RNAseq applications in genome studies
advertisement

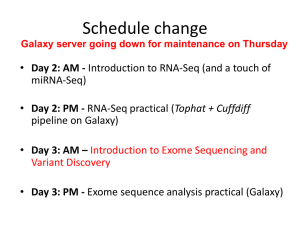
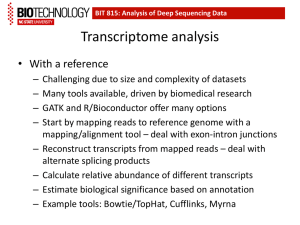
RNAseq Applications in Genome Studies Alexander Kanapin, PhD Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford RNAseq Protocols Next generation sequencing protocol cDNA, not RNA sequencing Types of libraries available: Total RNA sequencing polyA+ RNA sequencing Small RNA sequencing Special protocols: DSN treatment Ribosomal depletion Genome Study Applications transcriptome analysis identifying new transcribed regions expression profiling Resequencing to find genetic polymorphisms: SNPs, micro-indels CNVs cDNA Synthesis Sequencing details Standard sequencing polyA/total RNA Size slection Primers and adapters Single- and paired-end sequencing Strand-specific sequencing Beta version Sequencing only + or – strand Mostly paired-end Arrays vs RNAseq (1) Correlation of fold change between arrays and RNAseq is similar to correlation between array platforms (0.73) Technical replicates are almost identical, no need to run Extra analysis: prediction of alternative splicing, SNPs Low- and high-expressed genes do not match Array vs RNAseq (2) A bit of statistics Short reads distribution Expression values normalization Poisson Negative binomial Normal FPKM Normalized reads number VST (variance stabilized transformation) Differential expression analysis Replicates vs non-replicates Analysis Dataflow Illumina Pipeline (FASTQ) Alignment (BAM) FASTX Toolkit (FASTQ/FAST A) Expression profiles/RN A abundance Splice variants SNP analysis Software Short reads aligners Data preprocessing (reads statistics, adapter clipping, formats conversion, read counters) Cufflinks package RSEQtools R packages (DESeq, edgeR, baySeq, DEGseq, Genominator) Alternative splicing Fastx toolkit Htseq MISO samtools Expression studies Stampy, BWA, Novoalign, Bowtie,… Cufflinks Augustus Commercial software Partek CLCBio FASTQ: Sequence Data “FASTA with Qualities” @HWI-EAS225:3:1:2:854#0/1 GGGGGGAAGTCGGCAAAATAGATCCGTA ACTTCGGG +HWI-EAS225:3:1:2:854#0/1 a`abbbbabaabbababb^`[aaa`_N]b^ab^``a @HWI-EAS225:3:1:2:1595#0/1 GGGAAGATCTCAAAAACAGAAGTAAAAC ATCGAACG +HWI-EAS225:3:1:2:1595#0/1 a`abbbababbbabbbbbbabb`aaababab\aa_` SAM(BAM): Alignment Data Bitwis Read ID e flag Chr Pos S35_42763_ 4 0X 15401991 Insert MapQ CIGAR Mate ref Mate pos size Sequence 25518M * 0 Scores Extra tags 0CACACGATTCTCAAAGGT IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII XA:i:0 FPKM (RPKM): Expression Values Fragments Reads Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped fragments Nat Methods. 2008, Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Mortazavi A et al. C FPKM 10 NL 9 C= the number of reads mapped onto the gene's exons N= total number of reads in the experiment L= the sum of the exons in base pairs. Cufflinks package http://cufflinks.cbcb.umd.edu/ Cufflinks: Cuffcompare: Expression values calculation Transcripts de novo assembly Transcripts comparison (de novo/genome annotation) Cuffdiff: Differential expression analysis Cufflinks (Expression analysis) gene_id bundle_id chr left right FPKM FPKM_conf_lo FPKM_conf_hi ENSG00000236743 31390 chr1 459655 461954 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000248149 31391 chr1 465693 688071 787.12 731.009 843.232 OK ENSG00000236679 31391 chr1 470906 471368 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000231709 31391 chr1 521368 523833 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000235146 31391 chr1 523008 530148 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000239664 31391 chr1 529832 532878 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000230021 31391 chr1 536815 659930 2.53932 0 5.72637 OK ENSG00000229376 31391 chr1 657464 660287 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000223659 31391 chr1 562756 564390 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000225972 31391 chr1 564441 564813 96.9279 77.2375 116.618 OK ENSG00000243329 31391 chr1 564878 564950 0 0 0 OK ENSG00000240155 31391 chr1 564951 565019 0 0 0 OK status Cuffdiff (differential expression) Pairwise or time series comparison Normal distribution of read counts Fisher’s test test_id gene locus ENSG00000000003TSPAN6 ENSG00000000005TNMD