Savaysa
advertisement

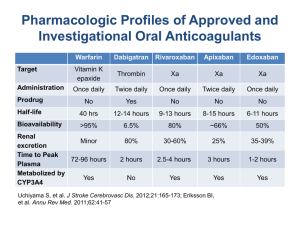
New Drug Introduction: Savaysa / Edoxaban Pharmacology Manufacturer Approval Date Indications Contraindications Black Box Warnings Warnings and Precautions Pregnancy/Lactation Pharmacokinetics Drug Interactions – Object Drugs Drug Interactions – Precipitant drugs Adverse Effects (Edoxaban 60mg) [Warfarin] Monitoring Efficacy Monitoring Toxicity Dosing Savaysa (edoxaban), is a factor Xa inhibitor to prevent stroke and systemic embolism and treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Edoxaban inhibits free factor Xa, and prothrombinase activity and inhibits thrombin-induced platelet aggregation. Daiichi Sankyo January 8th, 2015 To reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation Treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) following 5 to 10 days of initial therapy with a parenteral anticoagulant Active pathological bleeding Reduced efficacy in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation patients with CrCl >95 mL/minute – Avoid use in patients with CrCL >95 mL/minute Spinal/Epidural hematomas – with neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture May increase the risk of bleeding; serious, potentially fatal bleeding Not recommended for use in patients with mechanical heart valves or moderate to severe mitral stenosis Discontinue edoxaban at least 24 hours prior to elective surgery or invasive procedures. Category: C Lactation Recommendation: Excretion in breast milk unknown/not recommended. A – Bioavailability: 62% D – Vd: 107 L with ~55% protein binding M – Minimal via hydrolysis, conjugation and oxidation by CPY3A4; predominant metabolite (M-4) is active (<10% of parent compound) E – Urine (primarily unchanged); renal clearance: ~50% of total clearance. T1/2: 10 to 14 hours Anticoagulants, Antiplatelets, and Thrombolytics – Co-administration may increase the risk of bleeding P-glycoprotein Inducers: ↓concentration of Edoxaban Rifampin P-glycoprotein Inhibitors: concentration of Edoxaban NVAF: No dosage adjustment DVT/PE: Consider Edoxaban dose reduction when used with verapamil, quinidine, azithromycin, clarithromycin, erythromycin, oral itraconazole or oral ketoconazole. Vaginal Bleed (9%) [7.1%] Cutaneous soft tissue bleed (5.9%) [10%] Nose Bleeds (4.7%) [5.7%] GI bleeding (4.2%) [3.6%] Anemia (1.7%) [1.3%] - Lower GI bleeding (3.4%) [3.1%] Routine monitoring of coagulation tests not required Monitor for signs and symptoms of bleeding including neurological impairment. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: Oral: 60 mg once daily after 5 to 10 days of initial therapy with a parenteral anticoagulant. Patient weight ≤60 kg: 30 mg once daily Concomitant therapy with specific P-gp inhibitors: 30 mg once daily Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: Oral: 60 mg once daily Renal Adjustment Hepatic Adjustment Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: CrCl ≥51 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment recommended. CrCl 15 to 50 mL/minute: 30 mg once daily CrCl <15 mL/minute: Use is not recommended. Nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: CrCl >95 mL/minute: Use is not recommended. CrCl 51 to 95 mL/minute: No dosage adjustment recommended. CrCl 15 to 50 mL/minute: 30 mg once daily CrCl <15 mL/minute: Use is not recommended. Hemodialysis: Total edoxaban exposure reduced by <7% during a 4hour dialysis session. Use is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment due to intrinsic coagulation abnormalities. Cost: Brand – Generic Savaysa – edoxaban Coumadin® - warfarin (generic) Xarelto®– rivaroxaban Eliquis®– apixaban Dose 15 mg, 30 mg, 60mg tablets (30) 1 mg, 2 mg, 2.5 mg, 3 mg, 4 mg, 5 mg, 7.5 mg, 10mg tablets (30) 15 & 20 mg, starter pack (51) 10 mg, 15mg, 20mg tablets (30) 2.5 mg, 5mg tablets (60) $ 30 day $333 $4 (Discount Drug Plans) $642 $378 $378 Summary Savaysa (Edoxaban) is a factor Xa inhibitor, indicated to prevent stroke and systemic embolism in non-valvular atrial fibrillation and to treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. When used in the treatment of DVT/PE edoxaban requires 5 to 10 days of initial therapy with a parenteral anticoagulant. Edoxaban is typically given as a once daily 60mg dose, but should be administered at lower doses for patients with impaired renal or hepatic function or if the patient weights ≤60 kg. Edoxaban should not be used in NVAF patients with CrCL >95 mL/minute. The most common side effects of edoxaban include; vaginal, cutaneous soft tissue, nose, and GI bleeding. References: 1. Savaysa package insert. Daiichi Sankyo. January 2015. 2. Edoxaban: Drug information. Lexicomp Drug Information. Accessed through UpToDate on March 2, 2015. 3. Warfarin. Drug information. Lexicomp Drug Information. Accessed through UpToDate on March 2, 2015. 4. Rivaroxaban. Drug information. Lexicomp Drug Information. Accessed through UpToDate on March 2, 2015. 5. Apixaban. Drug information. Lexicomp Drug Information. Accessed through UpToDate on March 13, 2015. Date Prepared: 03/17/2015 Editor: Peter G. Koval, Pharm.D., BCPS Author: Tiffany Wong, Pharm.D. Candidate, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy