SDS-PAGE + Western Blot
Laboratory
What is Electrophoresis?
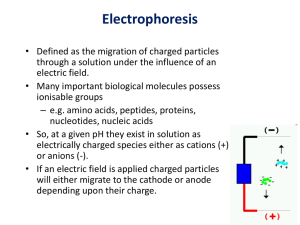
• Electrophoresis (to carry with electricity) is
the migration of charged molecules in an
electric field toward the electrode with the
opposite charge
• SDS-PAGE (Sodium dodecyl sulfate –
polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) is a form
of electrophoresis that treats samples with
SDS to denature proteins
Why is SDS-PAGE used?
• How many proteins are in my sample?
• What are the molecular weights of the proteins?
• What differences are there in proteins from
different sources?
• How pure is my protein of interest?
Why are proteins separated on SDSPAGE?
• Small size of proteins
• Gel matrix of polyacrylamide is tighter than
agarose – resolve smaller molecules
• Polyacrylamide – small DNA
• Agarose – large protein
- Agarose gels will never resolve as tightly as
polyacrylamide gels
Two phases of polyacrylamide.
• Upper stacking gel = 4%
acrylamide
• Lower resolving gel = 15%
• Discontinuous system –
results in all proteins
separating or resolving at
same time
• Stacking gel – allow
proteins to migrate rapidly
and be compressed at edge
of denser resolving gel
• Separating gel – begin to
separate as per their
molecular weights
How are protein bands formed?
• Two ion fronts sandwich protein bands
• SDS-PAGE running buffer – Tris and glycine (pH
8.3)
• Gel – Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.8)
• Chloride ions migrate rapidly than glycine ions
in an electric field
- When electrophoresis begins - proteins have
intermediate mobility - trapped between two
fronts -
How does polymerization start?
• Acrylamide and bis acrylamide monomers –
initiators – Ammonium persulfate (APS) and
catalyst – Tetramethylethylenediamine
(TEMED)
• Higher concentration of resolving gel is
poured – lower concentration stacking gel is
poured – sample comb is inserted into
unpolymerized stacking gel solution
Molecular weight of proteins
• Proteins – composed of 20 aa – 89 to 204
daltons
• Kilodalton (KD) – used for protein molecular
masses – 10 KD and 220 KD
Factors affecting mobility
• Electrical charge + mass = mobility
• SDS added in sample buffer and gel running
buffer
- Strong anionic (negatively charged) detergent
- Binds and coats proteins – denatured in linear
chains
- Mass determines migration
Denaturation of four structures of
proteins
• Primary, secondary,
tertiary and quaternary
• β-mercaptoethanol
(BME) or dithiothreitol
(DTT) – breaks disulfide
bonds
• Heat, reducing agent
and ionic detergent –
disrupt 2°, 3° and 4° results in linear chains
of aa
How to identify proteins in
polyacrylamide gel?
• Complex mixture of proteins
- Appear as distinct blue- stained bands(stained
gel)
- Positions and intensities – determine size and
abundance of proteins
- Specific proteins – Western blots – positive
identification by antibodies
Sources of errors
• Identical migration may be different proteins
of same sizes
• Proteins of similar composition, function and
evolutionary origin may be different in
molecular weight because of post
translational modifications
What are the different reagents that
will be used?
• Molecular weight markers – Precision plus
protein kaleidoscope prestained protein
standards
• Proteins genetically engineered to be specific
molecular weights then bound to dye
molecules – visible on gel
• Heated to 37 ° for 5 minutes
• Load 5 µl per gel
What are the different reagents that
will be used?
• Laemmli sample buffer – used to solubilize
proteins in fish muscle samples
- Mixture of Tris buffer + SDS + tracking dye
(bromophenol blue) + Glycerol
• Actin and Myosin standard – used to identify
conserved muscle proteins – positive control –
rabbit skeletal muscle consisting myofibrils
- Actin, myosin heavy chain, three myosin light
chains and tropomyosin- on destained gel
Actin and myosin standard
• Bands at 210 KD (myosin heavy) and 43 KD
(actin) – present in all of muscle samples
- Biologically active myosin has quaternary
structure - both heavy and light chains
- Myosin light chains (15-25 KD) vary in
molecular weight between fish species
What are the different reagents that
will be used?