ENSG00000000419DPM1 ENSG00000000457SCYL3 sample_1 sample_2 chrX:99883666-99894988 q1 chrX:99839798-99854882 q1 chr20:49551403-49575092 q1 chr1:169631244-169863408 q1 status q2 q2 q2 q2 value_1 value_2 NOTEST 0 NOTEST 0 NOTEST 15.0775 OK 32.5626 ln(fold_change) test_stat p_value significant 0 0 0 1 no 0 0 0 1 no 23.8627 0.459116 -1.39556 0.162848 no 16.5208 -0.678541 15.8186 0 yes Cufflinks: Alternative splicing trans_id bundle_id chr left effective_length status ENST00000503254 31391 ENST00000458203 31391 ENST00000417636 31391 ENST00000423796 31391 ENST00000450696 31391 ENST00000440196 31391 ENST00000357876 31391 ENST00000440200 31391 ENST00000441245 31391 ENST00000419394 31391 ENST00000448605 31391 ENST00000414688 31391 ENST00000447954 31391 ENST00000440782 31391 ENST00000452176 31391 ENST00000416931 31391 ENST00000485393 31391 ENST00000482877 31391 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 chr1 right FPKM 465693 470906 521368 523008 523047 529832 529838 536815 637315 639064 639064 646721 655437 657464 562756 564441 564878 564951 688071 471368 523833 530148 529954 530595 532878 655580 655530 655574 655580 655580 659930 660287 564390 564813 564950 565019 FMI frac FPKM_conf_lo 787.12 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2.53932 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 96.9279 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 FPKM_conf_hi coverage length 731.009 843.232 124.849 1509 440.26 OK 0 0 462 440.005 OK 0 0 842 842 OK 0 0 607 607 OK 0 0 402 402 OK 0 0 437 437 OK 0 0 498 498 OK 0 5.72637 0.185236 413 413 OK 0 0 629 629 OK 0 0 480 480 OK 0 0 274 274 OK 0 0 750 750 OK 0 0 336 336 OK 0 0 2823 2823 OK 0 0 802 802 OK 77.2375 116.618 21.1488 372 372 OK 0 0 72 72 OK 0 0 68 68 OK R/bioconductor Packages Based on raw read counts per gene/transcript/genome feature (miRNA) Differential expression analysis DESeq baySeq http://www-huber.embl.de/users/anders/DESeq/ Negative binomial distribution http://www.bioconductor.org/help/biocviews/release/bioc/html/baySeq.html Bayesian approach Choice of Poisson and negative binomial distribution edgeR DEGSeq Genominator … DESeq: Variance estimation SCV: the ratio of the variance at base level to the square of the base mean Solid line: biological replicates noise Dotted line: full variance scaled by size factors Shot noise: dotted minus solid DESeq: Differential Expression id B cells IFG expressio expressio log2FoldCh n n ange pValue ENSG00000000971 1.566626326 23.78874526 3.924546167 2.85599311970997e-17 ENSG00000001036 5.999081213 33.49328888 2.481058581 9.8485739442166e-13 ENSG00000001084 23.3067067 156.2725598 2.745247408 4.38856094441354e-33 ENSG00000001461 46.14566905 18.67886919 -1.304788134 2.66197080043655e-07 ENSG00000001497 68.54035056 35.87868221 -0.933826668 3.36052669642687e-05 ENSG00000001630 13.86061772 55.92825318 2.012585716 1.27410028391540e-13 ENSG00000002549 27.33856924 1096.051286 ENSG00000002587 15.64872305 2.223202568 -2.815333625 8.43968907932538e-10 ENSG00000002834 95.68814397 272.3502328 1.509051013 8.21570437569004e-16 ENSG00000003056 63.65513823 296.6257971 2.220295194 2.92583705156055e-30 ENSG00000003400 52.02308495 117.3028844 1.173014631 4.62918844505763e-08 ENSG00000003402 154.7003657 311.1815114 1.008279739 2.59997904482726e-08 ENSG00000003756 434.3712708 180.9106662 -1.263651217 3.58591978350734e-14 ENSG00000004399 1.199584318 56.96561073 5.569484777 9.87310306834046e-40 ENSG00000004455 145.4361806 331.8994483 1.190360014 3.17246841765643e-10 ENSG00000004468 17.27590102 128.1030372 2.89047182 1.99020901042234e-33 ENSG00000004534 331.0046525 176.1290195 -0.910218864 2.28719252897662e-07 ENSG00000004799 5.425570485 18.0426855 1.733567341 1.67150844663169e-06 ENSG00000004961 15.22078545 54.5536795 1.841633697 2.76802192307592e-11 ENSG00000005020 133.1474289 248.379817 0.899523377 3.00900687072175e-06 ENSG00000005022 86.49374889 154.5210394 0.837135513 3.79777250197792e-05 ENSG00000005238 0.818439748 8.567484894 3.387923626 7.38045118427266e-07 ENSG00000005249 1.442397316 17.22208291 3.577719117 2.69990749254895e-12 ENSG00000005379 25.15059092 4.02264298 -2.644376691 2.75953193496745e-12 ENSG00000005381 0.376344415 19.36188435 5.685021995 4.99727503015434e-18 ENSG00000005436 28.46288463 