery is its branch 7.Concerning the radial artery, the right descriptions include(ABCDE) A. In the wrist, it is used clinically for taking the pulse B. It arises from the brachial a. in the elbow C. Give off the superficial palmar branch to hand D. The principal artery of thumb is its branch 18 E. It takes part in the formation of deep palmar arch 8. Regarding the superficial palmar arch, the right descriptions include (ABCD) A. It is formed by the anastomsis of the terminal part of the ulnar artery with the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery B. It is covered by the palmar aponeurosis C. It lies on the flexor tendons of the fingers D. It gives off three common palmar digital arteries E. It gives off the principal artery of thumb 9. Concerning the deep palmar arch, the right descriptions include (ABDE) A. It is formed by the anastomsis of the terminal part of the radial artery with the deep palmar branch of the ulnar artery. B. It gives off three palmar metacarpal arteries C. It gives off three common palmar digital arteries D. It lies the proximal to the level of the superficial palmar arch E. The branches of the arch supply the bones and muscles of the hand 10. The superficial veins of the upper limb include(ACD) A. The cephalic vein B. The axillary vein C. The median cubital vein D. The basilic vein E. The radial vein 11. Regarding the cephalic vein, the right descriptions include(BDE) A. It ends in the brachial vein B. It ascends along the radial side of the arm C. It ascends the medial of the biceps brachii D. It begins the radial part of the dorsal venous rete of hand E. It ends in the axillary vein or subclavian vein 12. The axillary nerve(ABCE) A. leaves through the quadrangular space B. winds round the surgical neck of the humerus C. is injured, the deltoid muscle is paralyzed D. is injured ,the teres major is paralyzed E. arises from the posterior cord of brachial plexus 13. Concerning the median nerve, the right descriptions include (ACD) A. arises from the lateral cord and medial cord of the brachial plexus B. has branches in the arm C. supply the pronator teres D. in the palm, it is divided into a recurrent branch and three common palmar digital nerves E. supply all of the muscles in front of the forearm 14. Regarding the ulnar nerve, the right descriptions include (BDE) A. it arises from the lateral cord of the brachial plexus B. has no branches in the arm C. supply the pronator teres D. in the elbow, it is superficial and easily injured E. at the wrist, it is divided into a superficial and a deep palmer branches 15. Which do form the posterior wall of the axillary fossa (BDE) 19 A. serratus anterior B. teres major C. teres minor D. latissimus doris E. subscapularis 16. Which do pass through the quadrangular space (BE) A. the anterior humeral circumflex vessels B. the posterior humeral circumflex vessels C. the circumflex scapular vessels D. the radial nerve E. the axillary nerve 17.Which are branches of the second part of the axillary artery (BC) A. the superior thoracic artery B. the thoracoacromial artery C. the lateral thoracic artery D. the subscapular artery E. the thoracodorsal artery 18.The cubital fossa contains(ABDE) A. the tendon of the biceps brachii B. the median nerve C. the ulnar nerve D. the brachial artery E. the ulnar artery 19. Which are branches of the third part of the axillary artery (BDE) A. the thoracoacromial artery B. the subscapular artery C. the lateral thoracic artery D. the anterior humeral circumflex artery E. the posterior humeral circumflex artery 20.Which do transmit the carpal canal(ABCD) A. the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficislis B. the tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus C. the tendons of the flexor pollicis longus D. the median nerve E. the ulnar nerve Answer questions 1. Describe the boundaries and contents of the ①axilla, ②cubital fossa and ③carpal tunnel. 2. Write out the beginning, ending and branches of the ①axillary artery, ②brachial artery, ③radial artery and ④ulnar artery. 3. Describe the formation, position and main branches of the brachial plexus. 4. Describe the groups, area of drainage of the axillary lymph nodes. 5. Describe the lymph drainage of the breast. 6. Describe the beginnings, course and endings of cephalic and basilic veins. 7. Describe the origin, insertion, action and nerve supply of ①trapezius, ②latissimus dorsi, ③deltoid, ④biceps brachii and ⑤triceps. 20 8. Describe the distributions of the ①musculocutaneous, ②axillary nerve and ③radial nerve in arm. 9. Describe the innervation of the muscles of the ①arm, ②forearm . 10. Describe the distributions of the ①median, ②radial and ③ulnar nerves in forearm and hand. 11. Describe the formation of the superficial and deep palmar arches. 12. Briefly describe the innervation of the muscles which pronate and supinate the forearm.. 13. Briefly describe the innervation of the muscles and skin of the hand. The lower limb Single-choice questions 1. The capsule of the hip joint A. is attached along the intertrochanteric crest posteriorly. B. is attached along the intertrochanteric line anteriorly. C. proximally, it is attached to the margin of the lunate surface D. is directly related to the sciatic nerve posteriorly. E. the iliofemoral ligament lies in the lower and posterior part of the fibrous capsule. 2. The following structures pass through the greater sciatic foramen, except the : A. superior gluteal artery. B. sciatic nerve. C. obturator internus tendon. D. pudendal nerve. E. inferior gluteal nerve. 3. The posterior tibial artery: A. is a branch of the femoral artery. B. passes through the adduct canal. C. divided into medial and lateral plantar arteries. E. supplies dorsiflexors. D. is accompanied by the sural nerve. 4. The following structure which may be damaged by supracondylar femoral fracture A. politeal a. B. femoral a. C. common peroneal n. D. anterior tibial a. E. posterior tibial a. 5. Regarding the femoral triangle A. the femoral vein, artery, and nerve lie in the femoral sheath. B. the femoral nerve lies most medially in the femoral triangle. C. the lateral border of the femoral triangle is formed by the lateral border of sartorius muscle D. the femoral canal lies medial to the femoral vein. E. at the apex of the femoral triangle the femoral vessels pass into the obturator canal. 6. The following structure which is the branch of artery palpable deep to the ingunal ligament A. anterior tibial a. B. femoral a. C. politeal a. D. profunda femoris artery E. peroneal a. 21 7. The following nerves which damaged may result in foot drop? A. femoral n. B. tibial n. C. common peroneal n. D. obturator n. E. pudendal n. 8. Deep peroneal n. supplies A. Tibialis anterior B. tibialiis posterior C. Peroneus longus D. Peroneus brevis E. gastrocnemius 9.Which muscle can flex the hip joint and extend the knee joint? A. sartorius B. adductor longus C. biceps femoris D. quadriceps femoris E. gracilis 10. The following nerves which damaged may result in foot drop? A. femoral n. B. tibial n. C. common peroneal n. D. obturator n. E. pudendal n. 11. The following structure which may be damaged by supracondylar femoral fracture A. politeal a. B. femoral a. C. common peroneal n. D. anterior tibial a. E. posterior tibial a. 12. The following structure which is the branch of artery palpable deep to the ingunal ligament A. anterior tibial a. B. femoral a. C. politeal a. D. deep femoral artery E. peroneal a. 13. Which of the following muscles traverses the greater sciatic foramen? A. gluteus medius B. gluteus minimus C. gluteus maximus D. quadratus femoris E. Piriformis 14. The only innervation of the femoral nerve below the level of the knee is: A. the gracilis muscle B. the tibialis anterior muscle C. the skin of the lateral foot 22 D. the adductor longus E. the skin of the medial leg 15. Which of the following muscles attaches to the anterior superior iliac spine? A. pectineus B. sartorius C. rectus femoris D. vastus intermedius E. gracilis Multiple-choice questions 1. Gluteus maximus originates from A. gluteal surface of ilium B. dorsal aspect of sacrum C. coccyx D. sacrotuberous lig. E. sacrospinous lig. 2. The posterior facial compartment of the thigh consists of A. biceps femoris B. semitendinosus C. semimembranosus D. sciatic nerve E. tensor fasciae latae 3. The tibial nerve supplies: A. tibialis anterior. B. tibialis posterior C. gastrocnemius. D. soleus. E. skin of sole of the foot. 4.Structures that pass behind the medial malleolus beneath the flexor retinaculum A. tibialis posterior tendon B. flexor digitorum longus C. common peroneal n. D. tibial n. E. flexor hallucis longus 5. Concerning nerves of the lower limb: A. the obturator nerve supplies the muscles of the adductor compartment of the thigh. B. the sciatic n. leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen. C. the femoral nerve originates from the pelvic plexus. D. the superior gluteal n. supplies the gluteus maximus m. E. the sciatic n. may be damaged by posterior dislocation of the hip joint. 6. In the thigh A. satorius is attached to the anterior inferior iliac spine. B. the superior of the femoral ring is covered by femoral septum C. the great saphenous v. passes through the saphenous opening in the deep fascia and joins the femoral vein D. at the inguinal ligament the femoral v. is lateral to the femoral a. 23 E. laterally the deep fascia forms a thick band, the iliotibial tract. 7. At ankle and in the foot: A. the great saphenous vein is posterior to the medial malleolus. B. tibialis posterior tendon passes deep to the flexor retinaculum. C. eversion and inversion mainly take place at the ankle joint. D. the tendo calcaneus is attached to the talus. E. Dorsalis pedis artery begins in front of the ankle joint as a continuation of the anterior tibial a.. 8.Regarding vessels of the lower limb: A. the femoral a. is a direct continuation of the internal iliac a. B. the profunda femoris a. supplies the muscles of the medial and posterior compartments of the thigh. C. the popliteal a. has no branches in the popliteal fossa. D. the dorsalis pedis a. is a continuation of the anterior tibial a. in the foot E. the posterior tibial a. may be palpated behind the lateral malleoulus 9.The tibial nerve supplies: A. Tibialis anterior. B. Tibialis posterior C. Gastrocnemius. D. Soleus. E. Skin of sole of the foot. 10.The muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg include: A. an evertor of the foot B. an invertor of the foot C. a dorsiflexor of the ankle D. an extensor of the fifth digit (toe) E. one which attaches to the sustentaculum tali 11. In the thigh A. satorius is attached to the anterior inferior iliac spine. B. ovarian pain may be referred to medial skin of the thigh. C. the saphenous opening transmits the great saphenous v. D. at the inguinal ligament the femoral v. is lateral to the femoral a. E. semitendinosus is on the lateral side. 12. The tibial nerve supplies: A. hip flexors. B. knee flexors. C. anterior femoral skin. D. skin of the foot. E. plantarflexors. 13. The posterior tibial artery: A. is abranch of the femoral artery. B. is related to the medial malleolus. C. Divides into medial and lateal plantar ateries. D. supplies dorsoflexor. E. is accompanied by the sural nerve. 14. At ankle and in the foot: A. the great saphenous vein is posterior to the medial malleolus. B. tibialis posterior tendon passes deep to the flexor retinaculum. 24 C. eversion anf inversion mainly gale place at the ankle joint. D. the Achilles tendon is attached to the talus. E. the spring ligament is attached to the sustentaculum tali. 15. The capsule of the hip joint: A. is attached along the intertrochanteric crest posteriorly. B. carries blood vessels to the head of the femur. C. limit flexion of the hip. D. is directly related to the sciatic nerve posteiorly. E. has the psoas bursa as an immediate anterior relation. 16. The anterior tibial artery: A. is abranch od the femoral a. B. is related to the medial malleolus. C. divides into medial and lateral plantar arteries. D. supplies the dorsiflexor muscles. E. is palpable in the foot. 17. Regarding vessels of the lower limb: A. the femoral a. is a direct continuation of the internal iliac a. B. the profunda femoris a. supplies the muscles of the medial and posterior compartments of the thigh. C. the popliteal a. has no btanchese in the popliteal fossa. D. the dorsalis pedis a. is a continuation of the anterior fibula a. in the foot E. the posterior tibial a. may be palpated behind the lateral malleoulus. 18. Concerning nerves of the lower limb: A. the obturator nerve supplies the muscles of the adductor compartment of the thigh. B. the sciatic n. leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen. C. the femoral nerve originates from the pelvic plexus. D. the superior gluteal n.supplies the gluteus maximus m. E. the sciatic n. may be damabed by posterior dislocation of the hip joint. 19. Concerning nerves of the lower limb: A. the tibial n. endings by dividing into medial and lateral plantar nerves. B. trauma to the common peroneal n. fesult in footdrop. C. the saphenous n. passes bhind the medial malleolus to supply the medial side of the foot. D. the sciatic n. enters the thigh of the upper border of the piriformis m. E. the femoral n. supplies the anterior compartment of the thigh. ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. Describe the origin, insertion, action and nerve supply of ①gluteus maxim, ②piriformis, ③gastrocnemius and soleus, ④tibialis posterior, ⑤sartorius, ⑥quadriceps femoris, ⑦tibialis anterior. 2. Describe the structures passing through the suprapiriform foramen, infrapiriform foramen and lesser sciatic foramen. 3. Describe the origin, course and distribution of the sciatic nerve. 4. Describe the origin, branches and distribution of the femoral nerve. 5. Describe the origin and distribution of the①tibial nerves, ②superficial peroneal nerve and ③deep peroneal nerves.. 6. Describe the beginning and ending of the ①femoral artery, ②popliteal artery, ③anterior tibial atery, and ④posterior tibial artery. 7. Describe the innervation of the muscles of the thigh and leg. 25 8. Write out the structures that pass behind the medial malleolus beneath the flexor retinaculum from medial to lateral. 9. Describe the beginnings, course and endings of greater and lesser saphenous veins. 10. Describe the position and area drainage of the superficial and deep inguinal lymph nodes. 11. Describe the boundaries of the femoral ring. 12. Describe the boundaries and contents of the ①femoral triangle, ②adductor canal, ③popliteal fossa.④ malleolar canal. 13. A patient is stabbed in the thigh just below the middle of the inguinal ligament. What structures are in damage? What will be the effect of section of the major nerve here. 14. Describe the main arterial tree of the lower limb. Name three sites where peripheral pulse may be palpated. Where are these vessels liable to injury? 15. Describe the venous drainage of the lower limb, indicating the normal direction of blood flow between the superficial and deep veins. 16. A 20-year-old student twists his ankle playing basketball. There is marked tenderness anterior to the lateral malleolus. Name the bones constituting the ankle joint and state the injury that has occurred. List the muscle group acting on the joint and give their nerve supply. 17. Briefly describe the innervation of the muscles which evert and invert the foot. Head and neck Single Choice Questions 1.Which structure does not pass through parotid gland longitudinally A. Facial nerve B. Superficial temporal artery and vein C. External carotid artery D. Retromandibular vein E. Auriculotemporal nerve 2. Ventricle of larynx is located A. above vestibular fold B. above vocal fold C. below vocal fold D. laryngeal vestibule E. infraglotic cavity 3.The cervical sympathetic trunk A. has a constant, fixed number of ganglia B. lies anterior to the vertebrae C. extends from the base of the skull to the 5th lumbar vertebrae D. receives white rami from the cervical never. E. supplies postganglionic fibers to all cervical nerves 4. Which structure doesn’t belong to the carotid triangle A. Internal jugular vein B.External jugular vein C.Common carotid artery D.hypoglossal nerve E.Vagus nerve 26 5. Concerning the carotid sinus ,the right description is A. It is a dilatation at the posterior wall of the common carotid artery. B. It is a dilatation at the point of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery. C. It is a small ball struture behind the point of division of the common carotid artery. D. It is a chemoreceptor. E. All above are wrong. 6.All of the following are branches of the maxillary artery, EXCEPT A. middle meningeal A. B. buccal A. C. posterior auricular A. D. infraorbital A. E. inferior alveolar A. 7.There is parasympathetic fibers in all the following cranial nerves, EXCEPT: A. occulumotor n. B. facial n. C. glossopharyngeal n. D. vagus n. E. trigeminal n. 8.The following statements concerning the facial nerve are true, EXCEPT: A. The ganglion of the facial nerve is the geniculate ganglion. B. The buccinator muscle is innervated by a branch of the facial nerve. C. The greater petrosal n. is joined by a postganglionic sympathetic nerve. D. Submandibularalivary glands are innervated by parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve. E. The anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric are innervated by branches of the facial nerve. 9. The motor division of the trigeminal nerve leaves the skull through the A. Foramen rotundum B. Foramen ovale C. Superior orbital fissure D. inferior orbital fissure E. Foramen spinosum 10.Pick the false pair A. optic canal : optic nerve B. foramen ovale: mandibular nerve C. jugular foramen : glossopharyngeal nerve D. superior orbital fissure : oculomotor n. E. internal acoustic meatus : abducens n. 11.Branches of the trigeminal never include all of the following, EXCEPT A. auriculotemporal n. B. zygomatic n. C. frontal n. D. ethmoidal n. E. lacrimal n. 12. Which of the following is a branch of the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve? A. nasociliary n. B. mental n. C. lacrimal n. 27 D. infraorbital n. E. chorda tympani. 13. Ptosis(下垂) of the upper eyelid may be caused by injury to the A. oculomotor nerve B. abducent nerve. C. superior oblique m. D. superior rectus m. E. facial n. 14.All of the following are characteristics of the sinuses of dural mater, EXCEPT A. They terminate directly or indirectly in the internal jugular vein. B. They lie between the dura and the arachnoid mater. C. The wall of sinuses of dural mater has no smooth muscle. D.They connect with the veins outside the cranial cavity. E. They receive venous blood of the brain 15.The narrowest part of laryngeal cavity is A. aperture of larynx B. laryngeal vestibule C. rima vestibuli D. fissure of glottis E. ventricle of larynx 16. Which nerve conducts pain of anterior 2/3 of tongue A. lingual n. B. hypoglossal n. C. glossopharyngeal n. D. vagus n. E. facial n. 17. Which sinus opens into the superior nasal meatus A.frontal sinus B.maxillary sinus C.sphenoidal sinus D.anterior. and middle ethmoidal sinuses E.posterior. ethmoidal sinus 18. The description about the relations of hypophysis, right is A. anterior is dorsum sellae B. posterior is tuberculum sellae C. lateral is lesser wing of the sphenoid bone D. inferiorly close related to the nasal cavity E.superior is the optic chiasma 19.The nerve going with internal carotid a. pass through the cavernous sinus is A. optic n. B. occumolar n. C.abducent n. D.ophthalmic n. of trigeminal n. E.trochlear n. 20. The middle meningeal artery arise from A. external carotid a. 28 B. internal carotid a. C. superficial temporal a. D.maxillary a. E. facial a. 21.Infraorbital nerve A. is the branche of mandibular n. B. is the branche of maxillary n. C.passing through the infraorbital foramen to the facial muscle. D.distribute the maxillary teeth and gum E.distribute the mandibilar teeth and gum 22. The following structures pass through the parotid gland, Except A.internal carotid a. B.external carotid a. C.retromandibular v. D.auriculotemporal n. E.superficial temporal a. 23. Rrom superficial to deep the arrangement of the structures passing through the parotid gland is A.facial n., retromandibular v.;external carotid a. B.facial n., external carotid a., retromandibular v. C.retromandibular v.; facial n., external carotid a. D.retromandibular v.; external carotid a., facial n., E.external carotid a., facial n., retromandibular v.; 24.The nerve of controling masseter is A. facial nerve. B. maxillary nerve. C. vagus nerve. D. trigeminal nerve. E. lingual nerve. 