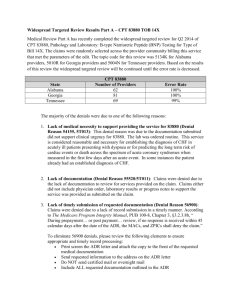
EXERCISE SHEET: Evidence table: The data below were extracted
advertisement
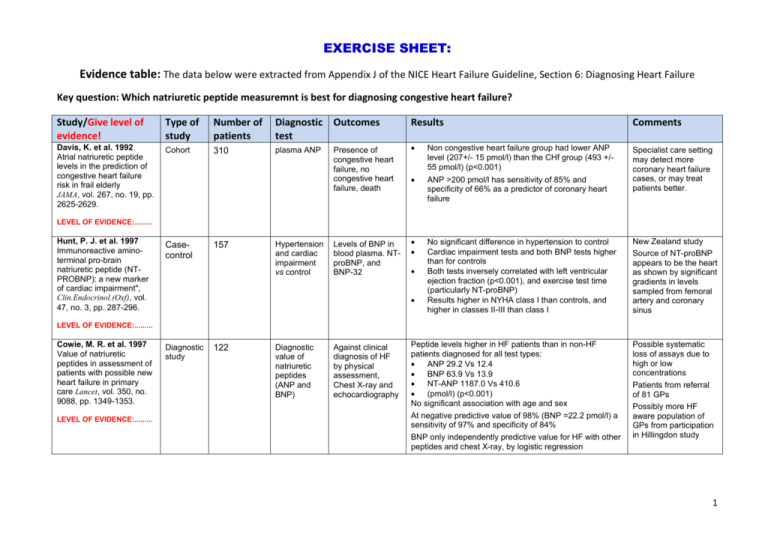
EXERCISE SHEET: Evidence table: The data below were extracted from Appendix J of the NICE Heart Failure Guideline, Section 6: Diagnosing Heart Failure Key question: Which natriuretic peptide measuremnt is best for diagnosing congestive heart failure? Study/Give level of evidence! Type of study Number of patients Diagnostic Outcomes test Davis, K. et al. 1992 Atrial natriuretic peptide levels in the prediction of congestive heart failure risk in frail elderly JAMA, vol. 267, no. 19, pp. 2625-2629. Cohort 310 plasma ANP Presence of congestive heart failure, no congestive heart failure, death Results Non congestive heart failure group had lower ANP level (207+/- 15 pmol/l) than the CHf group (493 +/55 pmol/l) (p<0.001) ANP >200 pmol/l has sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 66% as a predictor of coronary heart failure No significant difference in hypertension to control Cardiac impairment tests and both BNP tests higher than for controls Both tests inversely correlated with left ventricular ejection fraction (p<0.001), and exercise test time (particularly NT-proBNP) Results higher in NYHA class I than controls, and higher in classes II-III than class I Comments Specialist care setting may detect more coronary heart failure cases, or may treat patients better. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Hunt, P. J. et al. 1997 Immunoreactive aminoterminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NTPROBNP): a new marker of cardiac impairment", Clin.Endocrinol.(Oxf), vol. 47, no. 3, pp. 287-296. Casecontrol 157 Hypertension and cardiac impairment vs control Levels of BNP in blood plasma. NTproBNP, and BNP-32 New Zealand study Source of NT-proBNP appears to be the heart as shown by significant gradients in levels sampled from femoral artery and coronary sinus LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Cowie, M. R. et al. 1997 Value of natriuretic peptides in assessment of patients with possible new heart failure in primary care Lancet, vol. 350, no. 9088, pp. 1349-1353. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Diagnostic study 122 Diagnostic value of natriuretic peptides (ANP and BNP) Against clinical diagnosis of HF by physical assessment, Chest X-ray and echocardiography Peptide levels higher in HF patients than in non-HF patients diagnosed for all test types: ANP 29.2 Vs 12.4 BNP 63.9 Vs 13.9 NT-ANP 1187.0 Vs 410.6 (pmol/l) (p<0.001) No significant association with age and sex At negative predictive value of 98% (BNP =22.2 pmol/l) a sensitivity of 97% and specificity of 84% BNP only independently predictive value for HF with other peptides and chest X-ray, by logistic regression Possible systematic loss of assays due to high or low concentrations Patients from referral of 81 GPs Possibly more HF aware population of GPs from participation in Hillingdon study 1 Study/Give level of evidence! Type of study Number of patients Diagnostic test Outcomes Results Comments Maisel, A. S. et al. 2002 Rapid measurement of Btype natriuretic peptide in the emergency diagnosis of heart failure. New England Journal of Medicine., vol. 347, no.3, pp. 161-167. Diagnostic study n=1586 Age =64yrs, Male: 56%, History of HF: 33%, MI: 27%, COPD: 41%, DM: 25% USA, France, Norway Multinational trial to assess the utility of BNP in diagnosis of CHF in patients with dyspnoea. Reference standard: clinical assessment of HF cause by two independent cardiologists (agreement not stated) using patient records, chest Xray and cardiac function test results. Ref. std. measured in all patients regardless of the test result All patients were classified as to whether dyspnoea due to HF or otherwise blind to test result, other tests of cardiac function such as echocardiogram were strongly encouraged but not undertaken in all patients. Multivariate analysis of diagnostic use of natriuretic assay using historical, clinical , and roentgenographic parameters in a stepwise logistic regression using factors that had a significance at p=0.05 in bivariate analysis. This test may be useful if echocardiography is difficult or where there is a co-existing condition such as obesity or lung disease 147 Diagnostic value of natriuretic peptides (ANF and BNP) LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Selvais, P. L. et al. 1998 Cardiac natriuretic peptides for diagnosis and risk stratification in heart failure: influences of left ventricular dysfunction and coronary artery disease on cardiac hormonal activation. Eur J Clin Invest, vol. 28, no. 8, pp. 636-642. Diagnostic study BNP Test: fluorescence immunoassay kit. Against Left ventricular ejection fraction by echocard. and NYHA class Final diagnosis was of HF in 774 patients (47%), non cardiac causes inpatients with history of LV dysfunction 72 patients (5%) , and no finding of HF in 770 patients (49%). In 97% of patients with HF the final diagnosis was confirmed by the use of other tests Patients with final diagnosis