5th Grade Health Curriculum
advertisement

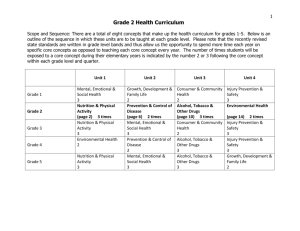
1 Grade 5 Health Curriculum Scope and Sequence: There are a total of eight concepts that make up the health curriculum for grades 1-5. Below is an outline of the sequence in which these units are to be taught at each grade level. Please note that the recently revised state standards are written in grade level bands and thus allow us the opportunity to spend more time each year on specific core concepts as opposed to teaching each core concept every year. The number of times students will be exposed to a core concept during their elementary years is indicated by the number 2 or 3 following the core concept within each grade level and quarter. Unit 1 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Mental, Emotional & Social Health 3 Nutrition & Physical Activity 3 Nutrition & Physical Activity 3 Environmental Health 2 Nutrition & Physical Activity (page 2) 3 times Unit 2 Unit 3 Growth, Development & Family Life 2 Prevention & Control of Disease 2 Mental, Emotional & Social Health 3 Prevention & Control of Disease 2 Mental, Emotional & Social Health (page 6) 3 times Consumer & Community Health 2 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 3 Consumer & Community Health 2 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 3 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs (page 10) 3 times Unit 4 Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Environmental Health 2 Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Growth, Development & Family Life (page 14) 2 times 2 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Nutrition and Physical Activity Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Balance 5 Benefits of Physical Activity Health Food Decisions To be ready to learn and to achieve their fullest potential, children need to be well nourished and physically active. In order to enhance physical, mental, emotional, and social health, students need to acquire the knowledge and skills to make healthy food choices and engage in lifelong physical activity. Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Unit Topic: Nutrition and Physical Activity Nutritional Facts Goal Setting/ Accessing Information Calories Nutrients Ingredients Aerobic Anaerobic Lifelong Short-term Long-term Fad 3 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Balance Enduring Understandings 1. The use of dietary guidelines when making choices can affect long term wellness. 2. Goal setting can enhance proper nutrition and physical activity. Guiding Questions a. What are some examples of serving sizes? Meat=deck of cards, large apple=2 servings, etc b. What is whole food? What is the difference between whole food and processed food? Give some examples of each. c. What type of food has more nutritional value? a. What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic exercise? b. What exercise burns more calories baseball or basketball, soccer or tennis, golf or dance? c. What are some of the long term risks associated with unhealthy eating? d. What are some of the short term risks associated with unhealthy eating? 4 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Balance Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. The relationship between calories, energy and nutrients. (1.1.1) 2. How portions and serving sizes are related to caloric need and nutritional values. 3. How to compare serving sizes, % daily value and ingredients using nutrition fact labels. 4. Techniques for safe food preparation, serving and storage. 5. Options for healthy food preparation (fry v. bake, trim fat, moderating sugar, fat salt, etc.). (1.1.1) 6. How family, culture, media and peers influence food choices. 7. The difference between a fad diet and a balanced diet. 8. Benefits of healthy eating and risks associated with unhealthy eating (short-term and long-term benefits and risks). 9. The importance of having a positive body image. 10. Body systems are strengthened by proper nutrition and physical activity. (1.1.6) 11. The importance of goal setting as it pertains to proper nutrition and physical activity. (1.1.1) AC Q – Quizzes P - Prompts O – Observations WS – Work Samples D – Dialogues SA – Student Self-Assessment T - Tests Students will be able to… AC Analyzing Influences 1. Describe how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.1 2. Identify the influences of culture on health practices and behaviors. 2.1.2 3. Identify how peers can influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors. 2.1.3 Accessing Information 4. Identify characteristics of valid health information, products, and services. 3.1.1 Decision Making 5. Identify health-related situations that might require a thoughtful decision. 5.1.1 6. List healthy options to health related issues or problems. 5.1.3 7. Predict the potential outcomes of each option when making a health-related decision. 5.1.4 8. Describe the outcomes of a health related decision. 5.1.6 Goal Setting 9. Set a personal health goal and track progress toward its achievement. 6.1.1 5 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Balance Instructional Plan/Suggested Activities (Correlations) Keep a physical activity and food log for 3 days. The log will have the calories of the food and the exercise will have how many calories were burned each day. This information should be on-hand so the student can look up the information during class if necessary. Some of these will be shared in class. Tell students to use the student page to interview a family member in the Health Teacher resource. After the interview, students should complete the remainder of the handout, and discuss and share the interviews. Have the students write down how they can improve the family member’s health. 