Complete Blood Count (CBC)
advertisement

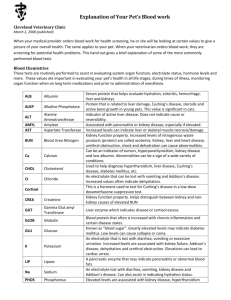
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT (CBC) Inflammation and Infection Poor Blood Clotting Anemia WBC (Total white blood cell count) Neutrophils • Monocytes Bands • Eosinophils Lymphocytes • Basophils Platelets RBC (Red blood cells) PCV (Packed Cell Volume) Hemoglobin MCV MCHC URINE BLOOD CHEMISTRIES be needed. ALT AST Jaundice Total Bilirubin Liver Disease Kidney Disease Intestinal Disorder Total Protein Albumin • A/G Ratio • Globulin Kidney Malfunction Creatinine Phosphorus • BUN Parathyroid Disorder, Cancer Calcium Phosphorus Diabetes Severe infection (sepsis) Glucose (Blood sugar) Inflammation of the Pancreas Amylase Lipase Adrenal Disease Decreased Kidney Function Sodium Potassium Muscle Injury CPK Hyperthyroidism Hypothyroidism T4, fT4 WBC pH Protein Glucose Tests for the presence of anemia (low blood cell levels) • MCH These tests help tell which type of anemia is present. A • RBC Morhphology reticulocyte count (to look for young red cells) may also Liver Disease Inflammation of the Pancreas Kidney Disease Urinary/Bladder Disease The cell counts tell how many of each type of white blood cells are present and whether or not they appear normal. White blood cells help fight infection. White blood cell numbers can increase in response to inflammation and infection. White blood cell numbers can decrease with severe infection, bone marrow disease, or (in cats) FeLV or FIV infection. Platelets help with blood clotting. It is important to make sure that these numbers remain normal or close to normal. This test evaluates the size, shape and overall red blood cell count. • ALP • GGT • Na/K Ratio • Chloride Ketones Bilirubin Bacteria Crystals Liver enzymes. These tests help indicate that there may be a problem with the liver. Liver enzyme levels may also be abnormal with inflammation of the pancreas or intestines. A test for jaundice. Increased levels usually indicate a liver disorder (with or without concurrent disease of the pancreas) or damaged red blood cells. Protein levels. Albumin may be decreased with disorders of the intestine, kidneys, liver or decreased nutrient intake. The globulin level may also decrease due to intestinal disease and may increase in response to inflammation or cancer. Tests of kidney function (should be run in conjunction with urinalysis for the most accurate assessment of kidney function. Elevated or decreased calcium levels can be a sign of a wide variety of diseases. A common cause of increased calcium in dogs is lymphosarcoma (a type of cancer). A glucose test will detect abnormally high blood sugar levels, which may indicate diabetes. Low levels may occur with liver disease, severe infection, certain types of cancer and Addison’s disease. Tests for inflammation of the pancreas. Levels can also be increased due to kidney disease or enteritis. Important body electrolytes. It is especially important that potassium levels be monitored in sick animals and in animals with decreased kidney function or adrenal disease. Muscle enzyme. Increased levels indicate muscle injury or inflammation. In cats, weight loss can also cause levels to increase. Thyroid test. In cats we look for levels above normal (hyperthyroidism). In dogs we look for subnormal levels (hypothyroidism). This is a screening test. Urinalysis is a very important means of evaluating; the presence of a urinary tract infection or inflammation of the urinary bladder, kidney function and diabetes, especially when done in conjunction with blood screening.