Table 6: Brain imaging studies of patients with hyperlipidemia
advertisement
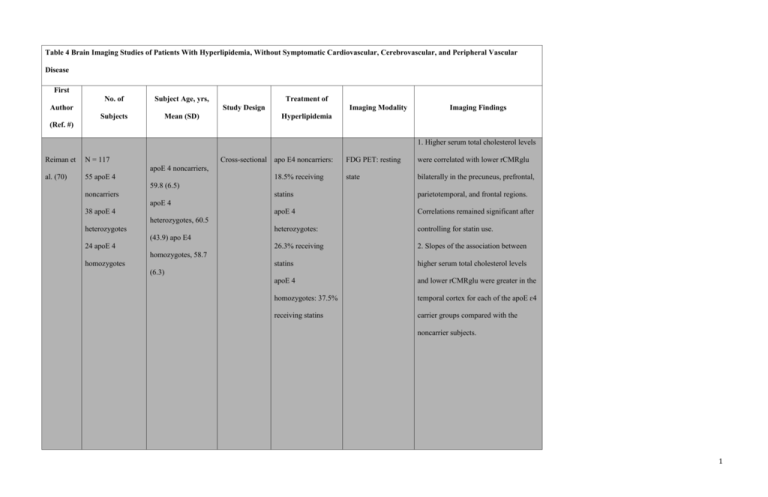
Table 4 Brain Imaging Studies of Patients With Hyperlipidemia, Without Symptomatic Cardiovascular, Cerebrovascular, and Peripheral Vascular Disease First No. of Subject Age, yrs, Author Treatment of Study Design Subjects Mean (SD) Imaging Modality Imaging Findings Hyperlipidemia (Ref. #) 1. Higher serum total cholesterol levels Reiman et N = 117 al. (70) 55 apoE 4 Cross-sectional apo E4 noncarriers: FDG PET: resting were correlated with lower rCMRglu state bilaterally in the precuneus, prefrontal, apoE 4 noncarriers, 18.5% receiving 59.8 (6.5) noncarriers statins parietotemporal, and frontal regions. apoE 4 Correlations remained significant after heterozygotes: controlling for statin use. 26.3% receiving 2. Slopes of the association between statins higher serum total cholesterol levels apoE 4 and lower rCMRglu were greater in the homozygotes: 37.5% temporal cortex for each of the apoE ɛ4 receiving statins carrier groups compared with the apoE 4 38 apoE 4 heterozygotes, 60.5 heterozygotes (43.9) apo E4 24 apoE 4 homozygotes, 58.7 homozygotes (6.3) noncarrier subjects. 1 N = 141 apo E4 noncarriers, 1. Structural MRI 70 apo E4 56.9 (4.6) 2. FDG PET: resting noncarriers, apo E4 42 apo E4 heterozygotes, 55.8 heterozygotes (3.9) 29 apoE4 apo E4 homozygotes homozygotes, 55.6 Reiman et state 1. CREGS was correlated with lower al. (71) Calculation of each regional to whole-brain PET Treatment data not subject’s CREGS Cross-sectional measurements of rCMRglu in the available. was based on a posterior cingulate, precuneus, cluster of (5.1) parietotemporal, and frontal regions. polymorphisms associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Sinha et 19 With Group 1: 13 1. 1H MRS 1. In the combined hyperlipidemic and with hyperlipidemia, 32.6 hyperlipidemic 2. SPECT normolipidemic groups, the Cho/Cr hyperlipidemia (6) subjects receiving ratio in the occipital region was high in Cross-sectional al. (65) 21 Without HMG-CoA reductase subjects with excess percentage of body without hyperlipidemia, 29.8 inhibitor treatment. fat. hyperlipidemia (4.5) 2. In the combined hyperlipidemic and 2 Group 2: 6 normolipidemic groups, the Cho/Cr hyperlipidemic ratio in the occipital region was low in subjects not subjects with low HDL-C. receiving statin 3. In the combined hyperlipidemic and treatment. normolipidemic groups, the NAA/Cho Group 3: 21 ratio in the occipital region was low in normolipidemic subjects with high total cholesterol and subjects. non–HDL-C levels. 4. 50% of subjects with hypertriglyceridemia demonstrated temporal hypoperfusion compared with 14% of subjects with normal triglyceride levels. 1. Higher LDL and total cholesterol 41 receiving lipidReceiving lipid- were associated with lower FA values lowering in the right hemisphere. The most lowering medication medication, 71.29 83 not receiving Williams robust associations occurred in frontal 33% of subjects (7.83) lipid-lowering et al. (69) 1. Structural MRI and temporal regions. LDL emerged as 2. DTI MRI the most robust predictor of white Cross-sectional receiving lipidNot receiving lipid- medication lowering medication. lowering matter tissue integrity as indexed by medication, 66.37 FA. (9.78) 2. Negative associations between HDL and FA were also mainly lateralized to 3 the right hemisphere and included sections of the anterior limb of the internal capsule, the external capsule, thalamic pathways, and frontal regions. 