ANG questions
advertisement

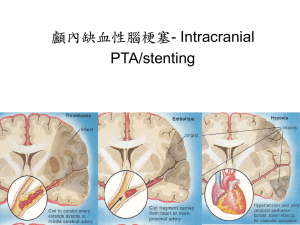
Blood supply of head and neck 1. What vitally important vessel passes behind palatine tonsil at the distance of 1,0 -1,5 cm ? Internal carotid artery. 2. What structure is the anatomic landmark of point of origin of external carotid artery? Upper margin of thyroid cartilage. 3. In what triangle of the neck manual pressure of carotid artery is executed to stop hemorrhage? In carotid triangle. 4. Damage of what artery, topographically linked with palatine tonsil is possibly to happen in surgery on tonsillectomy? Facial artery. 5. What arteries supply thyroid gland with blood? Superior thyroid artery, inferior and thyroid artery. 6. In what topographic formation of the neck does subclavicular vein pass? Pre-serratus space. 7. What areas of the cortex may experience ischemia in blood flow disorder in right anterior cerebral artery circulation? Medial surfaces of right frontal and parietal lobes. 8. To what formation on the cervical vertebrae is possibly to press carotid artery for temporally control of bleeding? To anterior tubercle of transverse process of 6-th cervical vertebra. 9. In what space of the neck is jugular venous arch located? In suprasternal inter-aponeurotic space of the neck. 10. Branches of what artery may be damaged in case of lower lip trauma in the area of angle of the mouth? Facial artery. 11. In what place manual pressure of superficial temporal artery may be executed to stop bleeding? In front of external auditory opening higher than zygomatic arch. 12. What cervical vein may be injured in damage of skin integuments above middle portion of sternocleidomastoid muscle? External jugular vein. 13. What arteries supply ethmoidal cells and mucosa of nasal cavity with blood? Anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries. 14. What facial vein may serve as the route of infection invasion along venous anastomoses into cavernous sinus? Angular vein. 15. Into what regional lymphatic nodes dissemination of tumor is possible in case of laryngeal neoplasm in the area of vocal folds? Profound cervical lymphatic nodes. 16. What artery supplies structures of limbic system with blood? Anterior cerebral artery. 17. Disorder of blood flow in circulation of what artery may lead to trunkal disturbances and suppression of vital functions? Basilar artery. 18. In what venous sinuses may pus penetrate in case of face phlegmon and retrograde venous blood flow from facial vein? Cavernous sinus. 19. In what cranial fossa will bleeding spread in case of venous sinus destruction in the area of jugular foramen? Posterior cranial fossa. 20. What pathology of venous sinus of cranial cavity does clinical picture of ocular muscles paralysis and disturbances along the pass of the first branch of trigeminal nerve indicate to? Cavernous sinus. 21. What artery must be dressed to stop bleeding in case of trauma forward from angle of mandible? Facial artery. 22. What vessel may be damaged in case of trauma with sharp object in the area of lower angle of carotid triangle? Common carotid artery. 23. Along what veins purulent infection from external head integuments in the area of mastoid process may penetrate into cranial cavity? Emissary mastoid veins. 24. In the circulation of what artery thrombosis happened, if bleeding is located in the left hemisphere and patient completely lost speech? In the circulation of medial cerebral artery. 25. In the circulation of what arteries blood flow is damaged in blockade of cardiovascular and respiratory brain centers? In circulation of vertebral and basilar arteries. 26. What artery is damaged in bleeding in the area of upper lip? Facial artery. 27. From what artery does dorsal artery of the tongue branch off? From lingual artery. 28. Branches of what arteries form arterial anastomosis in the area of medial angle of eye? Branches of external and internal carotid arteries. 29. What vein passes in the canal of mandible? Inferior alveolar vein. 30. What artery is damaged if patient presents hemorrhagic stroke in frontal lobe of the right hemisphere? Anterior cerebral artery. 31. In circulation of what artery is superior temporal gyrus located? Medial cerebral artery. 32. What artery may be injured in tracheotomy? Thyroid artery. 33. What large artery may be damaged in tonsillectomy? Internal carotid artery. 34. Bleeding from what artery may cause epidural hematoma in the cerebral temporal area? Medial meningeal artery. 35. Thrombosis of what venous sinus may cause purulent mastoiditis? Sigmoid sinus. 36. Damage of what artery is possible in fracture of mandible? Inferior alveolar artery. 