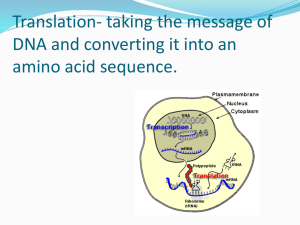
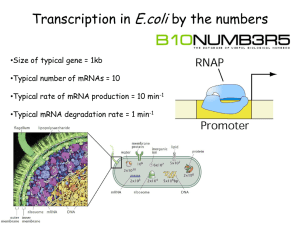
Reverse transcriptase
advertisement

Reverse transcription 1970 Temin คนพบเอนไซม จากไวรั ส (viral enzyme) ทีเ่ ปลีย ่ น RNA เป็ น DNA ้ ์ เรียกวา่ RNA-directed DNA polymerase หรือ reverse transcriptase mRNA Reverse transcriptase หรือ RNA-directed DNA polymerase cDNA (complementary DNA Reverse transcriptase - สั งเคราะหสาย DNA จากปลาย 5’ 3’ ์ - ตองใช ่ ตนของการสั งเคราะห ์ cDNA ้ ้ primer (tRNA) เป็ นจุดเริม ้ Reverse transcriptase มี 3 activities ทีใ่ ช้ในการทางานของไวรัส 1. RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity: เติม nucleotides เพือ ่ ใช้ในการสั งเคราะห ์ cDNA 2. RNase H: exonuclease สาหรับยอย ่ มีการสั งเคราะห ์ cDNA แลว ่ tRNA primer เมือ ้ 3. DNA-directed DNA polymerase: สั งเคราะห ์ ssDNA (single-stranded DNA)หลังจากที่ tRNA primer ถูกยอยแล วด ่ ้ วย ้ Rnase H แลว ้ Transcription mRNA capping polyadenylation nucleus Cap poly(A) Splicing Cap poly(A) cytoplasm mRNA transport Cap poly(A) Translation mRNA decay Translation RNA (mature mRNA) Protein • 5’ cap structure - 7-methyl guanosine residue • 3’ poly(A) tail - ~200 adenosine residues in mammals ~60 in yeast • Start codon - this defines the end of the 5’ untranslated region (5’UTR) • Stop codon - this defines the start of the 3’untranslated region (3’UTR) stop start Cap 5’UTR ORF 3’UTR poly(A) Prokaryotic ribosome Eukaryotic ribosome แบงได ่ ้ 3 stages:- การนา (Recruitment) ribosome ลงบน mRNA และจดจา (Recognition) จุดเริม ่ ตน(start codon)ของการ ้ translation • Initiation - • Elongation - การเคลือ ่ นทีข ่ อง ribosome ไปบน mRNA และแปรรหัส (Decoding) ของ mRNA และสั งเคราะห ์ สายโปรตีน (polypeptide chain) • Termination - การจดจารหัสหยุด (Recognition of the stop codon) และปลดปลอย ่ ribosome และสาย protein ออกจาก mRNA Translation initiation คือขบวนการที่ ribosome (และ initiator methionyl tRNA) ถูกนา (recruited) ลงไปที่ start codon. เป็ นขบวนการทีซ ่ บ ั ซ้อน แบงได ้ ตอนคือ ่ ้ 4 ขัน 1. การเตรียม 40S ribosomal subunit/ methionyl tRNAi 2. การเตรียมและการคัดเลือก mRNA (mRNA selection and preparation) 3. การจับกันของ 40S ribosome และ mRNA, การสแกนและการจดจา AUG (40S/ mRNA binding, scanning and AUG recognition) 4. การจับกันของ 40S และ 60S subunit (60S ribosomal subunit joining) f-Met-tRNAfMet : tRNA ทีจ ่ ดจา AUG (GUG, UUG, prokaryotic) COOH 3’-OH 5’-P 60S 60S 3 3 40S 40S 1A 1A 1 Ternary complex M 2 5 GTP M GTP 2 GDP 3 M GTP 5 2 1 1A GDP 2B 2 GTP • The mRNA is bound by eIF4F (eIF4E, eIF4G, eIF4A) • Pab1 binds the poly(A) tail and may recruit eIF4F • eIF4B and eIF4H facilitate the helicase activity of 4A eIF3 in the 40S complex and eIF4G in the mRNA complex interact 4G 4E 4B 4A Cap 4H 3 5 M GTP 1 2 1A AUG • The 40S complex scans each codon in a 5’ to 3’ direction looking for an AUG. • The eIF4A helicase activity irons out RNA hairpins allowing the 40S complex to move. • ATP hydrolysis is required 4G 4E 4B 4A Cap 4H 3 5 M GTP 1 2 1A AUG 3 5 M GTP 1 2 1A Cap AUG • eIF5 stimulates the GTPase activity of eIF2 leading to loss of most of the initiation factors M 1A Cap AUG GDP 3 1 5 2 60S 5B M 1A Cap AUG GTP 5B 1A GDP M Cap AUG 3 50S 1 3 30S 30S fM 1 2 50S fM GTP GTP 2 1 16SrRNA 3 SHINE AUG DELGARNO fM GTP 2 1 16SrRNA 3 SHINE AUG DELGARNO 3 50S 1 GDP fM 2 16SrRNA SHINE DELGARNO AUG • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upstream of each ORF). • Initiation is much less complicated than eukaryotes (Just three initiation factors IF1, IF2 and IF3) • Elongation and termination similar to eukaryotes Defined as the sequential addition of amino acids to the carboxyterminal end of the nascent peptide. Relies on three tRNA binding sites in the ribosome:1. The A site amino-acyl tRNA binding site 2. The P site peptidyl tRNA binding site 3. The E site where the empty tRNA is ejected from the ribosome naa aa aa aa aa 5’ E P A 3’ mRNA Four major steps:- 1. Amino acyl tRNA binding in the A site 2. GTP hydrolysis and guanine nucleotide exchange on eEF1A 3. Peptide bond formation 4. Translocation of mRNA and peptidyl-tRNA on the ribosomal surface eEF1B aa GDP eEF1A Amino-acyl tRNA binding naa aa aa aa aa E P A 5’ GTP eEF1A 3’ naa aa aa aa E P A 5’ mRNA 3’ mRNA Peptidyl transfer n+1aa n+1aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa aa 5’ E P A 3’ 5’ E P A mRNA mRNA translocation eEF= eukaryotic elongation factor GTP eEF2 3’ GDP eEF2 • Catalysed by eRF1 (eukaryotic release factor). • eRF1 recognises all three stop codons and its crystal resembles a tRNA even though it is a protein. structure • Hence the molecular mimicry model predicts that eRF1 gives termination by binding the ribosome in a similar way to tRNA. • eRF3 stimulates eRF1 activity in a GTP-dependent manner