3. Triglyceride levels revealed the fewest voxels showing significant associations with FA, including the genu of the corpus callosum. 4. Radial diffusivity qualitatively held greater associations with LDL in more anterior white matter regions, and axial diffusivity exhibited larger associations with LDL in posterior regions. 5. No significant group differences in mean FA between medication groups for all significant clusters. 5 with With homozygous 100% of subjects homozygous familial familial No white matter lesions in any of the hypercholesterolemia subjects in either group and no other hypercholesterolemi Schmitz et hypercholesterole with familial a, 23.4 (9.2) al. (66) mia Without familial 5 without familial hypercholesterolemi hypercholesterole a, 27.8 (3.2) Cross-sectional Structural MRI being treated with abnormality was identified in either HMG-CoA reductase group. inhibitors. 4 mia 1. 16% of subjects with heterozygous familiar hypercholesterolemia and 24% of subjects without familial hypercholesterolemia had ≥1 WMH. 39 with With heterozygous heterozygous familial 72% of subjects with familial hypercholesterolemi heterozygous No statistical difference in occurrence of WMHs between subjects with familiar hypercholesterolemia and Soljanlahti hypercholesterole a, 30.0 (13.6) familial 1. Structural MRI Cross-sectional et al. (68) mia Without familial subjects without familial hypercholesterolemia 2. MR angiography hypercholesterolemia. 25 without familial hypercholesterolemi were receiving statin 2. The mean intima-media thickness of hypercholesterole a, 30.6 (11.3) medication. the far wall of the left common carotid mia artery was greater in the subjects with familiar hypercholesterolemia compared with subjects without familial hypercholesterolemia. 1. Lower gray matter volume was Whalley et Treatment data not N = 82 al. (64) Age, 78.5 Cross-sectional associated with higher total cholesterol Structural MRI available. and LDL. 2. Cerebrospinal fluid volume 5 positively correlated with total cholesterol and LDL. 3. No association between white matter volume and total cholesterol. 14 with With heterozygous No significant difference in the 100% of subjects heterozygous familial proportion of subjects with and without with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemi familial hypercholesterolemia with familial Schmitz et hypercholesterole a, 39 (10) WMHs: WMH was observed in 3 of 22 Cross-sectional hypercholesterolemia Structural MRI al. (67) mia Without familial subjects without familial being treated with 22 without familial hypercholesterolemi hypercholesterolemia and in 1 of 14 lipid-lowering hypercholesterole a, 41 (12) with heterozygous familial medication. mia hypercholesterolemia. apo = apolipoprotein; CREGS = cholesterol-related genetic score; FDG = fluorodeoxyglucose; HDL-C = high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HMG-CoA = 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; MR = magnetic resonance; other abbreviations as in Tables 2, 3, and 5. 6