Text - icaam

Bernard R. Glick
Molecular Biotechnology
Text:
Molecular Biotechnology
B.R. Glick, J.J. Pasternak and C.L. Patten
ASM Press, Fourth Edition
Biotech Companies Worldwide
in 2004
Fundamentals of recombinant DNA technology
Overview of recombinant DNA cloning procedure
Plasmid pBR322
Strategy for selecting E. coli cells transformed with pBR322
pBR322
Francisco Bolivar Raymond Rodriguez
Screening a gene library with a labeled DNA probe (colony hybridization)
Immunological screening of a gene library (colony immunoassay)
Screening a genomic library for enzyme activity
Electroporation Tripartite conjugation
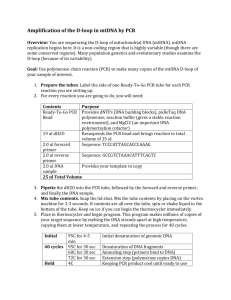
DNA synthesis and the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
The chemical synthesis of DNA
Gobind Khorana
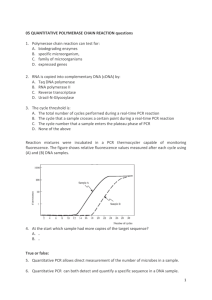
PCR: first cycle
Second PCR cycle
PCR: thirtieth cycle
PCR amplification of full length cDNA. The terminal transferase activity of reverse transcriptase adds mostly dCs to the ends of each full length first strand cDNA
Directed Mutagenesis and Protein Engineering
Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis
Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis with plasmid DNA
PCR-amplified oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis
Error-prone PCR
Random mutagenesis of a cloned target gene
DNA Shuffling
Addition of a disulfide bond between the N and C termini of
B. circulans xylanase stabilizes the protein. The activity at room temperature is doubled and it is largely protected against inactivation at high temperature
Engineering a calcium-independent subtilisn. Native enzyme loses its activity when the calcium-binding loop is deleted. After random mutagenesis, several mutants with low activity are isolated. These are combined into one mutant construct with high activity.
Altering multiple enzyme properties at once. Start with multiple copies of a Bacillus subtilisn gene. Error-prone PCR and then DNA shuffling.
Test for high activity at room temp and then stability at high temp