Otterhound Club of America and The Otterhound Club
advertisement

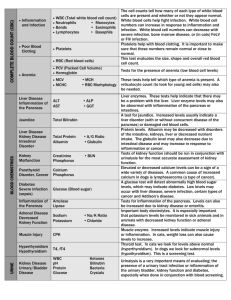
Manchester Terrier Health Survey LIST OF SOME POSSIBLE CONDITIONS WITH DEFINITIONS Anal glands Impaction Infection - Occurs when the anal glands fail to empty normally, leading to a build-up of secretions and requiring manual emptying. Can be a result of anal gland impaction. Autoimmune Disease Autoimmune haemolytic anaemia - Occurs when white blood cells attack the body’s red blood cells, leading to anaemia and jaundice. Cancer Carcinoma – Haemangiosarcoma – Lymphosarcoma/lymphoma – Osteosarcoma Soft tissue sarcoma – A A A A A malignant malignant malignant malignant malignant cancer, tumour tumour tumour tumour with the tumour(s) being formed of epithelial cells. of the blood vessels. of white blood cells. of bone. of soft tissue. Cardiovascular Conditions Atrial fibrillation – Cardiomyopathy – Congenital heart defect – Heart failure – Heart murmur (grade 1-6) – Pericardial effusion – Valve disease – An irregularity of the heart rhythm. Disease of the heart muscle. Further characterised as dilated, hypertrophic or restrictive. An abnormality of the heart structure or function which is present at birth. Inability of the heart to maintain a circulation sufficient to meet the body’s needs. An extra, abnormal heart sound. Build up of fluid in the sac surrounding the heart. Disease of the heart valve(s) interfering with the normal rate and smoothness of blood flow through the heart. Dermatologic (Skin) Conditions Atopy Ehlers-Danlos syndrome – Follicular dysplasia Hot spots Pattern baldness Pyoderma - Skin allergy, often seasonal, characterised by intense itchiness mainly of feet, face, chest and abdomen. Congenital hereditary syndrome of joint hyperextensibility, hyperelasticity and fragility of the skin and poor wound healing. Abnormality of the hair follicles resulting in late onset alopecia (hair loss). Acute moist dermatitis. Another name for follicular dysplasia. Bacterial infection of the skin. Digestive Conditions Bloat/GDV Colitis – Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency Foreign body obstruction Gastroenteritis – Bloat is a life-threatening condition seen most commonly in large, deepchested dogs in which the stomach swells, usually after eating, and may twist as in gastric torsion (GDV). Inflammation of the colon. Signs include diarrhoea, mucoid stools and straining. Insufficient secretion of digestive enzymes causing maldigestion and malabsorption with diarrhoea and weight loss. Obstruction of the gastrointestinal tract by a foreign object. Inflammation of the lining of the stomach and intestine, causing vomiting and diarrhoea. Gluten-sensitive enteropathy Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) Megaoesophagus Pancreatitis - Dietary sensitivity to gluten causing diarrhoea and poor growth in young dogs. Cyclic bouts of vomiting and diarrhoea. Pathological enlargement of the oesophagus. Potentially fatal inflammation of the pancreas. Ear Conditions Chronic ear infections Ear mites - Bacterial or fungal infections. Parasitic infestation of the ear. Endocrine (Hormonal) Conditions Addison’s Disease (Hypoadrenocorticism) Cushing’s Disease (Hyperadrenocorticism) Diabetes mellitus Hypothyroidism - Diminished hormone production by the adrenal gland causing weakness, vomiting, diarrhoea and a low heart rate. Hyperactivity of the adrenal glands. Signs include excessive eating, drinking and urination, muscle weakness, pendulous abdomen, hair loss and an increased susceptibility to infections. Relative or total lack of insulin production by the pancreas. Signs include excessive eating and drinking, often accompanied by weight loss. Inadequate hormone production by the thyroid gland characterized by lethargy, loss of hair and a general lowering of metabolic rate. Eye Conditions Cataracts Ectropion Entropion Lens luxation Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) - Clouding of the lens within the eye. A condition of the eyelids, most commonly affecting the lower eyelid, in which the skin droops turning the mucous membrane lining of the lid to the outside. Turning in of an eyelid, such that hair or eyelashes contact the cornea. Separation of the lens from its attachments allowing displacement. Gradual degeneration of the retina, leading eventually to a loss of sight. Haematological Conditions Haemophilia A Von Willebrand’s disease – Classical haemophilia, due to a deficiency of clotting factor VIII-C. An inherited, congenital clotting disorder causing mild bleeding tendencies. Hepatic (liver) Conditions Acute liver failure – Chronic liver failure – HepatitisPortosystemic shunt (PSS) - Sudden collapse of liver function which can rapidly be fatal. A gradual decline in liver function, primarily a disease of older hounds. Inflammation of the liver which can be caused by infection or toxic substances. An abnormality of the blood circulation system, resulting in blood from the heart bypassing the liver and entering the general circulation. Neurological (nervous system) Conditions Epilepsy (seizures) - A chronic disorder characterised by a sudden and complete loss of consciousness, associated with muscular convulsions. Oral & Dental Conditions Overshot jaw Undershot jaw - (Prognathism) Upper teeth protrude beyond lower. (Brachygnathism) Lower teeth protrude beyond upper. Orthopaedic (Musculoskeletal) Conditions Arthritis Intervertebral disc disease Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease Patellar luxation - Inflammation of a joint, resulting in pain which may affect movement. Pain and neurological deficits, and sometimes complete paralysis, resulting from displacement of part or all of an intervertebral disc. Necrosis and lysis of the femoral head, occurring in young dogs. Leads to lameness and a degenerative arthropathy, usually requires surgery. Dislocation of the patella (Knee cap) causing mild to severe, continuous or intermittent lameness. Reproductive Disease Benign prostatic hyperplasia – Cryptorchidism – Dystocia Eclampsia False pregnancy – Hermaphrodite – Litter resorption – Mastitis Prostatic cyst Prostatitis/infection/abscess – Pyometra Vaginitis - Enlargement of the prostate gland seen in intact dogs of middle age or older. Retention of one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) testicles in the abdomen. Difficult parturition (giving birth) to the point of needing human intervention. A syndrome including convulsions and coma occurring in animals soon after birth of the young. Development of all the signs of pregnancy without the presence of an embryo. An individual whose body contains both ovarian and testicular tissue. Re-absorption of the fetuses into the dam’s body part way through pregnancy. Inflammation of the mammary gland(s). A cyst within the prostate gland. May occur in association with benign prostatic hyperplasia or as a separate entity. Inflammation of the prostate gland. May be acute, causing fever and pain, or chronic causing difficulty urinating and constipation. Disease of the uterus in which the body and horns of the uterus become filled with fluid and develop a secondary bacterial infection. Vaginal infection with a discharge that makes the female lick excessively and she may become attractive to male dogs. Respiratory Conditions Chronic bronchitis Laryngeal paralysis Rhinitis - Inflammation of the airways, signs include fever and coughing. Paralysis of the voice box causing an altered bark, noisy respiration and/or respiratory obstruction. Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose. Signs include wheezing, sneezing and nasal discharge. Urologic (urinary system) Conditions Acute renal failure – Chronic renal failure – Cystitis - Sudden collapse of kidney function which can rapidly be fatal. A slow decline in kidney function, primarily a disease of middle to old age. Inflammation of the bladder.