1,2,3 1,2,3 4-9 1,2,3 6,7,8,11 1-9 6 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Mental, Emotional & Social Health Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Management Mental, emotional and social wellbeing is a foundation for building good health which includes a sense of security, identity, belonging, purpose and competence in order to strive toward a healthy and productive life. 5 Resources Stress Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Unit Topic: Mental, Emotional and Social Health Balance Stress Distress Eustress Balance Self-esteem Resource 7 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Mental, Emotional & Social Lens: Management Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions 1. A balance of social, emotional and physical health promotes wellness. a. What is balance? b. How can you balance your overall health? 2. Properly managing stress and expressing emotions can benefit overall health. a. What is the difference between positive and negative stress (distress and eustress)? b. What are some potential benefits and disadvantages of stress? c. What are some proper ways to express your emotions? d. Why is it important to manage stress and emotions? 3. Bullying is a type of violence that cannot be tolerated but is too often overlooked. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. How can you tell what someone else is feeling? What are the “triggers” that cause angry feelings? What do bullies want? What is a victim? How can a bystander help a victim? What are the steps to solve a problem? What can you do to help stop bullying? 8 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Mental, Emotional & Social Lens: Management Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. How stress affects social and emotional health. (1.1.1) 2. How sleep can affect your overall health. (1.1.1) 3. The importance of self-esteem. 4. Why it is important to know their individual strengths and weakness. 5. The importance of maintaining healthy relationships. 6. Available resources in the area of mental, emotional and social health (school counselor, teacher, principal, trusted adult, counselors within the community, physicians, etc.) (1.1.3, 1.1.5) 7. Importance of applying effective communication skills. 8. Empathy is the act of understanding how someone else may feel. 9. Feeling angry is normal. 10. A bully is someone who wants power over another person. 11. A victim is someone who is a target of the bully. 12. A bystander is someone who is not a bully or a victim. 13. There are many ways to solve problems. AC Q – Quizzes P - Prompts O – Observations WS – Work Samples D – Dialogues SA – Student Self-Assessment T - Tests Students will be able to… AC Analyzing Influences 1. Describe how the school and community can support personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.4 Interpersonal Communication 2. Demonstrate effective verbal and nonverbal communication skills to enhance health. 4.1.1 3. Demonstrate how to ask for assistance to enhance personal health. 4.1.4 4. Demonstrate refusal skills that avoid or reduce health risks. 4.1.2 5. Demonstrate nonviolent strategies to manage or resolve conflict. 4.1.3 Goal Setting 6. Identify resources to assist in achieving a personal health goal. 6.1.2 9 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Mental, Emotional & Social Lens: Management Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Lead up activity to Stress: give students a pretend pop quiz. Follow up with a discussion about how that activity made them feel both physically and emotionally. 2. Have students find related resources within their community using books, phonebooks, internet, people, etc. 3. Students create a family or individual crest/coat of arms that shows their identity and strengths. 4. Students create a poster or pamphlet to highlight refusal skills and nonviolent strategies to manage and resolve conflict. 2 1,2 N/A N/A 6 1,3,6 N/A 3,4 N/A 3 8-13 3-5 10 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Advocacy 5 Background Information Decision Making Goal Setting / Advocacy The use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs has major implications in the lifelong health of individuals. Implications include the effects, influences, prevention and treatment of the use of alcohol, tobacco products, and other types of drugs on the body. Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Refusal Skills Advocacy Treatment Short term and Long term Effects Overdose Withdrawal Unit Topic: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Treatment / Prevention Influences 11 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Lens: Advocacy Enduring Understandings 1. Advocacy leads to effective use of refusal skills lowering the risk of substance abuse. Guiding Questions a. What are different ways to say no to drugs? b. Why are refusal skills important? Why should you practice using them? c. How can you be an advocate in your school, home and community? 2. Personal responsibility, goal setting and influences can impact a. Why do we need to take responsibility for our own choices? healthy choices. b. Why is goal setting important? How can it help you say no to substance abuse? c. How can your peers and family influence your choices? 12 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Lens: Advocacy AC = Assessment Code: Critical Content and Skills Students will Know… 1. Different types of illegal drugs. 2. Short and long term effects of drug use. (1.1.1, 1.1.6) 3. Steps of decision making. 4. The role drug abuse can play in a person’s life and the lives of their family and friends. 