25.The facial artery comes from A. internal carotid A. B. external carotid A. C. Angular A. D .lingual A. E. superficial temporal A. 26.The nerve going through infraorbital foramen is A. frontal N. B. ophthalmic N. C. infraorbital N. D. maxillary N. E. mandibular N. 27. Concerning the apex of lung, which is true A. extends about 2.5cm above the medial one-third of clavicle B. extends about 2.5cm above the middlel one-third of clavicle C. extends about 2.5cm above the lateral one-third ofclavicle D. extends about 2.5cm above the medial half of clavicle 29 E. not extends above the clavicle 28.The parotid duct Open into A. Cheek mucosa B. Cheek mucosa near second molar of upper jaw C. root of tongue D. nasopharynx E. isthmus of fauces 29. The nerve controlling sternocleidomastoid muscle is A. hypoglossal nerve. B. glossopharyngeal nerve. C. accessory nerve. D. great auricular nerve. E. transverse nerve of neck 30.The structure passing through scalene fissure is A. internal carotid A. B. internal jugular V. C. brachial plexus D. cervical plexus E. subclavian V. 31.Which description about phrenic nerve is wrong A. come from brachial plexus B. run between subclavian A. and subclavian V. C. go down the anterior surface of anterior scalene muscle D. control diaphragm E. right phrenic n.comes to liver and gallbladder 32. The carotid triangle contains A. common carotid A. B. cervical superficial lymph nodes C. lingual A. D. phrenic N. E. facial A. 33.The strucure related to inferior thyroid artery is A. superior laryngeal N. B. vagus N. C. phrenic N. D. hypoglossal N. E. recurrent laryngeal N. 34.The superior laryngeal neve comes from A. hypoglossal N. B. cervical plexus C. lingual N. D. vagus N. E. glossopharyngeal N. 35. Which nerve conducts pain of posterior 1/3 of the tongue A. Submandibular nerve B. Hypoglossal nerve 30 C. Glossopharyngeal nerve D. Vagus nerve E. Facial nerve 36. Which gland is innervated by facial nerve A.Lacrimal gland B.Parathyroid gland C.Suprarenal gland D.Parotid gland E.Thyroid gland 37. Injuries of right hypoglossal nerve will cause A. the tongue can not be protruded B. the tongue can not be retracted C.the apex of tongue tend to right side when the tongue protrude D.the apex of tongue tend to left side when the tongue protrude E.supranuclear paralysis 38. Which ganglion belongs to the parasympathetic ganglion A. spinal ganglion B. celiac ganglion C. ciliary ganglion D. aorticorenal ganglion E. superior mesenteric ganglion 39. In action, the parasympathetic nerve tends to produce A. the wider opening of the pupil B. decreasing the rate of heart beating C. dilatation of bronchi D. increasing the rate of respiration E. elevation of the blood pressure 40. Which nerve conducts taste of anterior 2/3 of the tongue A. Submandibular nerve B. Hypoglossal nerve C. Glossopharyngeal nerve D. Vagus nerve E. Facial nerve 41. Which gland is innervated by glossopharyngeal nerve A. Lacrimal gland B. Sublingual gland C. Submandibular gland D. Parotid gland E. Thyroid gland 42. The recurrent (or inferior) laryngeal nerve innervates all the intrinsic laryngeal muscles, EXCEPT: A. lateral cricoarytenoid B. posterior cricoarytenoid C. cricothyroid D. vocalis E. transverse arytenoid 31 43. Which ganglion belongs to the sympathetic ganglion A. spinal ganglion B. superior cervical ganglion C. ciliary ganglion D. submandibular ganglion E. pterygopalatine ganglion 44. In action, the sympathetic nerve tends to produce A. the wider opening of the pupil B. decreasing the rate of heart beating C. constriction of bronchi D.decreasing the rate of respiration E. decreasing the blood pressure 45.The carotid sheath contains all of the following structures, EXCEPT A. internal carotid A. B. common carotid A. C. sympathetic trunk D. internal jugular V. E. vagus N. 46.The following statements about the phrenic nerve are correct, EXCEPT A. it passes anterior to the hilum of the lung B. it controls the movement of the diaphragm C. it is a branch of the brachial plexus D. it gives sensory supply to the pericardium E. it gives sensory supply to the diaphragm 47.Which of the following arteries is not a branch of the external carotid artery A. superior thyroid a. B. facial a. C. lingual a. D.inferior thyroid a. E.superficial temporal a. 48 Which nerve may be easily damaged when the superior thyroid artery is ligated A.The external branch of superior laryngeal nerve B.The internal branch of superior laryngeal nerve C.The recurrent laryngeal nerve D.The vagus nerve E.The cervical sympathetic trunk 49. The right recurrent laryngeal nerve usually loops around A. aortic arch B. axillary A C. ligamentum arteriosum D. subclavian A E. ansa cervicalis 50.Which of the following is not a branch of the maxillary nerve of the trigeminal nerve? A. zygomatic N. B. superior alveolar N. C. lacrimal N. 32 D. infraorbital N. E. nasopalatine N. Multiple choice questions 1.The structures passing through the parotid gland transversely include (ABC) A. facial n. B. transverse facial a.and v. C. maxillary a. D. superficial temporal a. E. retromandibular v. 2.The following descriptions about the facial vein, the right are (ABCD) A. originate from angular v. B. emptied into internal jugular v. C. communicated with the cavernous sinus D. contain no valve E. collect the blood from the thyroid gland 3. The branches of maxillary artery include (ABCD) A. middle meningeal a. B. inferior alveolar a. C. superior alveolar a. D. infraorbital a. E. supraorbital a. 4. The Scalp consist of (ABC) A. skin B. connective tissue C. aponeurosis D. loose connective tissue E. pericranium 5. The arteries supllied to the scalp include (ABCDE) A. occipital a. B. posterior auricular a. C. superficial temporal a. D. supraorbital a. E. supratrochlear a. 6. The nerves distributed to the scalp include (ABCDE) A. lesser occipital n. B. greater occipitl n. C. supraorbital n. D. supratrochlear n. E. auriculotemporal n. 7.The structures passing through the lateral wall of cavernous sinus include (BCD) A. optic n. B. oculomotor n. C. trochlear n. D. ophthalmic n. E. abducent n. 33 8. The structures which form the “parotid bed” include (ABE) A. the muscles attached to styroid process B. internal carotid a. and internal jugular v. C. external carotid a. D. facial n.and its branches E. posterior 4 cranial n. 9.The masticatory muscles include (ABCE) A. temporal muscle. B. masseter muscle C. medial pterygoid D. orbicularis oris E. lateral pterygoid 10.The branches of facial nerve include (ABCDE) A. temporal branches B. zygomatic branches C. buccal branches D. marginal mandibular branch E. cervical branch 11.The pterion surround by (ABDE) A. frontal bone B. parietal bone C. zygomatic bone D. sphenoid bone E. temporal bone 12.The vagus nerves ( ABC) A. special visceral efferent fibers originate from the ambiguous B. general visceral efferent fibers originate from the dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve C. left vagus nerve travels downwards posterior to the root of left lung D. right vagus nerve travels downwards anterior to the root of right lung E. supply all of visceral organs in the thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavities 13.The structures going through parotid gland are (ABCD) A. superficial temporal A.. V. B. auriculotemporal N. C. maxillary A. and V. D. facial N. E. mandibular N. 14.The carotid sheath contains (ABCD) A. common carotid A. B. internal jugular V. C. internal carotid A. D. vagus N. E. recurrent laryngeal N. 15.Which nerve fibers do belong to the vagus nerve? (ABC) A. the general visceral efferent fibers B. the general visceral afferent fibers C. the special visceral efferent fibers 34 D. the special visceral afferent fibers E. the general somatic efferent nerve fibers 16.Which nerve fibers belong to the facial nerve (ABC) A. the special visceral efferent fibers B. the general visceral efferent fibers C. the special visceral afferent fibers D. the general visceral afferent fibers E. the general somatic efferent fibers 17.The branches of the external carotid artery include (ABCE) A. maxillary A. B. superior thyroid A. C. occipital A. D. vertebral A. E. lingual A. 18. Regarding the larynx, which descriptions are right? (ACD) A. It lies in the neck region in front of C4 ~ 6. B. The laryngeal cavity can be divided into two partrs. C. The position of the larynx is higher in the child. D. The laryngeal prominence is on the thyroid cartilage. E. All above are right 19.The facial nerve (BD) A distributes the skin of face B supplies the muscles of face C is associated with nuclei of facial nerve, superior and inferior salivatory D distributes the taste buds on the anterior 2/3 of the tongue E supplies the submandibular, sublingual and parotid glands 20. Regarding the internal carotid artery, which descriptions are right ?(BCD) A It enters the cranial cavity through the jugular foramen. B It enters the cranial cavity through the carotid canal. C Has no branches in the neck. D At its beginning has pressure receptor E Passes through the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus. Answer Questions 1. Describe the layers Layers of frontal parietal occipital region. 2. Write out the structures passing through cavernous sinus. 3. Describe simply the position of parotid gland and the course of parotid duct. 4. Write out the layers of the incision for thyroid gland operation 5. Describe the boundaries and contents of carotid triangle and muscular triangle. 6. Write out the composed of masticatory muscles. 