2nd Grade Health Curriculum
advertisement

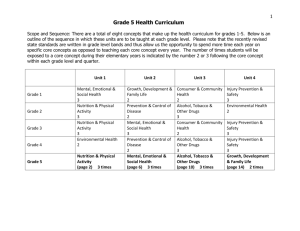
1 Grade 2 Health Curriculum Scope and Sequence: There are a total of eight concepts that make up the health curriculum for grades 1-5. Below is an outline of the sequence in which these units are to be taught at each grade level. Please note that the recently revised state standards are written in grade level bands and thus allow us the opportunity to spend more time each year on specific core concepts as opposed to teaching each core concept every year. The number of times students will be exposed to a core concept during their elementary years is indicated by the number 2 or 3 following the core concept within each grade level and quarter. Unit 1 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 5 Mental, Emotional & Social Health 3 Nutrition & Physical Activity (page 2) 3 times Nutrition & Physical Activity 3 Environmental Health 2 Nutrition & Physical Activity 3 Unit 2 Unit 3 Growth, Development & Family Life 2 Prevention & Control of Disease (page 6) 2 times Mental, Emotional & Social Health 3 Prevention & Control of Disease 2 Mental, Emotional & Social Health 3 Consumer & Community Health 2 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs (page 10) 3 times Consumer & Community Health 2 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 3 Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs 3 Unit 4 Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Environmental Health (page 14) 2 times Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Injury Prevention & Safety 3 Growth, Development & Family Life 2 2 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Nutrition and Physical Activity Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Awareness 2 Background Information Food Groups/Nutrients To be ready to learn and to achieve their fullest potential, children need to be well nourished and physically active. In order to enhance physical, mental, emotional, and social health, students need to acquire the knowledge and skills to make healthy food choices and engage in lifelong physical activity. Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Energy Nutrients: protein, vitamins, minerals (calcium), water, carbohydrates, & fats Goal Setting Food Groups Food Pyramid Unit Topic: Nutrition and Physical Activity Energy Goal Setting 3 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Awareness Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions 1. Healthy food choices enhance wellness. a. b. c. d. What is a healthy food choice? How does a healthy food choice affect wellness? How does our body get energy? What influences your food choices? 2. Physical activity enhances wellness. a. Why is physical activity important? b. What types of physical activity do you enjoy? 4 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Awareness Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. Where food comes from. 2. The food groups and types of food within each group. (Pyramid) 3. Basic nutrients and benefits to the body within different food groups and specific foods within each group. (1.1.1) 4. Effects of nutrients and proper nutrition on the body systems – muscular, skeletal, and digestive systems. (1.1.6) 5. How food provides energy for daily living. (1.1.1) 6. How family, culture, media and peers affect food choices. 7. Why it is important to be physically active. (1.1.1) 8. The importance of setting short-term goals related to nutrition and daily physical activity. 9. Different types of physical activity. 10. Proper nutrition and physical activity will enhance physical, mental, emotional, and social health. AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests Students will be able to… P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment Analyzing Influences 1. Identify how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.1 Decision Making 2. Identify situations when a health-related decision is needed. 5.1.1 Goal Setting 3. Identify a short-term personal health goal and take action towards achieving the goal. 6.1.1 4. Identify a short-term personal health goal and take action towards achieving the goal. 6.1.2 Practice Healthy Behaviors 5. Demonstrate healthy practices and behaviors to maintain or improve personal health. 7.1.1 6. Demonstrate behaviors that avoid or reduce health risks. 7.1.2 AC 5 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Nutrition and Physical Activity Lens: Awareness Suggested Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Sort foods into groups. (i.e. plant v. animal, food groups, etc.) 2. Use the pyramid guide to identify the food groups and the importance of physical activity. 3. Students set short-term goals related to nutrition and physical activity. 1 1,2 N/A 1 2,7 5 1,2 3,7,8,9 1,2,3,4,5,6 6 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Prevention and Control of Disease Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Prevention 2nd Transmission/Contraction Treatment Individuals can have a considerable measure of control over their own health and the chances of contracting most illnesses. Health-related choices and decisions regarding prevention of communicable and non-communicable diseases can include recognizing risk factors, identifying methods of contraction and transmission, as well as the prevention and treatment of disease. