IRTB - Arterial Access and Angioplasty
advertisement

IRTB - Arterial
Access and
Angioplasty
Dr Hilary White
Nottingham
Outline
Vascular access
Anatomy
Equipment
complications
Angioplasty
Closure
Cases
Patient selection
Warfarin and Clopidogrel should be stopped 1 week before (at least 3 days
before). INR <1.5
Stop Heparin 3 hours before
Aspirin omitted on the day
Metformin – stop 48 hours after procedure
Hypertension >180/110 mmHg
Smoking
Diabetes – check blood sugar
Renal failure – contrast induced nephropathy
CAN THEY LIE FLAT?
Pre-op
What does the request card say?
Intermittent claudication vs critical limb ischaemia
side?
Previous imaging
Check bloods
Consider equipment
Approach
The Kit
The WHO
035 vs 018
Access
Bail out kit – covered stents/ aspiration
catheters/ angiojet – Call For Help
Access
Antegrade vs retrograde
Anatomy
Hostile groin?
Time
Equipment
Experience
Seldinger Technique
The desired vessel or cavity is punctured with a
sharp hollow needle called a trocar, with
ultrasound guidance if necessary. A roundtipped guidewire is then advanced through the
lumen of the trocar, and the trocar is withdrawn.
(introduced in 1953)
Wikipedia
Vascular sheaths
Colour coded – red 4 Fr, grey 5 Fr, Green 6 Fr,
Orange 7 Fr, Blue 8 Fr etc
Different lenghts – standard 11 cm, 23 cm, 45
cm, 60 cm, 90 cm
Some are bright tipped
Different to guide catheters
Heparin
After access
Therapeutic anticoagulation for 30mins with 3000
IU IA, 45 mins with 5000 IU IA
Effect after 10-15 mins
After 1 hour consider additional bolus
For flushing – 1000-5000IU heparin/1 L of normal
saline
Other Drugs
During:
GTN – 100mcg – 200mcg IA – consider in
intervention in the infrapopliteal region
Papaverine 20mg IA – good for pressure
measurements (smooth muscle relaxant –
vasodilatation)
After:
Clopidogrel
Aspirin
Warfarin
Think about the steps
Access
Angiogram
IS THIS A STRAIGHT FORWARD ANGIOGRAM?
Heparin
Closure
Do no harm
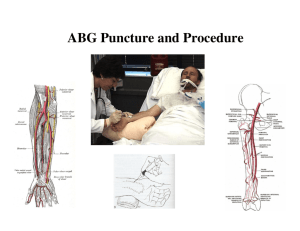
Brachial artery access
Easy to compress if bleeding risk
Easy to find with U/S
Anatomy ie easier to catheterise
mesenteric vessels, close to subclavians
Antegrade approach to radial fistula
Bilateral Femoral occlusions
Previous femoral surgery or on going
infection
Why Not?
Subclavian occlusion
Infection
Easier to reach from femoral
approach
Risk of stroke
Small vessels (particularly women)
Brachial Puncture Technique
Try to always use U/S
Map out anatomy with U/S (beware high take
off radial artery)
Sterile prep
Infiltrate local under U/S guidance
Micro puncture kit helps reduce the trauma
Complications of Brachial Artery
Puncture
Median nerve damage
Haematoma
False Aneurysm
Embolisation to Fingers
Dissection (with lower arm ischemia)
Stroke (especially posterior circulation)
Arterial Access Alternatives
Radial Artery (useful for fistulas and coronary
angios)
Axiliary Artery (risk of brachial plexus injury but
good calibre vessel)
Direct Carotid Puncture
Direct Aortic Puncture (historical)
Popliteal artery
Dorsalis pedis
Closure
Vascular closure devices:
Angio-Seal (St Jude Medical)
StarClose (Abbott)
Perclose/{erclose Proglide (Abbott)
Mynx (AccessClosure)
Exo-Seal (Cordis)
Complication rate 2 %
- incorrect deployment,
infection, stenosis, embolus,
local dissection.
Complications
(most common)
Dissection
Haematoma
False Aneurysm (Femoral or Inferior Epigastric)
Retroperitoneal Haemorrhage (patients can die
from this)
Infection
Questions?