7. Write out the connections of facial vein. 8. Write out Structures passing through the parotid gland 9. Write out the names of suprahyoid muscles 10. Briefly describe the origin, insertion and action of sternocleidomastoid and scalenus anterior 11. Briefly describe the boundaries and contents scalene fissure. 12. Briefly describe the begining and ending of common carotid a.. 35 13. Briefly describe the position and fnction of carotid sinus and carotid glomus. 14. Briefly describe the branches of external carotid a. and subclavian artery 15. Briefly describe the position and draining aera of superficial and deep lateral cervical lymph nodes. 16. Briefly describe the formation of the cervical plexus 17. Briefly describe the layers deep cervical fascia. 18. Briefly describe the relations of the thyroid gland. 18. Briefly describe the arteries of thyroid gland and relations with the branches of vagus nerve. 20. Briefly describe relations of cervical part of trachea anteriorly. Thorax Single choice questions 1. The upper respiratory tract consists of nose nose, and pharynx C. nose, pharynx, and larynx D.nose, pharynx, larynx, and trachea E.nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and principal bronchi 2. The lower respiratory tract consists of A. branches of principal trachea B. principal bronchi with their branches C.trachea and principal bronchi with their branches D.larynx, trachea, and principal bronchi with their branches E.pharynx, larynx, trachea, and principal bronchi with their branches 3. The frontal sinuses open into A. superior nasal meatuses B. middle nasal meatuses C. inferior nasal meatuses D. sphenoethmoidal recesses E. nasolacrimal ducts 4. The maxillary sinuses open into A. superior nasal meatuses B.middle nasal meatuses C.inferior nasal meatuses D.sphenoethmoidal recesses E.nasolacrimal ducts 5. The sphenoidal sinuses open into A. superior nasal meatuses B. middle nasal meatuses C. inferior nasal meatuses D.sphenoethmoidal recesses E.nasolacrimal ducts 6. The anterior and middle groups of the ethmoidal sinuses open into A. superior nasal meatuses B.middle nasal meatuses C.inferior nasal meatuses 36 D.sphenoethmoidal recesses E.nasolacrimal ducts 7. The posterior group of the ethmoidal sinuses open into A.superior nasal meatuses B.middle nasal meatuses C.inferior nasal meatuses D.sphenoethmoidal recesses E.nasolacrimal ducts 8. The laryngeal prominence belongs to A.thyroid cartilage B.lamina of cricoid cartilage C.arch of cricoid cartilage D.arytenoid cartilage E.epiglottic cartilage 9. Which cartilage is ring-shaped A. thyroid cartilage B.cricoid cartilage C.arytenoid cartilage D.epiglottic cartilage E.tracheal catilage 10.The narrowest part of the laryngeal cavity is A. aperture of larynx B. laryngeal vestibule C. rima vestibuli D.fissure of glottis E.ventricles of larynx 11.Which sinus opens into superior nasal meatus A. frontal sinuses B. maxillary sinuses C. anterior and middle groups of ethmoidal sinuses D.posterior group of ethmoidal sinuses E.sphenoidal sinuses 12. Which sinus opens into sphenoehmoidal recesses A. frontal sinuses B. maxillary sinuses C. anterior and middle groups of ethmoidal sinuses D. posterior group of ethmoidal sinuses E.sphenoidal sinuses 13.The ventricles of larynx are A.the lateral expansions of the larygeal cavity between vestibule and vocal folds B.between the two vestibular folds C.between the two vocal folds D.between the level of rima vestibuli and the fissure of glottis E.inferior to the fissure of glottis 14.The rima vestibuli is A.the slit between the two vestibular folds 37 B.the slit between the two vocal folds C.between the level of rima vestibuli and the fissure of glottis D.the narrowest part of the laryngeal cavity E.,inferior to the fissure of glottis 15.The fissure glottis is A. the slit between the two vestibular folds B. the slit between the two vocal folds only C. between the level of rima vestibuli and the fissure of glottis D. superior to the rima vestibuli E. inferior to the rima vestibuli 16.The intermedial cavity of larynx is A. the lateral expansions of the larygeal cavity between vestibule and vocal folds B. between the two vestibular folds C. between the two vocal folds D. between the level of rima vestibuli and the fissure of glottis E. superior to the rima vestibuli 17.The carina of trachea is A. a sagittal semilunar ridge inside the trachea B. a sagittal semilunar ridge inside the bifurcation of trachea C. a sagittal semilunar ridge inside the right principal bronchus D. a sagittal semilunar ridge inside the left principal bronchus E. a sagittal semilunar ridge inside the lobar bronchi 18.Conceeerning the apex of lung, which is true A.extends to 2~3 cm above the level of medial one-third of the clavicle B.extends to 2~3 cm above the level of middle one-third of the clavicle C.extends to 2~3 cm above the level of lateral one-third of the clavicle D.extends to 2~3 cm above the level of middle half of the clavicle E.doesn’t extend above the clavicle 19. From anterior to posterior, the arrangement of main structures of the root of lung is A. principal bronchi, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins B. pulmonary artery, principal bronchi, pulmonary veins C. pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery, principal bronchi D.principal bronchi, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery E. pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, principal bronchi 20. From superior to inferior, the arrangement of main structures of the root of left lung is A. principal bronchi, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins B.pulmonary artery, principal bronchi, pulmonary veins C.pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery, principal bronchi D.principal bronchi, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery E. pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, principal bronchi 21. From superior to inferior, the arrangement of main structures of the root of right lung is A.superior lobar bronchus, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins B.pulmonary artery, principal bronchi, pulmonary veins C.pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery, principal bronchi D.principal bronchi, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery E.pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, principal bronchi 38 22.The parietal pleura is divided into A. two portions B. three portions C.four portions D.five portions E.six portions 23.The pleural cavity is the potential space between the A.parietal and visceral pleurae B.costal and diaphragmatic pleurae C.costal and mediastinal pleurae D.costal and cupula pleurae E.diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleurae 24.The costodiaphragmatic recess is between the A. parietal and visceral pleurae B.costal and diaphragmatic pleurae C.costal and mediastinal pleurae D.costal and cupula pleurae E.diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleurae 25.The costomediastinal recess is between the A. parietal and visceral pleurae B. costal and diaphragmatic pleurae C.costal and mediastinal pleurae D.costal and cupula pleurae E.diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleurae 26.The inferior margins of the lungs are correspondence with which rib at midclavicular line A. 5th rib B.6th rib B. 7th rib C. 8th rib D. 9th rib 27. The inferior margins of the lungs are correspondence with which rib at midaxillary line A. 6th rib B. 7th rib C. 8th rib D. 9th rib E. 10th rib 28. The inferior margins of the lungs are correspondence with which rib at scapular line A. 7th rib B. 8th rib C. 9th rib D. 10th rib E. 11th rib 29.The inferior margins of the pleurae are correspondence with which rib at midclavicular line A. 7th rib B. 8th rib C. 9th rib 39 D. 10th rib E. 11th rib 30. The inferior margins of the pleurae are correspondence with which rib at midaxillary line A. 7th rib B. 8th rib C. 9th rib D. 10th rib E. 11th rib 31. The inferior margins of the pleurae are correspondence with which rib at scapular line A. 7th rib B. 8th rib C. 9th rib D. 10th rib E. 11th rib 32.The branches of the aortic arch don’t include A. brachiocephalic trunk B. left common carotid artery C. left subclavian artery D. some small branche to trachea and bronchus E. coronary artery 33.The superior vena cava is formed by the junction of the A. left brachiocephalic vein and right brachiocephalic vein B. left internal jugular vein and right internal jugular vein C. left internal jugular vein and left subclavian vein D. right internal jugular vein and left subclavian vein E. right internal jugular vein and right subclavian vein 34.The azygos vein commences as the continuation of the A. right ascending lumbar vein B. left ascending lumbar vein C. hemiazygos vein D. accessory hemiazygos vein E. posterior intercostal veins of the right side 35.The bronchopulmonary lymph nodes are in A. in the hilus of each lung B. in the angle between the trachea and principle bronchchi C. at the side of trachea D. in the lobes of each lung E. in the pulmonary segment 36.The efferents vessels of the bronchopulmonary lymph nodes end in the A. anterior mediastinal lymph nodes B. pulmonary lymph nodes C. bronchopulmonary lymph nodes D. tracheobronchial lymph nodes E. paratracheal lymph nodes 37.The phrenic nerve descends A. in front of the root of lung 40 B. behind the root of lung C. in front of the subclavian vein D. behind the subclavian artery E. behind the scalenus anterior 38. The anterior branch of the second thoracic nerves presents about the level of A. sternal angle B. nipple C. xiphoid process D. costal arch E. umbilicus 39. The anterior branch of the fourth thoracic nerves presents about the level of A. sternal angle B. nipple C. xiphoid process D. costal arch E. umbilicus 40. The anterior branch of the sixth thoracic nerves presents about the level of A. sternal angle B. nipple C. xiphoid process D. costal arch E. umbilicus 41. Which structure does belong to the right atrium? A. orifice of the coronary sinus B. tendinous cords C. trabeculae carneae D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. aortic orifice 42. Which structure does belong to the right atrium? A. orifice of the superior vena cava B. tendinous cords