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective and developmentally appropriate. Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Germs Unit Topic: Prevention and Control of Disease Risk Factors Universal Precautions Communicable & Non-communicable Germs (Bacteria & Virus) Universal Precautions Prevention Treatment Immunization Risk Factors 7 Grade: Second Subject: Health Unit: Prevention and Control of Disease Lens: Prevention Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions 1. Making healthy choices can help decrease risk factors. a. What is risk factor? b. What types of healthy choices can you make in the areas of sleep, exercise and nutrition? 2. Applying universal precaution can help prevent the transmission and contraction of germs. a. b. c. d. What are universal precautions? If you are sick what can you do to stop the spread of germs? How do germs get into your body? What can you do to help prevent yourself from contracting a cold or flu? 8 Grade: Second Subject: Health Unit: Prevention and Control of Disease Lens: Prevention AC = Assessment Code: Critical Content and Skills Students will Know… 1. What a germ is (bacteria and virus). 2. How germs are spread (transmission). (1.1.3) 3. How people contract germs. 4. How to prevent the spread of germs. (1.1.3) 5. Universal precautions. (If it is wet, sticky, and not yours, don’t touch it!) 6. Ways to minimize risk factors for illness (Sleep, exercise, proper nutrition). 7. The differences between communicable and noncommunicable diseases. 8. Where to go/who to go to for treatment advice (parents, school nurse, doctors, etc.) (1.1.5) 9. What an immunization is. (1.1.5) Nurse Presentation with classroom teacher present 1. Universal Precautions and Self Responsibility in Health Care. This will consist of 1 lesson in the general education classroom with classroom teacher present. AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests Students will be able to… Analyzing Influences P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment 1. Identify what the school can do to support personal health practices and behaviors.2.1.2 Decision Making 2. Identify situations when a health-related decision is needed.5.1.1 3. Differentiate between situations when a healthrelated decision can be made individually or when assistance is needed.5.1.2 Practice Healthy Behaviors 4. Demonstrate healthy practices and behaviors to maintain or improve personal health. 7.1.1 5. Demonstrate behaviors that avoid or reduce health risks.7.1.2 Advocacy 6. Make requests to promote personal health. 8.1.1 AC 9 Grade: Second Subject: Health Unit: Prevention and Control of Disease Lens: Prevention Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Use glitter and hand lotion to demonstrate the transmission of cold and flu virus. Follow up with proper hand washing techniques. 2. Class discussion and demonstration regarding Universal Precautions 1,2 1,2,3,4,5,7 2,4,5 1,2 2,3,4,5,7 1,2,4,5 3. Students create advocacy posters to inform others in the school about germ transmission, contraction and prevention. 1,2 1-9 1-6 10 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs (ATO) Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Effects 2 Effects Background Information The use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs has major implications in the lifelong health of individuals. Implications include the effects, influences, and prevention of the use of alcohol, tobacco products, and other types of drugs on the body. Suggested Time Frame: 9 weeks Vocabulary Drug Use Misuse Abuse Alcohol Tobacco Nicotine Addiction Prevention Unit Topic: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs Influences Prevention 11 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs Lens: Effects Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions 1. Early prevention begins with education. a. Why is it important to learn about tobacco, alcohol and other drugs? b. How can learning about the negative effects of alcohol, tobacco and other drugs prevent misuse and abuse? 2. The use/misuse/abuse of alcohol, tobacco and other drugs (ATO) affect physical, social and emotional well-being. a. How can using ATO affect your body? b. How can using ATO affect your family and friends? c. How can using ATO affect a person’s feelings? 12 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs Lens: Effects Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. The definition of a drug. 2. The difference between use, misuse and abuse of substances (use – appropriate, misuse – accidental, abuse – purposeful). 3. The definition of addiction. 4. The difference between medicine and nonmedicine drug use. 5. The harmful effects of medicine when used incorrectly (prescription and over the counter). 