ChIP-seq - STAT 115

ChIP-seq
Xiaole Shirley Liu
STAT115, STAT215
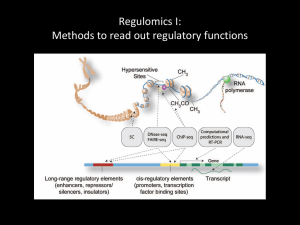
ChIP-chip/seq Technology
• Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation + microarray or high throughput sequencing
•
Detect genome-wide in vivo location of TF and other DNA-binding proteins
–
Find all the DNA sequences bound by TF-X?
–
Cook all the dishes with cinnamon
•
Can learn the regulatory mechanism of a transcription factor or DNA-binding protein much better and faster
2
Sonication (~500bp)
3
Immunoprecipitation
4
Reverse Crosslink and DNA
Purification
5
Sequence millions of 30mer ends of fragments
ChIP-Seq
ChIP-DNA
Noise
Map 30mers back to the genome
6
MACS: Model-based Analysis for ChIP-Seq
• Use confident peaks to model shift size
Binding
7
Peak Calls
• Tag distribution along the genome ~ Poisson distribution (λ
BG
= total tag / genome size)
•
ChIP-Seq show local biases in the genome
–
Chromatin and sequencing bias
8
Peak Calls
• Tag distribution along the genome ~ Poisson distribution (λ
BG
= total tag / genome size)
•
ChIP-Seq show local biases in the genome
–
Chromatin and sequencing bias
– 200-300bp control windows have to few tags
– But can look
ChIP
Control further
300bp
1kb
5kb
10kb Dynamic λ local
= max(λ
BG
, [λ ctrl
, λ
1k
,] λ
5k
, λ
10k
) http://liulab.dfci.harvard.edu/MACS/
Zhang et al, Genome Bio, 2008
Peak Call Statistics
• P-value and FDR?
•
Simulation: random sampling of reads?
• FDR = A / B (Ctrl/ChIP peaks are all FPs)
• MAT: Quality Control
<1% enriched
A B
Background 10
Enriched DNA
ChIP-seq Downstream Analysis
11
Target Gene Assignment
Yeast TF
Regulatory
Network
Protein
Transcribe Regulate
Gene
12
Human TF Binding Distribution
• Most TF binding sites are outside promoters
•
How to assign targets?
• Nearest distance?
•
Binding within 10KB?
• Number of binding?
•
Other knowledge?
13
Binding <> Functional
• Binding have effect on up genes at all hours, but only have effect on down genes at 12 hours
14
Stronger sites more function?
• Stronger sites are not closer to differentially regulated genes (not necessarily more functional)
15
Tang et al, Cancer Res 2011
Peak Conservation
• Evolutionary conservation
–
Can be used for ChIP QC
•
Conserved sites more functional?
– Majority of functional sites not conserved
16
Odom et al, Nat Genet 2007
Higher Order Chromatin Interactions
Chromatin confirmation capture
Interactions follows exponential decay with distance
Lieberman-Aiden et al, Science 2009
Hi-C
Direct Target Identification
• Binary decision?
•
Rank product of
• Regulatory potential
– Default λ 100kb
•
Differential expression
19
ChIP-chip/seq Motif Finding
• ChIP-chip gives 10-5000 binding regions ~200-
1000bp long. Precise binding motif?
– Raw data is like perfect clustering, plus enrichment values
• MDscan
–
High ChIP ranking => true targets, contain more sites
– Search TF motif from highest ranking targets first
(high signal / background ratio)
–
Refine candidate motifs with all targets
20
Similarity Defined by m-match
For a given w-mer and any other random w-mer
TGTAACGT 8-mer
TGTAACGT matched 8
A GTAACGT matched 7
TG C AAC A T matched 6
TG AC ACG Gmatched 5
AA TAAC AGmatched 4
m-matches for
TGTAACGT
Pick a reasonable m to call two w-mers similar
21
MDscan Seeds
A 9-mer
ATTGCAAAT
T TTGC G AAT
TTGCAAATC
ChIP-chip selected upstream sequences
Seed motif pattern
ATTGCAAAT
T TTGC G AAT
T TTGCAAAT
TTGCAAATC
TTGC G AAT A
TTGCAAAT T
TTGC CC ATC
T TTGCAAAT
GCAAATCCA
CAAATCCAA
GCAAAT T C G
CAAATCCAA
G AAATCCA C
GCAAATCCA
G G AAATCCA
G G AAATCC T
TGCAAATCC
TGCAAAT T C
GCCACCGT
A CCACCGT
A CCAC G GT
GCCAC G G C
…
22
Update Motifs With Remaining Seqs
m-matches
Extreme
High
Rank
Seed1
All ChIP-selected targets
23
Extreme
High
Rank
Seed1
Refine the Motifs
m-matches
All ChIP-selected targets
24
Further Refine Motifs
• Could also be used to examine known motif enrichment
•
Is motif enrichment correlated with ChIP-seq enrichment?
•
Is motif more enriched in peak summits than peak flanks?
•
Motif analysis could identify transcription factor partners of ChIP-seq factors
25
Estrogen Receptor
• Carroll et al, Cell 2005
•
Overactive in > 70% of breast cancers
• Where does it go in the genome?
•
ChIP-chip on chr21/22, motif and expression analysis found its “pioneering factor” FoxA1
ER
TF??
Estrogen Receptor (ER)
Cistrome in Breast Cancer
•
Carroll et al, Nat Genet 2006
• ER may function far away (100-200KB) from genes
• Only 20% of ER sites have PhastCons > 0.2
• ER has different effect based on different collaborators
NRIP
ER
AP1
Estrogen Receptor (ER)
Cistrome in Breast Cancer
•
Carroll et al, Nat Genet 2006
• ER may function far away (100-200KB) from genes
• Only 20% of ER sites have PhastCons > 0.2
• ER has different effect based on different collaborators
ER
AP1
NRIP
Cell Type-Specific Binding
• Same TF bind to very different locations in different tissues and conditions, why?
•
TF concentration?
•
Collaborating factors, esp pioneering factors
•
Interesting observations about pioneering factors
29
Summary
• ChIP-seq identifies genome-wide in vivo protein-
DNA interaction sites
•
ChIP-seq peak calling to shift reads, and calculate correct enrichment and FDR
•
Functional analysis of ChIP-seq data:
– Strong vs weak binding, conserved vs non-conserved
– Target identification
– Motif analysis
• Cell type-specific binding
Epigenetics
30