C. trabeculae carneae D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. aortic orifice 43. Which structure does belong to the right atrium? A. orifice of the inferior vena cava B. tendinous cords C. trabeculae carneae D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. aortic orifice 44. Which structure does belong to the right ventricle? A. orifice of the superior vena cava B. orifice of the inferior vena cava C. orifice of the coronary sinus D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. orifice of the pumonary trunk 41 45. Which structure does belong to the left ventricle? A. orifice of the superior vena cava B. orifice of the inferior vena cava C. orifice of the coronary sinus D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. aortic orifice 46. The right coronary artery arises from A. right aortic sinus B. left aortic sinus C. coronary sinus D. orifice of the coronary sinus E. orifice of the pulmonary trunk 47. The left coronary artery arises from A. right aortic sinus B. left aortic sinus C. coronary sinus D. orifice of the coronary sinus E. orifice of the pulmonary trunk 48. The thoracic duct begins at the A. right lumbar trunk B. left lumbar trunk C. cisterna chyli D. intestinal trunk E. left bronchomediastinal trunk 49. Opposite which thoracic vertebra the thoracic duct inclines to the left? A. 1st B. 3rd C. 5th D. 7th E. 9th 50. The thoracic duct ends by opening into the A. right venous angle B. left venous angle C. left subclavian vein D. left jugular vein E. right subclavian vein Multiple choice questions 1. Which sinuses do open into middle nasal meatus?(ABC) A. frontal sinuses B. maxillary sinuses C. anterior and middle groups of ethmoidal sinuses D. posterior group of ethmoidal sinuses E. sphenoidal sinuses 2. Which cartilages do belong to the laryngeal cartilages? (ABCD) A. thyroid cartilage 42 B. cricoid cartilage C. arytenoid cartilage D. epiglottic cartilage E. tracheal catilage 3. which of the following description about the lungs is true(ADE) A. apex of lung extends to 2~3 cm above the level of medial one-third of the clavicle B. apex of lung extends to 2~3 cm above the level of middle one-third of the clavicle C. apex of lung extends to 2~3 cm above the level of lateral one-third of the clavicle D. left lung is divided into two lobes E. right lung is divided into three lobe 4. The arrangement of main structures of the root of lungs, which is true(ABC) A. from superior to inferior of right root, superior lobar brobchus, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins B. from superior to inferior of left root, pulmonary artery, principal bronchi, pulmonary veins C. from anterior to posterior, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery, principal bronchi D. from anterior to posterior, principal bronchi, pulmonary veins, pulmonary artery E. from superior to inferior, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, principal bronchi 5. The branches of the aortic arch are(ABC) A. brachiocephalic trunk B. left common carotid artery C. left subclavian artery D. right common carotid artery E. right subclavian artery 6. The description about the projection of the inferior margins of lungs ,which is true (ACE) A. midclavicular line at 6th rib B. midclavicular line at 8th rib C. midaxillary line at 8th rib D. midaxillary line at 10th rib E. scapular line at 10th rib 7. The description about the projection of the inferior margins of pleurae ,which is true (BDE) A. midclavicular line at 6th rib B. midclavicular line at 8th rib C. midaxillary line at 8th rib D. midaxillary line at 10th rib E. scapular line at 11th rib 8. The parietal pleura includes(ABCD) A. costal pleura B. diaphragmatic pleura C. mediastinal pleura D. cupula of pleura E. visceral pleura 9. The pleura recess includes(ABC) A. costodiaphragmatic recess B. costomediastinal recess C. phrennicomediastinal recess D. cupula of pleura E. recess between the fissure of lungs 43 10.About the vagus nerve, which is true(ABCDE) A. right vagus nerve forms the posterior part of the esophageal plexus B. left vagus nerve forms the anterior part of the esophageal plexus C. right vagus nerve forms the posterior vagal trunk D. left vagus nerve forms the anterior vagal trunk E. recurrent laryngeal nerves differ in origin and course on both sides 11. Which structures do belong to the right atrium? (ABC) A. orifice of the coronary sinus B. orifice of the superior vena cava C. orifice of the inferior vena cava D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. aortic orifice 12. Which structures do belong to the right ventricle? (AE) A. tricuspid valve B. mitral valve C. orifice of the coronary sinus D. orifices of the pulmonary veins E. orifice of the pumonary trunk 13. Which structure do belong to the left ventricle? (BE) A. tricuspid valve B. mitral valve C. orifice of the coronary sinus D. orifice of the pulmonary trunk E. aortic orifice 14. The components of the conduction system of the heart include(ABCD) A. sinoatrial node B. atrioventricular node C. atrioventricular bundle D. Purkinje fibers E. cardiac muscle cells 15. The right coronary artery supplies blood to(ABCD) A. right atrium B. lateral wall of the right ventricle C. posterior wall of the right ventricle D. posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum E. lateral wall of the left ventricle 16. The left coronary artery supplies blood to (ABCD) A. left atrium B. anterior wall of the left ventricle C. lateral wall of the left ventricle D. anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum E. lateral wall of the right ventricle 17. The tributaries of the coronary sinus are (ABC) A. great cardiac vein B. middle cardiac vein C. small cardiac vein 44 D. anterior cardiac vein E. smallest cardiac vein 18. Which sinuses do belong to the pericardial cavity? (ABC) A. transverse pericardial sinus B. oblique pericardial sinus C. anterior inferior sinus of pericardium D. right aortic sinus E. left aortic sinus 19. Which structures do pass through the hiatus or foramen of the diaphragm? (ABCDE) A. aorta B. esophagus C. inferior vena cava D. vagus nerve E. thoracic duct 20. Which structures do belong to the superior mediastinum? (ABD) A. thymus B. superior vena cava C. inferior vena cava D. aortic arch E. pericadium Answer questions 1. describe the positions and openings of the paranasal sinuses. 2. list the arrangement of main structures of the root of lung. 3. Write out the formation of superior vena cava and the blood collection area of superior vena cava. 4. write out the components of the conduction system of the heart. 5. Briefly describe the distribution of the right and left coronary artery. 6. Briefly describe parts of laryngeal cavity. 7. Briefly describe the definitions of pleura and pleural cavities; the portions of parietal pleura, pleural recesses, and surface markings of inferior margins about lungs and pleura. 8. Briefly describe the shape and structures of lung, and intrapulmonary structures 9. Briefly describe the portions of mediastinum. 10. Briefly describe the structures of the right and left side of mediastinum. 11. Briefly describe the features of left and right principal bronchi. 12. Briefly describe the relations of aortic arch and esophagus. 13. Briefly describe the location, surface structures of the heart. 14. Briefly describe the structures about four chambers of heart. 15. Briefly describe the location and drainage and opening of coronary sinus 16. Briefly describe the location of ligamentum arteriosum. 17. Briefly describe the beginning, ending and portions of aorta 18. Briefly describe the branches off the aortic arch. 19. Briefly describe the beginning, ending, and drainage of the azygos v., left and right brachiocephalic v.. 20. Briefly describe the courses and the branch distributions of vagus n. in thorax 21. Briefly describe the beginning, ending, and drainage of thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct. 45 答案:Ⅰ. 1-5CCBBD,6-10BAABD,11-15DEAAB,16-20DBACB,21-25ACABC,26-30BCDBD, 31-35EEAAA,36-40DAABC,41-45AAAEE,46-50ABCBB Ⅱ.1ABC,2ABCD,3ADE,4ABC,5ABC,6ACE,7BDE,8ABCD,9ABC,10ABCDE,11ABC, 12AE,13BE,14ABCD,15ABCD,16ABCD,17ABC,18ABC,19ABCDE,20ABC Abdomen Single Choice Questions 1.The palatine tonsil lies A. in oral cavity B.between palatoglossal arch and palatopharyngeal arch C. in pharyngeal recess D. in piriform recess E. in posterior wall of pharynx 2.The major duodenal papilla lies in A. superior part of duodenum B. descending part of duodenum C. horizontal part of duodenum D. ascending part of duodenum E. duodenojejunal flexure 3.The major digestive gland is A. buccal glands B. esophageal gland C. submandibular gland D. gastric gland E. intestinal gland 4.The structure under inferior surface of tongue is A. foramen cecum of tongue B.lingual tonsil C. sublingual caruncle D. vallate papilla E. limiting sulcus 5.pharyngeal opening of auditory tube lies in A. nasopharynx B. oro pharynx C. laryngopharynx D. epiglottic vallecula E. inferior meatus; 6.Which structure doesn’t belong to stomach A. angular notch B. pyloric antrum C. Antrum of stomach D. pyloric canal E. fundus of stomach 7.The beginning of jejunum is A. pylorus 46 B. angular notch C. transverse part of duodenum D. duodenojejunal flexure E. left colic flexure 8.The shortest segment of large intestinal is A. ascending colon B. descending colon C. sigmoid colon D. cecum E. anal canal 9.The dentate line is formed by A. anal canal B. transverse fold of rectum C. anal columns D. anal valves E. anal sinus 10.The opening of hepatopancreatic ampulla lied in A. Superior portion of duodenum B. pyloric antrum C. Calot's triangle D. major duodenal papilla E. minor duodenal papilla 11.Which structure belong to renal cortex A. minor renal calices B. renal column C. renal papillae D. renal pelvis E. renal pyramid 12.The superior extremity of kidney is in neighborhood of A. Diaphragm B. Superior portion of duodenum C. head of pancreas D. suprarenal gland E. pylorus 13.Female ureter crosses A. above uterine artery B. under uterine artery C. in front of uterine artery D. inside uterine artery E. lateral to uterine artery 