• Dithiothreitol (DTT) or β-mercaptoethanol
(BME) – added to Laemmli buffer to ensure
complete breakage of disulfide bonds.
- Reduces formation of background bands
• Ready Gel precast gels – 15% Tris-HCl gels
- Resolves smaller molecular weight proteins
What are the different reagents that
will be used?
• Electrophoresis running (1X TGS) buffer –
Tris-glycine-SDS (TGS) running buffer contains
Tris to buffer the pH, glycine to provide ions to
transmit current, and SDS to maintain
denaturation of proteins in gel.
• Bio-Safe Coomassie protein stain – High
affinity between dye and proteins
- Wash gel 3 times with DI H2O before staining
What are the different reagents that
will be used?
• Bio-Safe Coomassie protein stain – Optimal
staining time is 1 hour – gentle shaking
- Destaining of gel – protein bands become
intense
- Rinse the stained gel with several changes of a
large volume of deionized water
- And complete destaining overnight in water
What are the different materials
needed for each workstation?
• Fish samples, Blade/knife, water bath set to
95 degree, Prot/Elec pipet tips for gel loading,
Mini-protean 3 electrophoresis module (gel
box), Power supply, gel comb, staining trays,
DI H2O, etc
Steps
• Protein extraction from various fish samples
(March 18) – 25 minutes- March 18
• Run SDS-PAGE (March 25) – 30 minutes
- Stain one gel with Coomassie blue (March 25
+ 26)
• Another gel – western blot (March 25)- 2.5 hrs
• Immunodetection with antibodies(March 27)
Western Blot reagents and equipment
• Mini Trans-Blot Apparatus : Passes electric
current horizontally through gel – forcing
negatively charged proteins to migrate out of gel
onto nitrocellulose membranes
• Nitrocellulose membranes: Proteins bind to
positive charge
- Durable membrane can undergo multiple
washing and incubation steps
- White background to visualize color development
of proteins
Western Blot reagents and equipment
• Blotting paper – supports gel and
nitrocellulose
- Protects filter pads during assembly and
electrophoresis
- Facilitates uniform flow of buffer and current
through gel
- 100% cotton fiber – does not contain any
additives that may interfere with blotting
process
Western Blot reagents and equipment
• Filter pads: Press the gel and nitrocellulose
tightly and uniformly
- Eliminate bubbles – allows transfer of proteins
out of gel onto the membrane
- Should be cleaned in distilled water before use
Western Blot reagents and equipment
• Blotting buffer: Should be diluted to 1X
• Blocker: 5% nonfat dried milk powder in
phosphate buffered saline (PBS) and 0.025%
tween 20
• Surface area unoccupied by proteins- blocked
by incubating milk solution – before
incubation with primary antibody
Western Blot reagents and equipment
• Primary antibody: recognizes or bind protein
under study
- Injecting chicken myosin protein into mice
• Secondary antibody: binds to primary
antibody
- Polyclonal goat anti-mouse antibody
conjugated to horseradish peroxidase enzyme
- Injecting goats with primary mouse antibodies
•
•
•
This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the
U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity
employer and does not discriminate on the following basis:
against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age disability, political
affiliation or belief; and
against any beneficiary of programs financially assisted under Title I of the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (WIA), on the
basis of the beneficiary’s citizenship/status as a lawfully admitted immigrant authorized to work in the United States, or his
or her participation in any WIA Title I-financially assisted program or activity.
Disclaimer
• This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the
President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the
U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The
solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the
official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor
makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or
implied, with respect to such information, including any information on
linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information
or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued
availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution
that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an
individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses
require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.