weather test study guide
advertisement

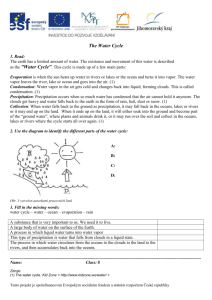
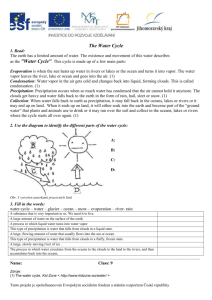
WEATHER TEST STUDY GUIDE W/ ANSWERS Vocabulary terms to know: 1. Water Cycle: The constant movement of water from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and back to the Earth’s surface. 2. Water Vapor: The gas form of water. 3. Evaporation: The process by which a liquid changes to gas. 4. Condensation: The process by which a gas changes to liquid. 5. Glaciers: Huge sheets of ice that cover portions of the Earth. 6. Precipitation: Water that falls from the sky to Earth’s surface. 7. Current: A stream of water that flows through the ocean like a river. 8. Weather: The condition of the atmosphere at a certain time and place. 9. Humidity: A measurement of the amount of water vapor in the air. 10. Run-off: Water that lands on the Earth’s surface and then runs back into rivers, lakes and oceans. 11. Cumulous Clouds: puffy white or grey clouds that indicate clear weather. 12. Stratus Clouds: low grey clouds that cover the sky and indicate rain or snow 13. Cirrus Clouds: high, wispy clouds that form high in the sky. 14. Meteorology: the study of weather. 15. Barometer: an instrument for measuring air pressure 16. Anemometer: an instrument for measuring wind speed. 17. Hygrometer: and instrument for measuring humidity. 18. Air Mass: A large body of air that has similar temperature and humidity throughout. 19. Front: a place where tow air masses meet. 20. Climate: the pattern of weather an area experiences over a long period of time. Be able to answer these questions: 1. Where is most of the water on Earth located? In the oceans 2. Where is most of Earth’s fresh water located? In glaciers and polar ice caps 3. Why isn’t rain water salty? Because only the water evaporates. The salt stays in the oceans. 4. What is the source of energy for the water cycle? The sun 5. What are the four parts of the water cycle? Evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and run-off 6. Where does water go when it evaporates? Into the air as water vapor 7. How do ocean currents affect weather? They cause weather patterns to move around the globe by moving warm and cool water to different parts of the ocean. 8. How do clouds form? Water vapor condenses and droplets form on tiny dust particles in the air. When many droplets come together a cloud is formed. 9. What are the four forms of precipitation? Rain, hail, sleet, and snow 10. What causes different types of precipitation? The temperature of the air: cold air causes sleet or snow, while hail is formed very high in the atmosphere. Rain forms in warmer air. 11. What tools do meteorologists use to make weather forecasts? Rain gauges, wind vanes, anemometers, barometers, hygrometers, thermometers, and weather satellites. They also use the history of weather to help predict what will happen in the future. 12. Which direction does air usually move across the United States? From west to east 13. Where do most weather changes occur? Along fronts; for example, we are likely to experience a change in weather when a cold front or a warm front passes through. 14. If a high pressure system is in your area, what kind of weather is likely? Clear weather, no rain 15. What is the difference between weather and climate? Weather is the conditions in the atmosphere at a particular place and time. Climate is the pattern of weather an area experiences over a long period of time. 16. How is weather different near the Equator than farther away from it? It is warmer and rainier near the Equator. The climate becomes colder as you move away from the equator. 17. At what temperature does water freeze or melt? 0˚Celsius or 32˚ Fahrenheit 18. At what temperature does water boil? 100˚Celsius or 212˚ Fahrenheit Be able to do the following things. 1. Draw and label the water cycle. 2. Recognize pictures that represent evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. 3. Identify three types of clouds and tell what kind of weather they indicate. 4. Match the names of weather instruments to their pictures and definitions. 5. Use a weather map to answer questions.