14.The trigone of bladder lies A. in internal surface of fundus of bladder B. below apex of urinary bladder C. body of bladder D.below neck of bladder E. in base of prostate 47 15. Second constriction of male urethra lies in A. Prostatic portion of urethra B. membranous part C. cavernous part D. external orifice of urethra E. internal urethral orifice 16.Hepatoduodenal ligament containes A. hepatic veins B. splenic v. C. hepatic portal vein D. left gastric v. E. celiac trunk 17. Which structure does divide the peritoneal cavity into supracolic and infracolic compartment? A. lesser omentum B. transverse mesocolon C. greater omentum D. greater omentum E. mesentery 18 The short gastric arteries come from A. celiac trunk B. right gastric a C. left gastric a D. splenic artery E. superior mesenteric a 19.Which nerve come from lumbar plexus A. sciatic nerve B. inferior gluteal nerve C. obturator nerve D. pudendal nerve E. posterior femoral cutaneous nerve 20.The innervation of umbilicus is A. 6th intercostal n. B.8th intercostal n. C.10th intercostal n. D.1th lumbar n. E. 2th lumbar n. 21.The piriform recess lies in A. nasopharynx B. oropharynx C. laryngopharynx D. isthmus of fauces E. vestibule of larynx 22.The limitation of pyloric antrum and pyloric canal A. angular notch B. pyloric valve 48 C. cardiac incisure D. Intermedia sulcus E. lesser curvature of stomach Multiple Choice Questions 1.Upper digestive tract consists of A. duodenum B. esophagus C. oral cavity D. pharynx E. Stomach 2.Lower digestive tract involve A. stomach B. jejunum C.ileum D. large intestine E. bile duct 3.Major salivary glands comprise A. Pancreas B. parotid gland C.gallbladder D. sublingual gland E. submandibular gland 4.Major digestive glands are A. Liver B. gallbladder C. Pancreas D. spleen E. sublingual gland 5.The isthmus of fauces be surround by A. root of tongue B. palatoglossal arch C. uvula D. hard palate E. gum 6. Periodontal tissues include A. gum B. dentin C. periodontal membrane D. dental pulp E. root of tooth 7.The muscle of tongue include A. genioglossus B. longitudinal muscle of tongue C. transverse muscle of tongue D. mylohyoid muscle 49 E. omohyoid m 8. which structures lie in the renal sinus A.minor renal calices B.major renal calices C.renal pelvis D.fatty tissues E.renal columns 9.The Oesophagus A. be divided in to cervical part、thoracic part abdominal part B.have three constrictions C.Secondary constrictionlies in superior aperture of thorax D. superiorly connect with oral cavity E.third constrictionlies in cardiac orifice 10.About the spleen ,the right descriptions are A.situated in the epigastric region B.its long axis is in line of the 10th rib C.is palpable below the left costal arch D.has two extremities E.hilum of spleen lies on the diaphragmatic surface 11.The duodenum include A. superior part B. descending part C. transverse part D. ascending part E. duodenojejunal flexure 12.Suspensory ligament of duodenum A. is plica of peritoneum B.contain suspensory m.of duodenum C.is the mark of the beginning of jejunum D.connected with duodenum E.is the membran of connective tissue 13.The large intestine include A. cecum B. appendix C. Colon D. rectum E. anal canal 14.The differentiation of large intestine and small intestine are A. large intestine have haustra of colon、colic band、epiploic appendages B. small intestine have no haustra of colon、colic band、epiploic appendages C. the cavity of large intestine is big D. the cavity of small intestine is small E. have plent of blood vesseles in small intestine 15.The Colon include A. ascending colon B. Transverse colon 50 C. sigmoid colon D. cecum E. descending colon 16.The structure of rectum are A.Sacral flexure of rectum B.Perineal flexure of rectum C.ampulla of rectum D. dentate line E. anal columns 17.The structures which can be seen in anal canal include A. anal columns B. anal valves C. anal sinuses D. dentate line; E. internal anal sphincter 18.The structure passing through first porta hepatis are A. hepatic veins B. the right and left branche of proper hepatic artery C. the right and left branche of hepatic portal vein D.left、Right hepatic duct E. nervus and lymphatic vesseles 19.Secondary porta hepatis A.lies in bare area of liver B.lies in superior part of sulcus for vena cava C. the left hepatic veins can be seen at there D. the intermediate hepatic veins can be seen at there E. the right hepatic veins can be seen at there 20.The hepatic pedicle contains A. Left、Right hepatic duct B. proper hepatic artery C. hepatic portal vein D. Common hepatic artery E. cystic duct 21.Calot's triangle formed by A. cystic duct B. common hepatic duct C. bare area of liver D. common bile duct E. inferior surface of the liver 22.The pancreas can be divided into A. head of pancreas B. body of pancreas C. neck of pancreas D. tail of pancreas E. pancreatic duct 51 23.The structure passing through renal hilus are A. renal a. B. renal v. C. renal pelvis D. ureter E. Nervus、lymphatic vesseles 24.The structures can be seen in coronal section of kidney are A. renal column B. renal pyramid C. renal cortex D. minor renal calices E. major renal calices 25.The coverings of kidney include A. fibrous capsule B. fatty renal capsule C. renal fascia D. renal sinus E. Peritoneum 26.The renal pedicle contains A. renal pelvis B. ureter C. renal a. D renal v. E.nervus and lymphatic vesseles 27.The ureter is divided into A. abdominal part B. pelvic part C. intramural part D. prostatic part E. membranous part 28.The shape of urinary bladder include A. apex of bladder B. fundus of bladder C. neck of bladder D. body of bladder E. trigone of urinary bladder 29.Trigone of urinary bladder surrounded by A. Left ureteral orifice B. Right ureteral orifice C. internal urethral orifice D. ureter intramural portion E. apex of bladder 30.The peritoneal cavity A. is encircled by parietal peritoneum and visceral peritoneum B. is divided into greater peritoneal cavity and omental bursa C. contains a little liquid 52 D.is abdominal cavity E.is a closed lacuna in male 31.The intraperitoneal viscera include A. stomach B. descending colon C. appendix D. sigmoid Colon E. anal canal 32.The retroperitoneal viscera include A. suprarenal gland B. pancreas C. spleen D. Transverse colon E. descending part of duodenum 33.The interperitoneal viscera include A.uterus B. ovary C. Liver D. pancreas E. spleen 34.The lesser omentum formed by A. gastrocolic ligament B. hepatogastric ligament C. Hepatoduodenal ligament D. suspensory m.of duodenum E. falciform ligament of liver 35.Omental bursa A.is the part of peritoneal cavity B. anterior wall is lesser omentum and posterior wall of stomach C. communicate with the greater peritoneal cavity by omental foramen D.lies in front of greater omentum E.lies in behind of pancreas 36.The omental foramen A.superior border is caudate lobe of liver B.inferior border is superior portion of duodenum C.anterior border is hepatoduodenal ligament D.posterior border is inferior vena cava E. anterior border is stomach 37.Arteries of stomach include A. left gastric a B. right gastric a. C. left gastroepiploic a D. right gastroepiploic a E. short gastric arteries 38.The lymphatic trunks entering into cisterna chyli are A. left lumbar trunk 53 B. right lumbar trunk C. intestinal trunk D. left bronchomediastinal trunk E. right bronchomediastinal trunk 39.Tributaries of inferior vena caval are A. hepatic veins B. renal v C. Left common iliac v. D. right common iliac v. E. hepatic portal vein 40.Tributaries of hepatic portal vein include A. superior mesenteric v. B. inferior mesenteric v C. hepatic veins D. splenic v. E. inferior rectal veins 41.The anastomosis of portal vein and inferior vena cava are A. Esophageal venous plexus B. rectal venous plexus C.periumbilical venous rete D. vertebral venous plexus E.pterygoid venous plexus 42.Sheath of rectus abdominis formed by A. transverse fascia B. Aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis C.Aponeurosis of obliquus internus abdominis D.Aponeurosis of transversus abdominis E. parietal peritoneum 43.The inguinal triangle is formed by A.superior epigastric artery B.inferior epigastric artery C.lateral border of rectus abdominis D.inguinal ligament E.transverse fascia 44.Inguinal canal: A.anterior wall is aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis B.inferior wall is inguinal ligament C.posterior wall is transverse fascia only D.superior wall is obliquus internus abdominis and Transversus abdominis E. round lig. of uterus pass through it in female 45.The“stomach bed”formed by A.pancreas B.Left suprarenal gland C.Right suprarenal gland D.spleen 54 E.Transverse colon 46.Common bile duct include A.supraduodenal part B.retroduodenal part C.pancreatic part D.intraduodenal part E. hepatopancreatic ampulla 47.Which structure is in front of right kidney? A.right lobe of liver B.right colic flexure C.descending portion of duodenum D.stomach E.pancreas 48.Which structure is in front of left kidney? A. stomach B.pancreas C.jejunum D.left colic flexure E.transverse part of duodenum 49.Suprarenal arteries include A.superior suprarenal arteries B.superior mesenteric artery C. middle suprarenal a. D.inferior suprarenal artery; E.celiac trunk 50.The direct branches of the abdominal aorta are A.left gastric a. B.middle suprarenal a. C.proper hepatic a. D.testicular a. E.inferior suprarenal a. ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. Write out the producing site and the discharging pathway of the bile. 2. list the segments and constrictiones the the ureter. 3. Briefly describe the location, shape, parts of stomach. 4. Describe the position, composition and contents of the inguinal canal. 5. Write out the the formation and tributaries of portal v., and the places of portal-systemic venous anastomoses. 6. Describe the parts and structures of pharynx. 7. Briefly describe the three constrictions of esophagus. 8. Briefly describe the layers of anterior and lateral wall of abdomen. 9. Briefly describe the Boundaries of inguinal triangle . 10. Briefly describe the lesser omentum, greater omentum, mesentery, mesoappendix, transverse . 