Veins
advertisement

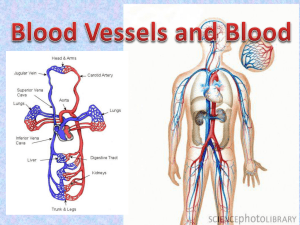
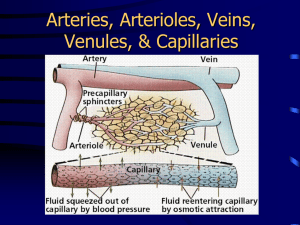
20 PART 1 Blood Vessels Types of Blood Vessels • Three major types of blood vessels are • Arteries • Capillaries • Veins • Arteries—carry blood away from the heart • Arterioles—the smallest arteries • Capillaries—the smallest blood vessels • Venules—receive blood from capillaries • Veins—receive blood from venules Structure of Blood Vessels • Composed of three layers (tunics) • Tunica intima • Innermost tunic • Contains the endothelium • Simple squamous epithelium • Vessels than 1 mm also have a subendothelial layer Structure of Blood Vessels • Composed of three layers (tunics) • Tunica media—sheets of smooth muscle • Contraction—vasoconstriction • Relaxation—vasodilation • Tunica externa • Composed of connective tissue • Lumen • Central blood-filled space of a vessel Types of Arteries • Elastic arteries—the largest arteries • Diameters range from 2.5 cm to 1 cm • Includes the aorta and its major branches • Sometimes called conducting arteries • High elastin content dampens surge of blood pressure Types of Arteries • Muscular (distributing) arteries • Lie distal to elastic arteries • Diameters range from 1 cm to 0.3 mm • Includes most named arteries • Tunica media is thick • Unique features • Internal and external elastic laminae Types of Arteries • Arterioles • Smallest arteries • Diameters range from 0.3 mm to 10 µm • Larger arterioles possess all three tunics • Diameter of arterioles controlled by • Local factors in the tissues • Sympathetic nervous system Capillaries • Smallest blood vessels • Diameter from 8 to 10 µm • Red blood cells pass through single file • Site-specific functions of capillaries • Lungs—oxygen enters blood, carbon dioxide leaves • Small intestines—receive digested nutrients • Endocrine glands—pick up hormones • Kidneys—remove of nitrogenous wastes Continuous Capillaries • Most common type of capillary • Occur in most organs • Tight junctions and desmosomes join epithelial cells • Intercellular clefts • Gaps of unjoined membranes • Allow small molecules in and out of capillaries Fenestrated Capillaries • Joined by tight junctions and desmosomes • Have pores in their endothelium • Occur where high rates of exchange occur • Intestines • Glomeruli of kidneys • Endocrine glands Sinusoids • Wide, leaky capillaries found in some organs • Usually fenestrated • Intercellular clefts are wide open • Occur in bone marrow and spleen • Sinusoids have a large diameter and twisted course Capillary Permeability • • • • • Four routes into and out of capillaries Direct diffusion Through intercellular clefts Through cytoplasmic vesicles Through fenestrations Low-Permeability Capillaries • Blood brain barrier • Capillaries have complete tight junctions • No intercellular clefts are present • Vital molecules pass through • Highly selective transport mechanisms • Not a barrier against: • Oxygen, carbon dioxide, and some anesthetics Capillary Beds • Network of capillaries running through tissues • Precapillary sphincters • Regulate the flow of blood to tissues • Tendons and ligaments—poorly vascularized • Epithelia and cartilage—avascular • Receive nutrients from nearby connective tissue Venous Vessels • Conduct blood from capillaries toward the heart • Blood pressure is much lower than in arteries • Venules are the smallest veins • Diameters from 8 to 100 m • Smallest venules—called postcapillary venules • Venules join to form veins Veins • Structural differences from arteries Lumens are larger • 65% of blood in veins at any given time • Tunica externa is thicker • Less elastin in walls • Walls are thinner than those of comparable arteries • Mechanisms to Counteract Low Venous Pressure • Valves in some veins • Particularly in limbs • Prevent backflow of blood • Not located in veins of thoracic and abdominal cavities • Skeletal muscle pump • Muscles press against thin-walled veins Vascular Anastomoses • Vessels interconnect to form vascular anastomoses • Organs receive blood from more than one arterial source • Neighboring arteries form arterial anastomoses • Provide collateral channels • Veins anastomose more frequently than arteries Pulmonary Circulation • Pulmonary trunk • Leaves the right ventricle • Divides into right and left pulmonary arteries • Superior and inferior pulmonary veins • Carry oxygenated blood into the left atrium • Vessels of pulmonary circuit • Thinner walls than systemic vessels • Maximum arterial pressure lower in pulmonary circuit Systemic Circulation • Systemic arteries • Carry oxygenated blood away from the heart • Aorta—largest artery in the body The Aorta • Ascending aorta—arises from the left ventricle • Branches—coronary arteries • Aortic arch—lies posterior to the manubrium • Branches • Brachiocephalic trunk • Left common carotid • Left subclavian arteries The Aorta • Descending aorta—continues from the aortic arch • Thoracic aorta—in the region of T5–T12 • Abdominal aorta—ends at L4 • Divides into right and left common iliac arteries 20 PART 2 Blood Vessels Arteries of the Head and Neck • Pairs of arteries supplying head and neck • Carotid arteries • Branches of subclavian arteries • Vertebral arteries • Thyrocervical trunk • Costocervical trunk Common Carotid Arteries • Located in the anterior triangle of the neck • Two branches of the common carotid artery • External carotid artery • Internal carotid artery Common Carotid Arteries • External carotid artery branches • Superior thyroid artery • Lingual artery • Facial artery • Occipital