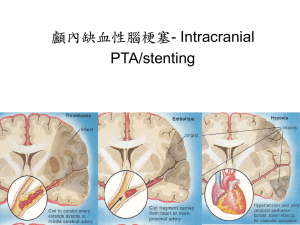
Dissector Bold terms 3
advertisement

Unit 3 Week 8 Day 1 Abdomen 78-87 Surface anatomy -Xiphoid process -Costal margin -Pubic symphysis -Pubic crest -Pubic tubercle -Anterior superior iliac spine -Tubercle of the iliac crest Quadrant system (RU, LU, RL, LL) -Transumbilical plane -Median plane Regional system (hypochondriac, epigastric, lumbar, umbilical, hypogastric, inguinal) -Midclavicular lines -Subcostal plane -Transtubercular plane Superficial Fascia -Camper’s fascia (fatty layer) -Scarpa’s fascia (membranous layer) -Superficial epigastric artery and vein -Anterior cutaneous nerves -Intercostal nerves (T7-T11) T7-Xiphoid process; T10-umbilicus; T12-superior to pubic symphysis; L1-pubic symphysis -Subcostal nerve (T12) -Iliohypogastric/ilioinguinal nerves (L1) -Lateral cutaneous nerves Abdominal Wall -External oblique (ribs 5-12; linea alba, pubic tubercle and iliac crest) -Internal oblique (ribs 10-12; linea alba, pubic crest; iliac crest) -Transversus abdominis -Inguinal canal -Superficial (external) inguinal ring (opening in external oblique aponeurosis) -Deep (internal) inguinal ring -Spermatic cord (male content of inguinal canal) -Round ligament of uterus (female content of inguinal canal) -Lateral (inferior) crus (margin of superficial inguinal ring; attached to pubic tubercle) -Medial (superior) crus (margin of superficial inguinal ring; attached to pubic crest) -Intercrural fibers -External spermatic fascia -Ilioinguinal nerve (sensory anterior external genitalia and medial thigh) -Inguinal ligament -Lacunar ligament (medial fibers of inguinal turn posteriorly) -Cremaster muscle and fascia (connect internal oblique to spermatic cord/round ligament) -Iliohypogastric nerve (superior to ilioinguinal nerve) -Conjoint tendon (aponeurosis of internal oblique fused with aponeurosis of transversus abdominis) -Transversalis fascia -Inferior epigastric vessels (medial to deep inguinal ring) -Rectus sheath -Rectus abdominis (ribs 5-7; symphysis/body of pubis): Flex trunk -Superior/Inferior epigastric vessels (ventral rami T7-T12) -Pyramidalis -Tendinous intersections -Anterior cutaneous branches (T7-T12) -Arcuate line (between pubic symphysis and umbilicus; posterior wall of rectus sheath) -Parietal peritoneum -Linea alba (aponeuroses external/internal obliques and transversus abdominis) Boundaries of inguinal canal -Deep-deep inguinal ring -Superficial-superficial inguinal ring -Anterior-aponeurosis of external oblique -Inferior-inguinal ligament/lacunar ligament -Superior-internal oblique/transversus abdominis -Posterior-transversalis fascia/conjoint tendon Hernias Indirect inguinal hernia-lateral to inferior epigastric vessels through deep inguinal ring Direct inguinal hernia-medial to inferior epigastric vessels and directly through Week 8 Day 2 Abdomen 87-96 -Falciform ligament (connect liver to anterior ab wall) -Coronary ligament (liver to diaphragm) (Left triangular and right triangular) -Gastrophrenic ligament (stomach to diaphragm) -Gastrosplenic ligament -Splenorenal ligament -Median umbilical fold (urachus-allantoic duct) -Medial umbilical fold (umbilical artery) -Lateral umbilical fold (inferior epigastric artery and vein) -Peritoneum (parietal and visceral) -Peritoneal cavity (potential space) -Intraperitoneal organs (stomach, small intestine, liver and spleen) -Retroperitoneal organs (ureters, suprarenal glands, kidneys) -Secondarily retroperitoneal (duodenum, pancreas, ascending colon and descending colon) -Gastrointestinal tract -Liver (right/left lobes-falciform ligament) -Gallbladder (right 9th costal cartilage) -Stomach -Spleen -Greater omentum -Small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) -Large intestine -Cecum (appendix attached) -Ascending colon (ends at right colic flexure) -Transverse colon (ends at left colic flexure) -Descending colon -Sigmoid colon (ends in pelvic cavity at 3rd sacral vertebral level) -Rectum (located in pelvis) -Lesser omentum (hepatogastric ligament/ hepatoduodenal ligament) -Round ligament of the liver (ligamentum teres hepatis): umbilical vein -Transverse mesocolon (phrenicocolic ligament) abdominal wall -Mesentery (jejunum and ileum from posterior ab wall) -Mesoappendix -Sigmoid mesocolon -Greater peritoneal sac -Lesser peritoneal sac (omental bursa): posterior to stomach/lesser omentum -Inferior recess (lowest part of lesser sac) -Superior recess (highest part of lesser sac) -Omentum foramen (epiploic foramen): connects the sacs Boundaries of Omentum Foramen -Anterior-hepatic portal vein/artery proper/bile duct -Posterior-IVC and right crus -Superior-caudate lobe of liver -Inferior-1st part of duodenum Stomach -Anterior surface -Greater curvature -Lesser curvature -Cardia -Cardial notch -Fundus -Body -Angular incisure (notch) -Pyloric part -Pylorus Liver -Right lobe -Left lobe -Diaphragmatic surface -Inferior border -Visceral surface (contact gallbladder and peritoneum) -Porta hepatis (fissure for vessels, lymphatics and nerves to enter liver) -Gallbladder Celiac trunk -Hepatoduodenal ligament (bile ducts, hepatic artery proper, hepatic portal vein, autonomic nerves and lymphatics) -Cystic duct -Common hepatic duct -Right hepatic duct -Left hepatic duct -Porta hepatis -Left/right hepatic artery -Cystic artery (from right hepatic to gallbladder) -Right gastric artery (from hepatic artery proper to lesser curvature of stomach) -Hepatic lymph nodes -Common hepatic artery -Gastroduodenal artery -Right gastro-omental artery -Anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal artery -Celiac trunk (from aorta at 12th thoracic vertebra) -Common hepatic artery -Left gastric artery -Splenic artery -Short gastric arteries (from splenic artery to fundus of stomach) -Left gastro-omental artery (from splenic) -Right Astro-omental (from gastroduodenal branch of common hepatic) -Hepatic portal vein -Left/right portal veins -Left/right gastric veins Spleen -Visceral surface (stomach, left kidney, transverse colon, pancreas) -Diaphragmatic surface (ribs 9-11) Liver -Right/left lobes -Inferior border (separates visceral from diaphragmatic surfaces) -Bare area -Coronary ligament -Visceral surface (right, left, caudate, and quadrate lobes) -Left fissure (ligamentum venosum/falciform ligament) -Right fissure (gallbladder/ IVC) -Porta hepatis (structures passing the hepatoduodenal ligament) -Anatomical lobes (falciform ligament division) -Functional lobes (bile drainage/vascular supply) -Hepatic lymph nodes -Celiac lymph nodes Gallbladder -Neck -Body -Fundus -Cystic artery -Spiral fold (neck continues into cystic duct) Week 8 Day 3 Abdomen 96-105 -Superior mesenteric artery -Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery -Intestinal arteries (end in vasa rectae) -Arcades (connect intestinal arteries) -Ileocolic artery (to the cecum) -Appendicular artery -Right colic artery (ascending colon) -Middle colic artery (transverse colon) -Superior mesenteric vein -Hepatic portal vein -Mesenteric lymph nodes -Superior mesenteric lymph nodes -Superior mesenteric plexus of nerves Small Intestine -Jejunum -Ileum -duodenojejunal junction -Suspensory ligament of duodenum (right crus to duodenojejunal junction) -Cecum -ileocecal junction -Root of the mesentery -Intestinal attach of mesentery -Inferior mesenteric artery (L2-L3) -Left colic artery (descending colon/ left third of