11. mesocolon, sigmoid mesocolon, lig. of liver, omental bursa, omental foramen, and pouches. 12. Briefly describe the location, shape and structures of duodenum. 55 13. Briefly describe the features of colon and cecum. 14. Briefly describe the location and structures of the caecum. 15. Briefly describe the location of the vermiform appendix,and surface marking of the root of vermiform appendix. 16.Briefly describe the location, shape and structures,and surface markings of liver. 13.Briefly describe the location, portions and structures of gallbladder,and surface markings of fundus of gallbladder. 14. Briefly describe the location, shape and structures of pancreas. 15. Briefly describe the composition of extrahepatic parts of biliary system. 16. Briefly describe the location, shape and structures of spleen. 17.Briefly describe the location and shape of kidney, structures passing through the hilus of kidney, internal structure of kidney; structures in renal sinus, and capsules enclosing the kidney. 18. Know the course of ureter. 19. Briefly describe the location of abdominal aorta 20. Briefly describe the branches off abdominal aorta to the abdominal viscera. 21. Briefly describe the branch supplying of the celiac trunk, sup. and inf. mesenteric a.. 22. Briefly describe the location of inf. vena cava; 23. Briefly describe the main tributaries of inf. vena cava. 24. Briefly describe the location and shapes or structures of rectum. 25. Briefly describe the structures of anal canal. 26. Briefly describe the location, shapes or portions of urinary bladder. 27. Briefly describe the place of trigone of blader. Pelvic and perineum Single-choice questions 1. The bony pelvis (A) A. is formed by the two hip bones, sacrum, coccyx and their joints. B. can be divided into abdominal and pelvic part by the terminal line. C. is enclosed at the inferior pelvic aperture by perineum. D. is wider, shorter and more funnel-shaped in female than in male. E. pelvic outlet is formed by the terminal line. 2. The levator ani does not include (A) A. coccygeus. B. levator prostate. C. puborectalis. D. pubococcygeus. E. iliococcygeus. 3. The pelvic diaphragm (E) A. encloses the whole inferior aperture of the pelvis. B. is located in the anal triangle. 56 C. D. E. consists of levator ani, sphincter ani externus, superior and inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm. has a hiatus of pelvic diaphragm for digestive and urogenital canal. can support the pelvic viscera. 4. The perineum (B) A. is all of the soft tissue enclosing pelvic inlet. B. can be divided into urogenital and anal region. C. ends anteriorly at the external reproductive organs D. ends posteriorly at the anus. E. is a triangle-shaped region. 5. The hiatus of the pelvic diaphragm(A) A. is a cleft between the anteromedial margin of pelvic diaphragm. B. is filled with the urogenital diaphragm. C. is enclosed by superior and inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm. D. is the main channel connecting the pelvic spaces and perineal space. E. is penetrated by the membranous part of the urethra in male. 6. The retropubic space (B) A. is located between the urinary bladder and rectum or uterus. B. is usually used for extra-peritoneal operation of urinarry bladder. C. is rich in venous plexus and unsuitable for organ separation. D. is suitable for exudation absorption. E. doesn’t communicating with other pelvic spaces 7. The retrorectal space (E) A. surround the inferior part of the ampulla of rectum. B. is the space between the sacrum and presacral fascia. C. is rich in venous plexus and unsuitable for rectus separation. D. communicates downwards with the ischioanal fossa. E. communicates upwards with the retroperitoneal space . 8. Which one is right about the rectum (D) A. It continues upwards with the sigmoid colon at the level of pelvic inlet. B. It continues downwards with the anal canal at the level of dentate line. C. The upper part is not covered by peritoneum. D. It has sacral and perineal flexures in the sagittal plane. E. It is a intraperitoneal viscera. 9. Concerning Hilton’s line,the the wrong description is (E) A. lies at the interval between the sphincter ani internus and externus. B. is about 1cm below the dentate line. C. is also called white line. D. is continuous upwards with the anal pecten. E. can not be felt in digital examination of the anal canal. 57 10. Which one is wrong about the relations of the rectum (B) A. The sacral plexus is behind it. B. It is separated from the prostate by rectovesical pouche in male. C. It is separated from the seminal vesicle by rectovesical pouche in male. D. It is separated from uterus by rectouterine pouch in female. E. It is separated from the vagina by rectouterine pouch and fascial septum in female. 11. Through the anterior wall of the rectum , we can not palpate(E) A. prostate. B. seminal vesicle. C. ampulla ductus deferentis. D. neck of uterus. E. urethra. 12. The urinary bladder (E) A. may raised into the peritoneal cavity when it is filled with urine. B. contacts with prostate posteriorly (male). C. contacts with posterior part of fornix of vagina (female). D. contacts with the urogenital diaphragm at the apex. E. is entirely within the lesser pelvis when it is empty 13. The mark to find the uriteric orifice in urinary bladder is (C) A. trigone of bladder. B. internal urethral orifice. C. interureteric fold. D. urethral ridge. E. vesical uvula. 14. The pelvic part of ureter (D) A. descends immediately behind the internal iliac artery. B. crosses lateral to the external vessels, umbilical artery, obturator nerve and vessels. C. crosses posteriorly over the ductus deferens (male). D. passes lateral to the fornex of the vagina and is crossed by uterine artery. E. ends on the inferior of the urinary bladder as the internal urethral orifice. 15. The prostate (A) A. is located between the apex of bladder and urogenital diaphragm. B. is placed in front of the uterus. C. has venous plexus between the prostatic capsule and sheath. D. can not be touched during check-up. E. is pierced by the ductus deferens. 16. Which one is wrong about the prostate?(C) A. It is a chestnut-shaped organ. B. It may be divided into anterior, middle, posterior and two lateral lobes. C. The urethra passes through the middle lobe of the gland. D. There is prostatic sulcus along the middle line on the posterior surface. 58 E. The ejaculatory duct penetrates the base and opens on seminal colliculus. 17. Which one is wrong about the uterus? (D) A. It can be divided into three parts-fundus, body and neck. B. The isthmus is a slight constriction at the junction between the neck and body. C. The lower part of the neck can insert into the vagina. D. The cavity in the uterus is called cavity of uterus. E. The body is bent forward at the junction with the neck (anteflection). 18. Which one is wrong about the uterine artery (E) A. It arises from the internal iliac artery. B. It descends in front of the ureter to the base of broad ligament. C. It crosses above the ureter just lateral to the neck of the uterus. D. It sends branches to vagina, uterine tube and ovary. E. It should be protected during hysterectomy (子宫切除术). 19. The ligaments that protect the uterus from prolapse is(下垂) (D) A. broad ligament of uterus. B. suspensory ligament of ovary. C. round ligament of uterus. D. cardinal ligament of uterus. E. uterosacral ligament. 20. Which one is wrong about the position of the uterus (D) A. Its inferior end is above the ischial spine. B. The urinary bladder is in front of it. C. The uterine tube, ovaries, broad ligament are on both sides of it. D. The rectum is behind it. E. Its lower part penetrates the urogenital diaphragm. 21. The ovary (E) A. is situated in the ovary fossa between the common and internal artery. B. is a retroperitoneal viscera. C. is connected to the uterus by proper ligament of ovary at its superior extremity. D. is attached to the front of the broad ligament of uterus by mesoovarium. E. is suspended to the pelvic wall by suspensory ligament of ovary. 22. Fertilization(受精) usually occures in (D) A. cavity of uterus. B. uterine part of uterine tube.. C. isthmus of uterine tube. D. ampulla of uterine tube. E. infundibulum of uterine tube. 23. Which one is wrong about the uterine tube (D) A. It is situated on the upper margins of the broad ligament of uterus. 59 B. C. D. E. Its medial end opens into the cavity of uterus by uterine orifice. Its lateral end open into peritoneal cavity by abdominal orifice. It can be divided into three part: isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum. It is usually distinguished from the small intestine by fimbriae. 24. Which one is wrong about the vagina (B) A. The upper end surrounds the lower part of neck of uterus. B. The anterior wall is longer than the posterior one. C. The posterior fornix of vagina is near the rectouterine pouch. D. The anterior wall contacts with urinary bladder and urethra. E. The posterior wall contacts with the anterior wall of rectum. 25. Anal canal (A) A. continues with the rectum at the level of pelvic diaphragm. B. terminates at the dentate line. C. is about 7~8 cm in length. D. has two flexures in sagittal plane. E. has a dilated upper part called ampulla of rectum. 26. Below the dentate line (E) A. The epidermis is skin. B. The epidermis is innervated by somatic nerve. C. The lymph is drained into the superficial inguinal lymph node. D. The blood is drained into the internal iliac vein. E. All of the above are is right. 27. The ischioanal fossa (D) A. is located between the rectum and ischium. B. communicates anteriorly with the superficial perineal space. C. communicates posteriorly with the gluteal region through greater sciatic foramen. D. has pudendal canal on its lateral wall. E. is traversed by the obturator nerve. 28. The pudendal canal (E) A. runs in the center of the ischioanal fossa. B. is a cleft formed by superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm. C. communicates with the obturator canal. D. communicates with the greater sciatic foramen. E. contains the pudendal nerve and internal pudendal vessels. 