6. Types of tobacco products and their effects on body systems – nervous, respiratory, circulatory and digestive systems. (1.1.6) 7. Types of alcohol products and their effects on body systems – nervous, respiratory, circulatory and digestive systems. (1.1.6) 8. Social and emotional effects of alcohol. (1.1.2) 9. Family and peers can influence their choices relating to substance use. 10. The benefits of not using tobacco, alcohol and other drugs. (1.1.1) AC Q – Quizzes P - Prompts O – Observations WS – Work Samples D – Dialogues SA – Student Self-Assessment T - Tests Students will be able to… AC Analyzing Influences 1. Identify how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. 2.1.1 Accessing Information 2. Identify trusted adults and professionals who can help promote health. 3.1.1 Decision Making 3. Differentiate between situations when a healthrelated decision can be made individually or when assistance is needed. 5.1.2 Practice Health Behaviors 4. Demonstrate behaviors that avoid or reduce health risks. 7.1.2 13 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs Lens: Effects Suggested Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Use medicine/candy comparison shadow box. (Here’s Looking at You) 2. Use role playing activities to demonstrate use v. misuse v. abuse 1,2 1,4,5 1,2 2 3. Use various and appropriate children’s books within the classroom. Follow up with class discussions. 4. Students write a letter to a friend to include the proper use and storage of medicine. 1,2 2 1-10 2,4,5 2,3,4 3,4 1,2,3,4 2,3,4 14 Critical Content/Concept Web Unit Topic: Environmental Health Conceptual Lens: Grade: Unit Overview Advocacy Individuals need to be aware of the impact of environmental issues and hazards on personal health. Environmental health may include precautions and behaviors to safeguard personal health, and practices that will reverse or slow down environmental pollution and related problems. 2 Pollution Reduce, Reuse & Recycle Suggested Time: 9 Weeks Vocabulary Unit Topic: Environmental Health Reduce Reuse Recycle Pollution Environment Hazard Conservation Habitats Hazardous waste 15 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Environmental Health Lens: Advocacy Enduring Understandings Guiding Questions 1. Conservation actions can shape a healthier environment. a. How does keeping the environment clean benefit your health? b. Why is it important to reduce, reuse, and recycle? c. What are some ways to reduce, reuse, and recycle? d. In what way does pollution harm the air, water, land and living things? e. What can you do to keep our air, water and land clean? f. How do you discard computers, paint, tires and biohazard waste, etc.? g. What does cutting down trees do to the environment? (good or bad) h. What happens when we destroy or take away the grounds for wildlife? 16 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Environmental Health Lens: Advocacy Critical Content and Skills AC = Assessment Code: Students will Know… 1. Ways to reduce, reuse, and recycle. (1.1.1) 2. How pollution affects the air, water and land. 3. How a clean environment keeps you healthy. 4. Environmentally safe ways to discard waste materials in landfills (i.e. paint, tires, biohazard materials and computers. 5. How the relationship between habitats and the environment affect our health and the health of the earth. AC Q – Quizzes O – Observations D – Dialogues T - Tests P - Prompts WS – Work Samples SA – Student Self-Assessment Students will be able to… Advocacy 1. Encourage peers and family to make positive health choices. 8.1.2 AC 17 Grade: 2 Subject: Health Unit: Environmental Health Lens: Advocacy Suggested Instructional Plan/Activities (Correlations) 1. Make a poster of reduce, reuse and recycle. 2. Write down any hazardous waste you have at home and work with parents on how to dispose it. (take home project) 1 1 1 2,3 1 1 18 IDAHO CONTENT STANDARDS HEALTH EDUCATION Kindergarten to Grade 2 Standard 1: Comprehend Core Concepts Core Concepts of Health Education for K-Grade 2 are defined below: Alcohol, Tobacco & Other Drugs The use of alcohol, tobacco, and other drugs has major implications in the lifelong health of individuals. Implications include the effects, influences, and prevention of the use of alcohol, tobacco products, and other types of drugs on the body. Nutrition & Physical Activity To be ready to learn and to achieve their fullest potential, children need to be well nourished and physically active. In order to enhance physical, mental, emotional, and social health, students need to acquire the knowledge and skills to make healthy food choices and engage in lifelong physical activity. Injury Prevention & Safety Unintentional and intentional injuries rank among the greatest threats to the health of children and young adults. Knowledge about prevention through safe living habits, healthy decisions, violence prevention, emergency response and an understanding of the consequences of ones decisions will help to prevent many injuries. Mental, Emotional & Social Health Mental, emotional and social well-being is a foundation for building good health which includes a sense of security, identity, belonging, purpose and competence in order to strive toward a healthy and productive life. Prevention & Control of Disease Individuals can have a considerable measure of control over their own health and the chances of contracting most illnesses. Health-related choices and decisions regarding prevention of communicable and non-communicable diseases can include recognizing risk factors, identifying methods of contraction and transmission, as well as the prevention and treatment of disease. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective and developmentally appropriate. Consumer & Community Health Consumers need to understand how health care services are provided as well as how individuals can take an active role in deciding on the use of health related services and products. Community health may include recognizing appropriate health professionals and products. 19 Growth, Development & Family Life A healthy family unit is vital to the well-being and successful development of children and youth. Growth and development includes the stages of life, and changes in relationships with others that accompany social development and the aging process. Information should be factual, medically accurate, objective and developmentally appropriate. Environmental Health Individuals need to be aware of the impact of environmental issues and hazards on personal health. Environmental health may include precautions and behaviors to safeguard personal health, and practices that will reverse or slow down environmental pollution and related problems. Goal 1.1: Students will comprehend core concepts related to health promotion and disease prevention to enhance health including: Alcohol, Tobacco and Other Drugs; Nutrition and Physical Activity, Injury Prevention and Safety; Mental, Emotional and Social Health; Prevention and Control of Disease; Consumer and Community Health; Growth, Development and Family Life; and Environmental Health. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.1.1.1. Identify that healthy behaviors affect personal health. K-2.H.1.1.2. Recognize that there are multiple dimensions (i.e. emotional, intellectual, physical and social) of health. K-2.H.1.1.3. Describe ways to prevent communicable diseases. K-2.H.1.1.4. List ways to prevent common childhood injuries. K-2.H.1.1.5. Describe why it is important to seek health care. K-2.H.1.1.6. Identify body systems. Standard 2: Analyzing Influences Goal 1.1: Students will analyze the influence of family, peers, culture, media, technology, and other factors on health behavior. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.2.1.1 Identify how the family influences personal health practices and behaviors. K-2.H.2.1.2 Identify what the school can do to support personal health practices and behaviors. K-2.H.2.1.3 Describe how the media can influence health behaviors. 20 Standard 3: Accessing Information Goal 1.1 Students will demonstrate the ability to access valid information and products and services to enhance health. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the students will be able to: K-2.H.3.1.1 Identify trusted adults and professionals who can help promote health. K-2.H.3.1.2 Identify ways to locate school and community health helpers. Standard 4: Interpersonal Communication Goal 1.1: Students will demonstrate the ability to use interpersonal communication skills to enhance health and avoid or reduce health risks. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.4.1.1. Demonstrate healthy ways to express needs, wants, and feelings. K-2.H.4.1.2 Demonstrate listening skills to enhance health. K-2.H.4.1.3 Demonstrate ways to respond when in an unwanted, threatening, or dangerous situation. Standard 5: Decision Making Goal 1.1: Students will demonstrate the ability to use decision-making skills to enhance health. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.5.1.1 Identify situations when a health-related decision is needed. K-2.H.5.1.2 Differentiate between situations when a health-related decision can be made individually or when assistance is needed. Standard 6: Goal Setting Goal 1.1 Students will demonstrate the ability to use goal-setting skills to enhance health. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.6.1.1. Identify a short-term personal health goal and take action towards achieving the goal. K-2.H.6.1.2. Identify who can help when assistance is needed to achieve a personal health goal. 21 Standard 7: Practice Healthy Behavior Goal 1.1. Students will demonstrate the ability to practice health-enhancing behaviors and avoid or reduce health risks. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.7.1.1. Demonstrate healthy practices and behaviors to maintain or improve personal health. K-2.H.7.1.2. Demonstrate behaviors that avoid or reduce health risks. Standard 8: Advocacy Goal 1.1. Students will demonstrate the ability to advocate for personal, family, and community health. K-2nd Grade Objectives Objective(s): By the end of Second Grade, the student will be able to: K-2.H.8.1.1. Make requests to promote personal health. K-2.H.8.1.2. Encourage peers and family to make positive health choices.