of HF had a natriuretic peptide level of 675 pg/ml, those without HF had a level of 110 pg/ml, and those who had baseline LV dysfunction and had Dyspnoea without an exacerbation of HF had a peptide level of 346 pg/ml. The difference between each of these groups was significant at p<0.001for each comparison A B-type natriuretuc cut-off value of 100 pg/ml had a sensitivity of 90% a sensitivity of 76% and an accuracy of 83% fro differentiating congestive HF from other causes of dyspnoea B-type natriueretic values varied significantly with patient NYHA class as determined by cardiologists, with the level in class I averaging 144 pg/ml, in class II it was 389 pg/ml. In class III the reading was 640 pg/ml, and in class IV the level was 817 pg/ml (p<0.0010 for comparison of groups In a multiple logistic regression analysis the addition of B=type natriuretic peptide added to the combined explanatory power of history, symptoms, signs, radiological studies, and laboratory findings. A value of 100pg/ml or higher was the strongest independent predictor of congestive HF with an OR 29.60 (95% CI 17.75 to 49.37) Significant correlation of the three peptide measures and left ventricular dysfunction BNP r=-0.59 N-proANF r=-0.53 ANF r=-0.30 (p<0.001) BNP performed better than others at grading severity of congestive heart failure (p<0.05) Larger proportion of women in control group. Used NYHA class rather than ejection fraction for receiveroperating analysis. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... 2 Study/Give level of evidence! Type of study Number of patients Diagnostic Outcomes test Yamamoto, K. et al. 1996 Superiority of brain natriuretic peptide as a hormonal marker of ventricular systolic and diastolic dysfunction and ventricular hypertrophy.", Hypertension, vol. 28, no. Diagnostic study 94 Diagnostic ability of BNP, CANP, and NANP 6, pp. 988-994 Against Left ventricular ejection fraction and mass by echocardiography, and end diastolic pressure , and time constant of left ventricular relaxation by catheterisation Results Comments For each physiological variable BNP showed the strongest correlation (ejection fraction, left ventricular mass, relaxation time) and was significantly better than C-ANP or N-ANP, no significant difference in Left ventricular end diastolic pressure Sensitivity 73% and specificity 83% to detect any abnormality of left ventricular structure or function at BNP= 14.7 pmol/l Significant structural and functional abnormalities in patients without clinical evidence of heart failure All test interpreted blind Minnesota study. Age: 62 yrs, 57% male. Used control patients to define baseline peptide levels and the elevated level set at this plus 3 SD. 42% of patients presenting with dyspnoea had HF as their final diagnosis, and 26% had a final diagnosis of pulmonary disease Of the patients with the final diagnosis of HF the mean BNP level was 759 pg/ml compared to 61 pg/ml in the pulmonary patients (p<0.001) BNP level of 94 pg/ml had a sensitivity of 86%, a specificity of 98%, and an accuracy of 91% The best clinical predictors of final diagnosis for dyspnoea were history of HF, and heart size and venous hypertension on chest X-ray The addition of BNP levels to the multivariate regression substantially increased the explanatory power of the model and was a significant independent variable (p<0.001) All tests were conducted on all patients, with two independent cardiologists determining whether dyspnoea was relating to HF (according to Framingham criteria), or to other conditions. The coefficient of variation at 28.8ng/l is 9.5% for intra-assay precision and 10% for inter-assay precision. The lowest conc. of BNP distinguishable is <5.0 ng/l. Patients who are on dialysis or have endstage renal failure may have elevated BNP levels and would need standard diagnostic criteria to be assessed. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Morrison, L. K. 1996 Utility of a rapid Bnatriuretic peptide assay in differentiating congestive heart failure from lung disease in patients presenting with dyspnea", Journal of the American College of Cardiology., vol. 39, no. 2, pp. 202-209 LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Diagnostic study 321 USA Test compared with duplicated cardiologist defined evaluation as to whether the patients presented with HF or other causes of dyspnoea A multivariate model was used to assess the additive predictive value of BNP over clinical findings 3 Extract the data from the two papers appraised in the previous small group session! Study/Give level of evidence! Type of study Number of patients Diagnostic Outcomes test Results Comments Landray et al. 2000. Measuring brain natriuretic peptide in suspected left ventricular systolic dysfunction in general practice: cross-sectional study. BMJ 320:985–6. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Smith et al. 2000 Biochemical diagnosis of ventricular dysfunction in elderly patients in general practice: observational study. BMJ 320:906–8. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE:......... Summarize conclusions: 4