artery • Posterior auricular artery • Superficial temporal artery • Maxillary artery Common Carotid Arteries • Internal carotid artery branches • Ophthalmic artery • Anterior cerebral artery • Anterior communicating artery • Forms part of the cerebral arterial circle • Middle cerebral artery Subclavian Arteries • Right subclavian artery • Originates from brachiocephalic trunk • Left subclavian artery • Arises as third branch from the aortic arch Vertebral Arteries • Vertebral arteries • Supply posterior brain • Join to form the basilar artery • Basilar artery • Divides into two posterior cerebral arteries • Posterior communicating arteries • Connect posterior cerebral arteries to middle cerebral arteries Thyrocervical and Costocervical Trunks • Thyrocervical trunk • Sends two branches posteriorly over scapulae • Sends one branch anteriorly to the inferior part of the thyroid gland • Costocervical trunk • • Sends a branch superiorly to deep muscles of the neck Sends a branch inferiorly to intercostal spaces Arteries of the Thorax • Internal thoracic arteries • Supply anterior thoracic walls • Anterior intercostal arteries • Branches of internal thoracic arteries • Posterior intercostal arteries • Inferior nine pairs arise from thoracic aorta Arteries of the Upper Limb • Subclavian artery • Enters the axilla as the axillary artery • Axillary artery becomes the brachial artery at the inferior border of teres major • Brachial artery divides into • Radial artery and ulnar artery Arteries of the Abdominal Aorta • Inferior phrenic arteries • Celiac trunk • Superior mesenteric artery • Suprarenal arteries • Renal arteries • Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) arteries • Inferior mesenteric artery • Common iliac arteries 20 PART 3 Blood Vessels Arteries of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs • Internal iliac arteries • External iliac artery • Femoral artery • Popliteal artery • Anterior tibial artery • Posterior tibial artery Systemic Veins • Three major veins enter the right atrium • All medium and large arteries have deep locations accompanied by deep veins • Superficial veins lie just beneath the skin • Multivein bundles—venous plexuses • Unusual patterns of venous drainage • Dural sinuses • Hepatic portal system Venae Cavae and Tributaries • Superior vena cava • Returns blood from body regions superior to the diaphragm • Inferior vena cava • Returns blood from body regions inferior to the diaphragm • Superior and inferior vena cava • Join the right atrium 20 PART 4 Blood Vessels Veins of the Head and Neck • Dural sinuses • Superior and inferior sagittal sinuses • Straight sinus • Transverse sinuses • Sigmoid sinus Veins of the Head and Neck • Internal jugular veins • Drain blood from brain • Superiorly it lies lateral to the internal carotid artery • Inferiorly it lies lateral to the common carotid artery • External jugular veins • Tributaries drain scalp • Empty into subclavian vein Veins of the Thorax • Azygos vein • Hemiazygos vein • Accessory hemiazygos vein Veins of the Upper Limbs • Deep veins • Follow the paths of companion arteries • Have the same names as the companion arteries • Superficial veins • Visible beneath the skin • Cephalic vein • Basilic vein • Median cubital vein • Median vein of the forearm Superficial Veins • • Form anastomese frequently Median cubital vein is used to obtain blood or administer IV fluids Veins of the Abdomen • Lumbar veins • Gonadal (testicular or ovarian) veins • Renal veins • Suprarenal veins • Hepatic veins The Hepatic Portal System • A specialized part of the vascular circuit • Picks up digested nutrients • Delivers nutrients to the liver for processing • Two capillary beds • First capillary bed in stomach and intestines • Second capillary bed is in liver sinusoids The Hepatic Portal System • Tributary veins of the hepatic portal vein • Superior mesenteric vein • Splenic vein • Inferior mesenteric vein 20 PART 5 Blood Vessels Portal Systemic Anastomoses • Scarring and degeneration of liver • Leads to blockage of liver sinusoids • Raises blood pressure in hepatic portal system and leads to portal hypertension • Portal hypertension leads to emergency anastomoses for portal blood • Veins of inferior esophagus, hemorrhoidal veins, veins of superficial abdominal wall Veins of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs • Deep veins • Share the name of the accompanying artery • Superficial veins • Great saphenous vein empties into the femoral vein • Small saphenous vein empties into the popliteal vein Disorders of the Blood Vessels • Aneurysm • Deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb • Venous disease • • Microangiopathy of diabetes Arteriovenous malformation Blood Vessels Throughout Life • Fetal circulation • All major vessels in place by month 3 of development • Differences between fetal and postnatal circulation • Fetus must supply blood to the placenta • Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Vessels to and from the Placenta • Umbilical vessels run in the umbilical cord • Paired umbilical arteries • Unpaired umbilical vein • Fetal vessels and structures • Ductus venosus • Ligamentum teres • Ligamentum venosum • Medial umbilical ligaments Shunts Away from the Pulmonary Circuit • Foramen ovale • Ductus arteriosus Blood Vessels in Adulthood • Atherosclerosis begins in youth • Consequences evident in middle to old age • Males • Between ages 45 and 65, more males than females experience atherosclerosis • Experience heart disease and atherosclerosis later in life