transverse) -Sigmoid arteries (form arcades) -Superior rectal artery (right/left branches) -Inferior mesenteric vein -Splenic vein -Superior mesenteric vein -Inferior mesenteric nodes Large intestine -Cecum (with appendix) -Appendicular artery -Colon -Rectum -Anal canal -Teniae coli -Haustra -Omental appendices (epiploic) Duodenum -Superior (L1) -Descending (L2): bile/pancreatic duct -Horizontal (L3): anterior to IVC -Ascending (L2) Pancreas -Head (uncinate process) -Neck -Body -Tail -Main pancreatic duct -Accessory pancreatic duct (superior to main) -Posterior superior/anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries -Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery -Dorsal pancreatic artery -Greater pancreatic artery -Left gastro-omental artery Hepatic portal vein -Superior mesenteric vein -splenic vein -Hepatic portal vein -Gastroesophageal -Anorectal -Paraumbilical -Retroperitoneal Stomach -Gastric folds (rugae) -Pyloric antrum -Pyloric canal -Pyloric sphincter -Pyloric orifice Duodenum -Circular folds (plicae circulares) -Major/greater duodenal papilla -Minor/lesser duodenal papilla Cecum -Ileocecal orifice -Superior/inferior lips of ileocecal valve -Opening of appendix Transverse colon -Semilunar folds (plicae semilunares) -Haustra Unit 3 Week 9 Pre Quiz 3 Day 1 105-112 Posterior Ab Viscera -Testicular artery and vein -Right and left testicular arteries (aorta at L2) -Ovarian vessels (anterior to ureter) Retroperitoneal space -Kidneys, ureters, suprarenal glands, aorta, IVC, sympathetic trunks Kidneys -Perirenal fat -Renal fascia -Superior pole -Left renal vein (anterior to renal arteries/aorta) -Lest testicular/ovarian vein -Left suprarenal vein -Left renal artery -Renal pelvis -Ureter -Right renal artery -Renal capsule -Renal cortex -Renal medulla -Renal pyramids/renal columns -Renal sinus -Renal papilla -Minor calyx -Major calyx Suprarenal glands -Right suprarenal gland (triangular) -Left suprarenal gland (semilunar) -Superior suprarenal arteries (inferior phrenic) -Middle suprarenal arteries (aorta) -Inferior suprarenal artery (renal) Aorta/IVC -Unpaired arteries to the GI tract (celiac, sm, im) -Paired arteries to 3 paired organs (suprarenal, renal, and gonadal) -Paired arteries to abdominal wall (inferior phrenic and lumbar) -Lumbar artery -Bifurcation of abdominal aorta (L4) -Common iliac arteries (from bifurcation) -IVC Posterior Ab Wall -Psoas major (lumbar vertebrals-lesser trochanter) -Psoas minor (tendon anterior to major) -Iliacus (iliac fossa-lesser trochanter) -Iliopsoas -Quadratus lumborum (12th rib/lumbar transverse processes-iliolumbar ligament/iliac crest) -Transversus abdominis (posterior to quadratus lumborum) Lumbar Plexus -L1-L4 (within psoas major) -Genitofemoral nerve (anterior to psoas major) -Subcostal nerve (inferior to rib 12) -Iliohypogastric/ilioinguinal nerves -Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh (deep to inguinal ligament) -Femoral nerve (deep to inguinal ligament) -Obturator nerve -Lumbosacral trunk (ventral ramus L4-L5) Sympathetic trunk -Lumbar splanchnic nerves -Rami communicantes Diaphragm -Hemidiaphragms -Central tendon -Sternal part (attach xiphoid) -Costal part (attach inferior six ribs) -Lumbar part (formed by 2 crura) -Right crus (L1-L3) -Esophageal hiatus -Left crus (L1-L2) -Arcuate ligaments -Lateral arcuate ligament (anterior quadratus lumborum) -Medial arcuate ligament (anterior psoas major) -Median arcuate ligament (unpaired-anterior of aorta) -Venal caval foramen (T8 at central tendon) -Esophageal hiatus (T10 at right crus) -Aortic hiatus (T12) -Left/right phrenic nerves -Greater splanchnic nerve -Celiac ganglion (largest on aorta) Week 9 Post quiz 3 Day 2 