11.16816604 -1.349689587 4.23389957443192e-06 5.325233754 1.97553508993745e-133 Visualization: Genome Viewers Web based: Gbrowse (http://gmod.org/wiki/Gbrowse) UCSC Genome Browser (http://genome.ucsc.edu/) Standalone Integrated Genome Viewer (http://www.broadinstitute.org/software/igv/) IGV: Differential Expression Visualization An Introduction to ChIPSequencing analysis Linda Hughes What is ChIP-Seq? Chromatin-Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)- Sequencing ChIP - A technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to the protein. Sequencing – A technique to determine the order of nucleotide bases in a molecule of DNA. Used in combination to study the interactions between protein and DNA. ChIP-Seq Applications Enables the accurate profiling of Transcription factor binding sites Polymerases Histone modification sites DNA methylation ChIP-Seq: The Basics ChIP-Seq Analysis Pipeline Sequencing Base Calling Read quality assessment 30-50 bp Sequences Genome Alignment Enriched Regions Visualisation with genome browser Differential peaks Motif Discovery Combine with gene expression Peak Calling ChIP-Seq: Genome Alignment Several Aligners Available BWA NovoAlign Bowtie Currently the Sequencing analysis pipeline uses the Stampy as the default aligner for all sequencing. All aligner output containing information about the mapping location and quality of the reads are out put in SAM format ChIP-Seq Peak Calling The main function of peak finding programs is to predict protein binding sites First the programs must identify clusters (or peaks) of sequence tags The peak finding programs must determine the number of sequence tags (peak height) that constitutes “significant” enrichment likely to represent a protein binding site ChIP-Seq: Peak Calling Several ChIP-seq peak calling tools Available MACS PICS PeakSeq Cisgenome F-Seq ChIP-Seq: Identification of Peaks Several methods to identify peaks but they mainly fall into 2 categories: Tag Density Directional scoring In the tag density method, the program searches for large clusters of overlapping sequence tags within a fixed width sliding window across the genome. In directional scoring methods, the bimodal pattern in the strand-specific tag densities are used to identify protein binding sites. ChIP-Seq: Determination of peak significance To account for the background signal, many methods incorporate sequence data from a control dataset. This is usually generated from fixed chromatin or DNA immunoprecipitated with a nonspecific antibody. Calculate false discovery rate account the background signal in ChIP-sequence tags Assess the significance of predicted ChIP-seq peaks ChIP-Seq: Determination of peak significance More statistically sophisticated models developed to model the distribution of control sequence tags across the genome. Used as a parameter to assess the significance of ChIP tag peaks t-distribution Poisson model Hidden Markov model Primarily used to assign each peak a significance metric such as a P-value FDR or posterior probability. ChIP-Seq: Output chr start end length summit tags -10*log10(pvalue) fold_enrichment FDR(%) chr1 13322611 13322934 324 101 16 58.38 6.95 73.89 chr1 14474379 14475108 730 456 63 63.73 5.98 73.81 chr1 23912933 23913336 404 155 19 57.86 8.49 73.33 chr1 24619496 24619679 184 92 44 449.34 34.00 94.12 chr1 24619857 24620057 201 100 73 780.66 56.41 100 chr1 26742705 26743590 886 252 69 132.27 7.52 chr1 26743625 26745342 1718 1422 165 141.40 4.34 chr1 33811805 33814279 2475 289 256 98.13 3.74 74.50 chr1 34516074 34517165 1092 496 206 59.13 5.22 74.42 chr1 34519503 34520082 580 334 58 53.56 4.74 70.59 chr1 34529691 34530276 586 286 40 77.33 6.12 74.63 chr1 34546832 34547631 800 311 208 233.96 5.56 chr1 34548528 34549155 628 343 39 81.43 5.75 75.15 chr1 34570690 34571225 536 267 31 98.69 7.15 74.50 69.25 70.36 73.01 ChIP-Seq: Output A list of enriched locations Can be used: In combination with RNA-Seq, to determine the biological function of transcription factors Identify genes co-regulated by a common transcription factor Identify common transcription factor binding motifs ChIP-Seq: Need help? http://seqanswers.com/ Good for: Publications Answering FAQ Troubleshooting Contacting the programs authors