37. Sinus of what dura mater passes in the area of cranial sagittal suture? Superior sagittal sinus. 38. What artery may be damage in destruction of upper portion of greater palatine canal? Descending palatine artery. 39. Into what sinus of cranial cavity may pus penetrate along anastomoses in the area of nasal root and lower eyelid? Cavernous sinus. 40. Branches of what artery execute basic blood supply of the inner ear? Basilar artery. 41. What artery may be compressed in osteochondrosis of cervical part of the spinal column (passes through transversal foramina of cervical vertebrae)? Vertebral artery. 42. What large artery passes in the area of anterior wall of tympanic cavity? Internal carotid artery. 43. What lymphatic nodes are the first to react to periodontitis in the area of lower molars? Submandibular. 44. What lymphatic nodes are the first to react to purulent process in the external acoustic meatus? Parotid lymphatic nodes. 45. What venous vessel may be injured in the area of lateral edge of sternocleidomastoid muscle in case of knife wound? External jugular vein. 46. In the area of what triangle of the neck does lingual artery pass? Pirogov’s (lingual) triangle. 47. What structures form vascular-nervous fascicle of the neck? Common carotid artery, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein. 48. Name topographic portions of internal carotid artery: Cervical portion, petrous portion, cavernous portion, cerebral portion. 49. Name branches of internal carotid artery which branch off in its petrous portion: Carotid-tympanic arteries. 50. Name branches of internal carotid artery in its cerebral portion: Ocular artery, anterior cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, medial cerebral artery, posterior communicating artery. 51. Name arteries which form part of arterial circle of cerebrum: Branches of internal carotid artery: anterior cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, proper internal carotid artery, posterior communicating artery. Branches of subclavicular artery: posterior cerebral arteries from basilar artery. 52. What branch of what artery passes inside the optic nerve? Inside the optic nerve central retinal artery passes which is the branch of ophthalmic artery. 53. How does ophthalmic artery get into orbital cavity? Ophthalmic artery gets into eye-pit together with optic nerve through optic canal. 54. Name topographic portions of maxillary artery: Retromandibular portion, subtemporal portion, pterygo-palatine portion. 55. Name branches of maxillary artery in pterygo-palatine portion and cranial structures through which these branches leave pterygo-palatine fossa: In pterygo-palatine portion the following branches branch off form maxillary artery: through inferior orbital fissure infra-orbital and zygomatic artery exit into orbital cavity; through pterygo-palatine foramen pterygo-palatine artery exits into nasal cavity; through grater palatine canal descending palatine artery passes into oral cavity. 56. What groups are distinguished in external carotid artery? Anterior medial and posterior groups. 57. Name arteries of anterior group of branches of external carotid artery: Superior thyroid artery, facial artery, lingual artery. 58. Name arteries of median group of branches of external carotid artery: Ascending pharyngeal artery, maxillary pharyngeal artery, superficial temporal artery. 59. Name arteries of posterior group of branches of external carotid artery: Sternocledomastoid artery, occipital artery, posterior auricular artery. 60. Name branches of ophthalmic artery taking part in blood supply of upper eyelid: Lacrimal artery, lateral palpebral artery, supraorbital artery, supratrochlear artery, medial palpebral artery, dorsal nasal artery. 61. Name main flows of superior vena cava: Right and left brachiocephalic veins, azygous vein. 62. Name jugular veins: Internal, external and anterior jugular veins. 63. What structures pass in jugular foramen? Internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus and accessory nerves. 64. What vascular structures pass through superior orbital fissure? Through superior orbital fissure superior ophthalmic vein passes. 65. What vessels does jugular venous arch connect? Jugular venous arch connects anterior and external jugular veins against each other. 66. Where do external jugular veins run into? External jugular veins run into venous angle of its side or in subclavicular vein of its side. 67. What structures of head are supplied with blood both from external and from internal carotid arteries (i.e. being anastomosis between circulations of these two arteries)? Upper and lower eyelids.