29. Superficial fascia of perineum (C) A. can be divided into two layers. B. extends backwards with the superficial fascia in anal region. C. continues with Scarpa’s fascia. D. is not joined with the deep fascia of perineum. E. is separated from the inferior fascia of pelvic diaphragm with superficial perineal space. 60 30. Which one is wrong about the deep fascia of perineum (E) A. It can be divided into two layers. B. It attaches laterally to the pubic arches. C. It attaches posteriorly to the line between the ischial tuberosities. D. It encloses the deep perineal space. E. It is also called Colles’ fascia. 31. The superficial perineal space does not contain (E) A. suferficial transverse muscle of peritoneum. B. crura of penis. C. ischiocavernosus or bulbocavernous. D. bulb of urethra (male). E. bulbourethral gland. 32. The deep perineal space does not contain (E) A. membranous part of urethra. B. sphincter of urethra. C. bulbourethral gland. D. deep transverse muscle of perineum. E. bulb of vestibule 33. Which space is enclosed (B) A. superficial perineal space B. deep perineal space C. retropubic space D. retrorectal space E. ischioanal fossa 34. The internal spermatic fascia is continuous with(E) A. scarpa’s fascia. B. aponeurosis of obliquus externus abdominis. C. aponeurosis of obliquus internus abdominis. D. aponeurosis of transversus abdominis. E. transverse fascia. 35. Which muscle does not insert to the perineal central tendon(C) A. superficial transverse muscle of perineum. B. deep transverse muscle of perineum. C. ischiocavernousus. D. bulbocavernousus. E. urethrovaginal sphincter 36. Which one is wrong about the perineum in female in narrow sense.(D) A. It is located between the external reproductive organs and the anus. B. It contains the perineal central tendon. 61 C. D. E. It is easier tore up during childbirth. It is poor developed in female. It is also called obstetrical perineum. 37. Which one is not the important surface landmark (E) A. pubic crest. B. pubic arch. C. ischial tuberosity. D. apex of coccyx. E. promontory of the sacrum. 38. Which is wrong about the internal iliac artery (D) A. It arises from the common artery. B. It is a short trunk descending into the lesser pelvis. C. The ureter runs anterior to it. D. Send out the inferior epigastric a. E. The internal iliac vein accompanies the artery on its medial side. 39. The internal iliac artery doesn’t send(D) A. superior gluteal artery. B. obturator artery. C. internal pudendal artery. D. superior rectal artery. E. inferior vesical artery. 40. Which is wrong about the nervous plexus in the pelvis (C) A. The sacral plexus lies in front of the piriformis. B. The sacral sympathetic trunk runs medial to the anterior sacral foramen. C. The sacral plexus belong to the syspathetic n. D. The pelvic plexus is also called inferior hypogastric plexus. E. The branches distribute to the pelvic organs. 41. Which is wrong concerning the Superficial fascia of perineum.(B) A. Is called Colles’ fascia also B. Continues with Camper’s fascia. C. Continues with Dartos coat. D. Continues with Superficial fascia of the penis. E. Scarpa’s fascia. 42. During a straddle (骑跨) injury, the urine can not spread into (E) A. penis. B. scrotum. C. superficial perineal space. D. anterior wall of abdomen. E. retropubic space. 62 43. Which part of the ductus deferens can be easy palpated under the skin (B) A. testicular part. B. funicular part. C. inguinal part. D. pelvic part. E. ampulla ductus deferentis 44. The second stricture of male urethra is at (D) A. internal orifice urethra. B. prostatic part. C. cavernous part. D. membranous part. E. external orifice urethra. 45. In male, the anterior urethra refers to(C) A. prostatic part. B. membranous part. C. cavernous part. D. bulbous part. E. bulbous part and Membranous part. 46. The epididymis(B) A. attaches to the anterior surface of the testes. B. is the storehouse for sperm. C. can be divided into head, neck, body and tail. D. secrets male hormone. E. consists of rete testis. 47. The penis can be divided into(B) A. head, body and tail. B. head, body and root. C. head, neck and body. D. head, neck and crus. E. head, neck and crus. 48. The internal reproductive organ is (E) A. mons pubis. B. lesser lips of pudendum. C. bulb of vestibule D. clitoris. E. great vestibular gland. 49. The deep perineal space does not contain (D) A. Deep transverse perineal m. B. Sphincter urethrae C. Bulbo-urethral gland. 63 D. E. perineal nerve. Artery of penis 50. The internal pudendal artery(D) A. Arises from the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. B. Passes through the lesser sciatic foramen to enter the gluteal region. C. Runs along the lateral surface of the obturator internus. D. Supplies the perineum. E. Runs below the pudendal nerve in the pudendal canal. Multi-choice questions 51. The parietal pelvic fascia on the surface of the obturator internus forms (BCD) A. obtrurator membrane. B. obturator fascia. C. obturator canal. D. tendinous arch of levator ani. E. pudendal canal. 52. The visceral pelvic fascia forms (BC) A. pudendal canal. B. prostatic sheath. C. cardinal ligament of uterus. D. superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm. E. retrorectal space. 53. Pelvic fascial spaces include(CD) A. deep perineal space. B. superficial perineal space C. retropubic space. D. retrorectal space.. E. ischioanal fossa. 54. The splanchnic nerve in the pelvis are (ACD) A. sacral sympathetic trunk. B. superior hypogastric plexus. C. pelvic plexus. D. pelvic splanchnic nerves. E. sacral plexus. 55. Peritoneum in pelvis forms (BDE) A. the uterosacral ligament. B. the rectouterine pouch. C. the round ligament of uterus. D. the mesovarium. E. the vesicouterine pouch. 64 56. During the digital examination, we can feel (BCDE) A. ovary. B. prostate. C. seminal vesicle. D. uterus. E. ampulla of ductus deferens. 57. The muscle referring to the anorectal ring are (ACDE) A. sphincter ani internus. B. subcutaneous part of sphincter ani externus. C. superficial part of sphincter ani externus. D. deep part of sphincter ani externus. E. puborectalis. 58. Superficial fascia of perineum(ACE) A. is also called Colles’ fascia. B. Is continuous with Camper’s fascia C. Is continuous with dartos coat. D. Is continuous with albuginea of the penis. E. Is continuous with Scarpa’s fascia. 59. The pedendal nerve innervates (ABCE) A. superficial transverse muscles of perineum. B. deep transverse muscles of perineum. C. sphincter ani externus D. sphincter ani internus. E. levator ani. 60. Structures passing through the superficial and deep perineal space are (BC) A. anal canal B. vagina. C. urethra. D. Obturator artery. E. Inferior gluteal nerve. 61. Muscles insert at the perineal central tendon are (ABCDE) A. sphincter ani externus. B. superficial transverse muscles of perineum. C. deep transverse muscles of perineum. D. levator ani. E. sphincter of urethra. 62. On the lateral wall of the ischoanal fossa, there are (ABDE) A. pudendal canal. B. obturator internus. C. sacrotuberous ligament. 65 D. E. ischial spine ischial tuberosity. 63. The superficial perineal space in female contains (ABCDE) A. crus of clitoris. B. bulb of vestibule. C. great vestibular gland. D. superficial transverse muscle of perineum E. ischiocaverbousus. 64. The urogenital diaphragm is composed of (BCDE) A. superficial transverse muscle of perineum. B. deep transverse muscle of perineum. C. sphincter of urethra. D. superior fascia of urogenital diaphragm. E. inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm. 65. Rectovesical or rectovaginal septum (ABCD) A. is between the rectum and urinary bladder or vagina. B. is in coronary plane. C. contacts upwards to peritoneum. D. ends downwards at the pelvic diaphragm. E. contains prostate in male. 66. The rectal cancer can metastasize to (BDE) A. superior mesenteric lymph node. B. inferior mesenteric lymph node. C. superficial inguinal lymph node. D. internal iliac lymph node. E. sacral lymph node. 67. Behind the urinary bladder, there are (BCD) A. ovary. B. rectum(male). C. neck of uterus. D. anterior wall of vagina. E. prostate. 68. The blood supplying the rectum comes from(CD) A. superior mesenteric artery. B. femoral artery. C. superior rectal artery. D. inferior rectal artery. E. anal artery. 69. The spermatic cord consists of (BDE) 66 A. B. C. D. E. Ejaculatory duct. ductus deferens. Seminal vesicle. pampiniform plexus testicular artery. 70. The pudendal nerve (ACDE) A. arises from the sacral plexus. B. leaves the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen. C. enters the pudendal canal through the lesser foramen. D. pass through the pudendal canal. E. gives off dorsal nerve of penis(clitoris) ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. Write out the parietal and visceral branches of the internal iliac artery. 2. Write out the position, shape and relation of the uterus. 3. Write out the position and formation of the pelvic diaphragm, and the structures pierceing it. 4. Write out the position, contents of the deep perineal space. 5. Write out the internal reproductive organs in male. 6. Briefly describe the composition of spermatic cord ,. 7. Briefly describe the location and function of epididymis. 5. Briefly describe the location and lig. of ovary. 6. Briefly describe the location, shapes or potions uterine tubes. 7. Briefly describe the location, posture, shapes, portions, and cavity of the uterus. 8. Briefly describe the supporting structures or lig. for the uterus. 9. Briefly describe the features of the male and female urethrae. 10. Briefly describe the beginning and ending of common iliac a. and v. 11. Briefly describe the beginning and ending of external and internal iliac a. and v. 12. Briefly describe the relations of uterine a. and ureter. 13. Briefly describe the location and contents of superficial perineal space. 14. Briefly describe the location and contents of deep perineal space. 15. Briefly describe the location and contents of ischiorectal fossa. 16. Briefly describe the formations of pelivic diaphragm urogenital diaphragm. 67