Breast Implants And Whole Body Vibration
advertisement

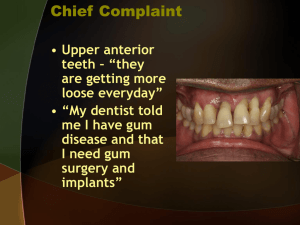
Breast Implants and Whole Body Vibration There are several options and types of breast implants available in Canada. The implant itself can either be saline or silicone based. The saline implant is a silicone elastomer shell that is filled with saline which is a salt water solution. If the implant ruptures the saline solution can be reabsorbed by the body. To ensure a small incision these implants are usually inserted empty and then filled to the desired size once in place. There are several shapes that plastic surgeons use, and textured implants are also available to help reduce the risk of a capsular contracture which is a more common complication of breast implants. Silicone implants are available in Canada on a restricted basis as there were concerns over the safety of the implant from Health Canada. Silicone implants are a silicone elastomer shell filled with a silicone gel. A larger surgical incision is required because the implants come prefilled. There are various shaped implants available and due to consistency of the silicone allows it to maintain its shape and has a natural feel. Due to the consistency of newer silicone filler the implant will maintain its shape even when cut into. There are two types of placement for implants subglandular and submuscular. The subglandular placement is over the pectoral muscle and under the breast tissue. It is usually done with the newer type of silicone implants known as the cohesive gel implants, or when someone has more breast tissue as there is a smaller risk of seeing rippling of the implant which may occur with a saline implant. Although controversial it is felt that the risk for capsular contractures is greater with this placement. Recovery time is thought to be less post surgery. The submuscular placement is when 2/3 of the implant is placed below the pectoralis muscle. The bottom 1/3 sits below the muscle. It is the more common placement in Canada and is used with saline implants and women with less breast tissue to avoid seeing rippling of the implant. Recovery time post surgery is greater due to a greater amount of tissue being cut into and the pectoralis muscle being stretch. It also takes longer for the implant to settle into place. There are four typical surgical sites which include the armpit, the areola, the crease of the breast and the navel. Silicone implants are prefilled so are typically inserted with an areolar incision or at the crease. Complications of breast implants include typical issues that may arise following any surgery, as well as issues specific to the implants themselves. These include capsular contractures, ruptures or deflation, implant displacement, symmastia, Mondor’s cord, change in sensation around the nipple and breast, difficulties with breast feeding, wrinkling of the breast and issues with the incisional scar. Directly following surgery for breast augmentation it is recommended to avoid heavy lifting, bending and strenuous activities that may increase pain and delay healing 1. Return to exercise can generally be done around one month; however, due to individual differences with recovery, it is advisable to discuss this timeline with the plastic surgeon 1. There is little research available regarding the effects of exercise, or an early return to exercise with recent breast augmentation. Following submuscular implants, women considered athletic (weight lifts more than 6 hours a week) took longer to return to their exercise routine and were less likely able to perform exercises involving the pectoralis muscle, compared to those who had subglandular placed implants 2. With respect to breast distortion and submuscular placement of breast implants, weight lifting and exercise were most problematic 3. It was suggested that women who are involved more in exercise may find a subglandular placement more preferable, as less distortion may occur 3. THIS IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. WE DO NOT DIAGNOSE OR PRESCRIBE. PLEASE CONSULT YOUR HEALTH PROVIDER. 25 Curity Avenue, Unit 2A, Toronto, ON M4B 3M2 416-285-6055 fax 416-285-8918 info@t-zonehealth.com www.t-zonevibration.com -2There is no research available to look at the effect of Whole Body Vibration (WBV) on breast implants. In general, synthetic implants (included in this list are pacemakers, recent stents, and brain implants) are considered a contraindication to using WBV. Contraindications are recommended due to the lack of research in a particular area or when there is a known consequence. Without research, it cannot be determined if the benefits to using WBV would outweigh any potential risks. For synthetic implants there is a concern that the vibration will cause migration of the implant. It can also not be determined if the vibration would cause an implant to rupture. It is not advisable to use WBV directly following surgery, as it will affect the healing of the surgical incision. Therefore, it is essential for an individual following breast augmentation to discuss any new exercise routine including the addition of WBV with her plastic surgeon. It is important that a doctor understands WBV to help an individual determine if there are any contraindications specific to his/her medical history. A doctor can also help determine when it is most appropriate to return to more strenuous activities following surgery based on an individual’s rate of healing and any complications that may have occurred. If an individual has been cleared to use WBV by their doctor, it should be started at a reduced intensity and duration. An individual should be aware of symptoms related to the rupture of an implant and should self monitor for any other possible complications including displacement of the implant. If any symptoms or complications occur while using the WBV platform, it should be discontinued immediately and symptoms should be discussed with a doctor. If an individual is symptom free and adapting to the WBV, intensity can be increased and exercises added within the appropriate fitness level. It is advisable to take extreme caution or avoid placing the arms/trunk on the platform or any other position that would increase the intensity of vibration felt in the chest. In general, if an individual experiences pain, dizziness or shortness of breath while using the WBV platform it should be discontinued immediately. References 1. http://www.docshop.com/education/cosmetic/breast/augmentation/recovery/, retrieved April 21, 2010. 2. Sarbak JM, Baker JL Jr. 2004. Effects of breast augmentation on pectoralis major muscle function in the athletic woman, Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 24(3), 224-8. 3. Spear SL, Schwartz J, Dayan JH, Clemens MW. 2009. Outcome assessment of breast distortion following submuscular breast augmentation. Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, 33(1), 44-8. Various models and machines on the market have been used for the purpose of conducting research. Also, a variety of frequencies (speeds) and amplitudes (platform variation) which may or may not be known to us have been used. We do not guarantee or claim users will achieve similar results with our T-Zone Whole Body Vibration machine. THIS IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY. WE DO NOT DIAGNOSE OR PRESCRIBE. PLEASE CONSULT YOUR HEALTH PROVIDER. 25 Curity Avenue, Unit 2A, Toronto, ON M4B 3M2 416-285-6055 fax 416-285-8918 info@t-zonehealth.com www.t-zonevibration.com