5. Types of help/community resources available for treatment for substance abuse. (1.1.5) 6. How to use refusal skills to avoid substance abuse. 7. How family, peers, school and community can influence positive choices. (1.1.3) 8. The steps of goal setting. 9. The importance of goal setting to reduce substance abuse. 10. The four steps of Advocacy a. Choose a healthful action to communicate b. Collect information about the action c. Decide how to communicate the information d. Communicate your message to others AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests Students will be able to… P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment Accessing Information 1. Locate resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information. 3.1.2 Interpersonal Communication 2. Demonstrate refusal skills that avoid or reduce health risks. 4.1.2 Decision making 3. Describe the outcomes of a health related decisions. 5.1.6 Advocacy 4. Express opinions and give accurate information about health issues. 8.1.1 5. Encourage others to make positive health choices. 8.1.2 AC 13 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Lens: Advocacy Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Students create advocacy posters, public service announcements or pamphlets. 2. Role-play using skits or commercials. 3. Read and discuss the “Forever Secret” (Here’s Looking at You) 1 4-10 1-5 1,2 1-10 1-5 1,2 4,7 1,3,4,5 14 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Growth, Development and Family Life Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Changes 5 Social Changes Families A healthy family unit is vital to the wellbeing and successful development of children and youth. Growth and development includes the stages of life, and changes in relationships with others that accompany social development and the aging process. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective, and developmentally appropriate. Suggested Time: 9 Weeks Vocabulary Puberty Stages Relationships Aging Process Adoption Divorce Foster Care Life Cycle Unit Topic: Growth, Development & Family Life Physical and Emotional Changes Relationships 15 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Growth, Development & Family Life Lens: Changes Enduring Understandings 1. Physical, emotional and social health changes occur as individuals progress through the different stages of life. 2. Effective communication can enhance relationships with family, friends and others. Guiding Questions a. What are the stages of life? b. What changes occur as we age? a. Do you communicate the same way with your friends and family? b. What is effective communication? c. What is the difference between verbal and nonverbal communication? 16 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Growth, Development & Family Life Lens: Changes Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. The Life Cycle consists of stages from birth to death. 2. Signs of physical, emotional, and social changes related to puberty and aging. (1.1.2) 3. Habits for healthy growth and aging. 4. Ways to communicate respect for self, family and others. 5. Changes in families affect everyone. Nurses Presentation in the regular classroom (parent permission required) 6. Physical changes as it relates to puberty. AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment Students will be able to… Analyzing Influences 1. Describe how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.1 2. Describe how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.4 Practice Health Behaviors 3. Identify responsible personal health behaviors.7.1.1 AC 17 Grade: 5 Subject: Health Unit: Growth, Development & Family Life Lens: Changes Suggested Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Conduct interviews with family regarding family health history. 2. Create a timeline of your family history to show the aging process. 3. Nurse shows growth and development video 1,2 1,2 1 1,3 1,2,3 1,2,6 1,2 1,2 2 18 IDAHO CONTENT STANDARDS HEALTH EDUCATION Grades 3-5 Standard 1: Comprehend Core Concepts Core Concepts of Health Education for Grades 3-5 are defined below: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs The use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs has major implications in the lifelong health of individuals. Implications include the effects, influences, prevention and treatment of the use of alcohol, tobacco products, and other types of drugs on the body. Nutrition & Physical Activity To be ready to learn and to achieve their fullest potential, children need to be well nourished and physically active. In order to enhance physical, mental, emotional, and social health, students need to acquire the knowledge and skills to make healthy food choices and engage in lifelong physical activity. Injury Prevention & Safety Unintentional and intentional injuries rank among the greatest threats to the health of children and young adults. Knowledge of prevention through safe living habits, healthy decisions, violence prevention, emergency response and an awareness of the consequences of ones decisions, will help to prevent many injuries. Mental, Emotional & Social Health Mental, emotional and social wellbeing is a foundation for building good health which includes a sense of security, identity, belonging, purpose and competence in order to strive toward a healthy and productive life. Prevention & Control of Disease Individuals can have a considerable measure of control over their own health, including the risks of contracting most illnesses. Health-related choices and decisions regarding prevention of communicable and non-communicable diseases can include recognizing risk factors, identifying methods of contraction and transmission, as well as the prevention and treatment of disease including HIV. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective and developmentally appropriate. 19 Consumer & Community Health Consumers need to understand how health care services are provided and how individuals can take an active role in determining the use of health related services and products. Community health includes providing valid and appropriate health information, education, services, and products. Growth, Development & Family Life A healthy family unit is vital to the well-being and successful development of children and youth. Growth and development includes the stages of life, changes that occur during puberty, and changes in relationships with others that accompany social development and the aging process. Family living includes healthy relationships, information regarding growth and development, and disease including HIV and their prevention. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective and developmentally appropriate. *Reference to Idaho Education Code Title 33, Chapter 16, Sections 1608-1611 Environmental Health Individuals need to be aware of the impact of environmental issues and hazards on personal health. Environmental health may include precautions and behaviors to safeguard personal health, and practices that will reverse or slow down environmental pollution and related problems. Goal 1.1: Students will comprehend core concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health including: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs; Nutrition and Physical Activity, Injury Prevention and Safety; Mental, Emotional and Social Health; Prevention and Control of Disease; Consumer and Community Health; Growth, Development and Family Life; and Environmental Health.. Grade 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.1.1.1. Describe the relationship between healthy behaviors and personal health. 3-5.H.1.1.2 Identify examples of emotional, intellectual, physical, and social health. 3-5.H.1.1.3 Describe ways in which a safe and healthy school and community environment can promote personal health. 3-5.H.1.1.4 Describe ways to prevent common childhood injuries and health problems. 3-5.H.1.1.5. Describe when it is important to seek health care. 3-5.H.1.1.6. Describe the impact of health behaviors on body systems. 20 Standard 2: Analyzing Influences Goal 1.1: Students will analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behavior. Grade 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.2.1.1 Describe how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 3-5.H.2.1.2 Identify the influences of culture on health practices and behaviors. 3-5.H.2.1.3 Identify how peers can influence healthy and unhealthy behaviors. 3-5.H.2.1.4 Describe how the school and community can support personal health practices and behaviors. 3-5.H.2.1.5 Describe ways that technology can influences personal health. Standard 3: Accessing Information Goal 1.1. Students will demonstrate the ability to access valid information and products and services to enhance health. Grade 3-5 Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.3.1.1 Identify characteristics of valid health information, products, and services. 3-5.H.3.1.2 Locate resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information. Standard 4: Interpersonal Communication Goal 1.1: Students will demonstrate the ability to use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks. Grade 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.4.1.1 Demonstrate effective verbal and nonverbal communication skills to enhance health. 3-5.H.4.1.2 Demonstrate refusal skills that avoid or reduce health risks. 3-5.H.4.1.3 Demonstrate nonviolent strategies to manage or resolve conflict. 3-5.H.4.1.4 Demonstrate how to ask for assistance to enhance personal health. Standard 5: Decision Making Goal 1.1: Students will demonstrate the ability to use decision-making skills to enhance health. 21 Grade 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.5.1.1 Identify health-related situations that might require a thoughtful decision. 3-5.H.5.1.2 Analyze when assistance is needed when making a health-related decision. 3-5.H.5.1.3 List healthy options to health related issues or problems. 3-5.H.5.1.4 Predict the potential outcomes of each option when making a health-related decision. 3-5.H.5.1.5 Choose a healthy option when making a decision. 3-5.H.5.1.6 Describe the outcomes of a health related decisions. Standard 6: Goal Setting Goal 1.1 Students will demonstrate the ability to use goal-setting skills to enhance health. Grades 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.6.1.1 Set a personal health goal and track progress toward its achievement. 3-5.H.6.1.2 Identify resources to assist in achieving a personal health goal. Standard 7: Practice Healthy Behavior Goal 1.1. Students will demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce health risks. Grades 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.7.1.1 Identify responsible personal health behaviors. 3-5.H.7.1.2 Demonstrate a variety of healthy practices and behaviors to maintain or improve personal health. 3-5.H.7.1.3 Demonstrate a variety of behaviors that avoid or reduce health risks. Standard 8: Advocacy Goal 1.1. Students will demonstrate the ability to advocate for personal, family, and community health. Grades 3-5 Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Fifth Grade, the student will be able to: 3-5.H.8.1.1 Express opinions and give accurate information about health issues. 3-5.H.8.1.2 Encourage others to make positive health choices.