Arteries, Arterioles, Veins, Venules, & Capillaries
advertisement
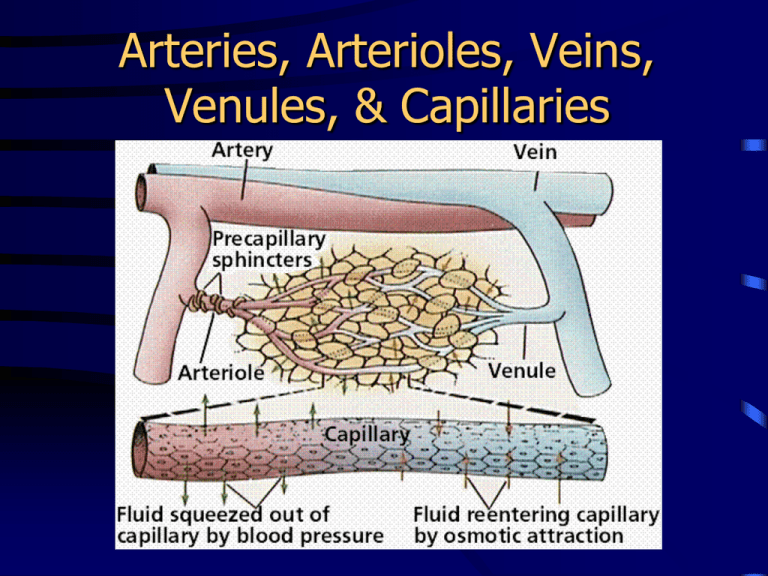
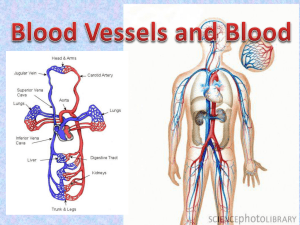
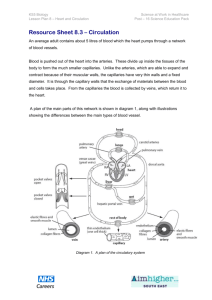
Arteries, Arterioles, Veins, Venules, & Capillaries Arteries • Large hose-like vessels • Carry blood away from the heart. • Have thick, multilayered muscular walls. • Walls are capable of stretching to accommodate the “pulse” of blood when the heart beats. Arteries • Capable of expanding and contracting to change and maintain the blood pressure. • NO valves • Blood spurts • Blood inside them is high in oxygen & low in carbon dioxide except in pulmonary artery. Arteries • Blood inside is bright red • Blood inside is under High pressure • Examples: Coronary (heart), Brachial (arms), Carotid (head), Femoral (legs), Renal (kidney). Arterioles • Tiny branches off of the arteries. • Cannot be seen with unaided eye microscopic • Thinner, less muscular walls (compared to arteries) • Feed blood into the capillaries. • Narrower than arteries, but wider than capillaries. Capillaries • Flow and pressure of blood is controlled by sphincters that are outside of the capillaries. • Microscopic vessels ~ 8 µm in diameter. • Erythrocytes (rbc’s) pass through in single file. • Walls are only one cell thick (to facilitate diffusion of materials/exchange). Capillaries • Thinness allows for easy diffusion outward or inward through the single cell layer. • Form capillary beds networks of vessels linking arterial and venous blood. Capillaries • Oxygen , nutrients and other materials move out of the capillaries and into the extracellular fluid and then into cells. • Carbon dioxide, wastes and other materials are picked up and move into the capillaries: (both involve diffusion for the movement). Venules • Vessels larger than capillaries but smaller (i.e. narrower and thinner walls) than veins. Veins • Larger inside diameter compared to arteries • Take blood towards the heart • Thinner, less muscular walls than arteries, but still 3 layers • No stretching or contracting of walls except by external muscles. • Contain valves to help return the blood to the heart (compensate for lower venous pressure, less muscle in walls, and large diameter). Veins - Valves Veins • • • • • Blood: Moves smoothly. Low in oxygen except pulmonary circulation. Dull red. Low pressure. Examples: cardiac (heart), brachial (arms), jugular (head), femoral (legs), renal (kidney). Varicose Veins (copy this) • When the valves don’t function properly, blood leaks backwards and pools in veins • Veins sag, stretch and swell, creating bulging knarled vessels The END!!