113-124 133-137 Pelvic inlet (superior pelvic aperture) -transition pelvic cavity-abdominal cavity -divides greater (false) pelvis and lesser (true) pelvis Pelvic outlet -Inferior margin of pubic symphysis -Ischiopubic ramus -Ischial tuberosity -Sacrotuberous ligament -Tip of the coccyx Pelvic cavity -Rectum, bladder, internal genitalia Pelvic diaphragm -separates pelvic cavity from perineum Skeleton of Pelvis -Hip bones (os coxae) -Sacrum -Pubis -Ischium Perineum -anal canal, urethra, external genitalia -Ilium -Acetabulum -Coccyx -Iliac fossa -Iliopubic eminence -Arcuate line -Pecten pubis -Superior pubic ramus -Pubic symphysis -Pubic arch -Ischiopubic ramus -Obturator foramen -Ischial tuberosity -Ischial spine -Sacral promontory -Anterior sacral foramina -Sacrotuberous ligament -Sacrospinous ligament -Greater sciatic foramen -Lesser sciatic foramen -Greater/lesser sciatic notches -Greater/lesser sciatic foramina -Anterior sacroiliac ligament -Posterior sacroiliac ligament -Iliolumbar ligament -Subpubic angle -Pelvic brim -Superior margin of pubic symphysis -Posterior border of pubic crest -Anterior border of the ala (wing) of the sacrum Anal triangle -Perineum (diamond) -Anal triangle (posterior) -Urogenital triangle (anterior) -Gluteus maximus -Inferior cluneal nerves -Sacrotuberous ligament Ischioanal fossa (wedged-shaped) -Inferior rectal nerve/vessels -Dorsal nerve of the penis (paired) -Penis (root-bulb/crura, body/shaft, glans, corona, prepuce, frenulum, external urethral orifice) -Superficial external pudendal vein -Prostatic urethra -Membranous urethra -External anal sphincter (subcutaneous, superficial, deep) -Inferior surface of pelvic diaphragm (medial boundary) -Fascia of obturator internus (lateral boundary) -Pudendal canal -Pudendal nerve -Internal pudendal artery/vein Male external genitalia/perineum -Scrotum -Dartos fascia (dartos m) -Scrotal ligament (gubernaculum testis) -Scrotal septum -Coverings of spermatic (external spermaticexternal oblique; cremasteric-internal oblique; internal spermatic-transversalis) -Ductus deferens (vas deferens) -Pampiniform plexus of veins -Artery of ductus deferens -Testicular artery -Tunica vaginalis (visceral/parietal/cavity) -Epididymis (tail/body/head) -Tunica albuginea (fibrous capsule) -Septa/lobules -Posterior prostate scrotal nerve/vessels -Colles’ fascia (membranous layer of superficial perineal) -Dartos fascia -Perineal membrane -Superficial perineal pouch (superficial transverse perineal, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernous, crura of the penis and bulb) -Perineal body -Dorsal surface of the penis -Superficial dorsal vein of the penis -Buck’s fascia (deep fascia of the penis) -Deep dorsal vein of the penis -Prostatic venous plexus -Dorsal artery of the penis (paired) -Spongy urethra -Navicular fossa -Bulbourethral glands -Tunica albuginea of corpora cavernosa -Tunica albuginea of corpus spongiosus -Septum penis -Deep perineal pouch (membranous urethra, external urethral sphincter, bulbourethral glands, branches of internal pudendal, branches of pudendal) -Urogenital diaphragm Female external -Vulva -Mons pubis -Anterior labial commissure -Labium majus -Clitoris (prepuce, glans, frenulum) -Labium minus -Vestibule of vagina (between minora) -External urethral orifice -Vaginal orifice -Openings of paraurethral ducts -Frenulum of labia minora -Posterior labial commissure -Posterior labial nerve/vessels -Colles’ fascia (membranous layer of superficial perineal) -Perineal membrane -Superficial perineal pouch (ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, superficial transverse perineal, crus of clitoris, bulb of vestibule and greater vestibular gland) -Perineal body -Perineal membrane -Commissure of the bulbs -Deep perineal pouch (urethra, vagina, external urethral sphincter, branches of internal pudendal, branches of pudendal) -Urogenital diaphragm Week 10 Pelvis and Perineum 124-133; 137-147 Male Pelvic Cavity (bladder, internal genitalia, rectum) -Peritoneum -Rectovesical pouch -Paravesical fossa -Pararectal fossa Male Internal Genitalia -Perineal membrane (deep to bulb) -External urethral sphincter muscle -Membranous urethra -Prostatic urethra -Spongy urethra -Interior of prostatic urethra: Urethral crest, seminal colliculus, prostatic sinus, prostatic utricle, opening of ejaculatory duct -Ductus deferens -Deep inguinal ring -Rectovesical septum -Ampulla of ductus deferens -Seminal vesicle -Ejaculatory duct -Prostate (apex, base, lobes) Bladder, Rectum, and Anal canal -Endopelvic fascia -Retropubic space (prevesical space) -Puboprostatic ligament -Bladder (apex, body, fundus, base, neck) -Bladder surfaces (superior, posterior, inferolateral) -Internal urethral sphincter -Wall of urinary bladder -Detrusor muscle -Trigone -Internal urethral orifice -Orifices of ureters -Ampulla of the rectum -Anorectal flexure -Transverse rectal folds -Anal canal -Anal columns -Superior rectal artery/vein -Pectinate line -External/internal anal sphincter muscles -Internal hemorrhoids -External hemorrhoids Internal iliac artery/Sacral plexus -Common iliac artery -External/Internal iliac arteries -Umbilical artery -Medial umbilical ligament -Superior vesical arteries -Obturator artery -Aberrant obturator artery -Inferior vesical artery -Middle rectal artery -Internal pudendal artery -Inferior gluteal artery -Iliolumbar artery -Lateral sacral artery -Superior gluteal artery -Prostatic venous plexus -Vesical venous plexus -Rectal venous plexus -Deep dorsal vein of penis Nerves -Sacral plexus -Coccygeal plexus -Inferior hypogastric plexus -Lumbosacral trunk (L4/L5) -Sciatic nerve (L4-S3) -Superior gluteal artery -Ventral ramus of spinal nerve S1 -Inferior gluteal artery -Ventral rami of spinal nerves S2-3 -Pudendal nerve (S2-4) -Pelvic splanchnic nerves (nervi erigentes) -Sacral portion of sympathetic trunk -Ganglion impar -Gray rami communicates -Sacral splanchnic nerves Pelvic Diaphragm -Urogenital hiatus -Anal hiatus -Tendinous arch of levator ani -Levator ani -Puborectalis -Anorectal flexure -Pubococcygeus -Anococcygeal raphe -Iliococcygeus -Coccygeus -Obturator internus -Internal iliac, external iliac, common iliac, sacral and lumbar nodes Female Pelvic Cavity -Adnexa (ovaries, uterine tubes and ligaments of uterus) -Peritoneum -Vesicouterine pouch -Rectouterine pouch (Pouch of Douglas) -Paravesical fossa -Pararectal fossa -Broad ligament of uterus -Uterine tube -Mesosalpinx -Mesovarium -Mesometrium -Parametrium -Round ligament of uterus -Ovarian ligament (in broad lig & connects ovary to uterus) -Suspensory ligament of ovary -Endopelvic fascia (extreperitoneal fasciasupports uterus) -Uterosacral (sacrogenital ligament) -Uterosacral fold -Transverse cervical ligament (cardinal ligament) -Pubocervical (pubovesical) ligament -Pubic symphysis -Sacrum Female Internal genitalis -External urethral orifice -External urethral sphincter -Vagina -Vaginal fornix (anterior, lateral, posterior) -Uterus (fundus, body, isthmus, cervix) -Uterus surfaces: vesical, intestinal -Uterine cavity -Endometrium -Myometrium -Perimetrium -Parametrium -Uterine tube (isthmus, ampulla, infundibulum, fimbriae) -Ovary -Tubal (distal) extremity -Uterine (proximal) extremity -Ovarian fossa (bounded by ureter, external iliac v, uterine tube) -Suspensory ligament of the ovary Internal Iliac artery/Sacral plexus -Uterine artery -Vaginal artery