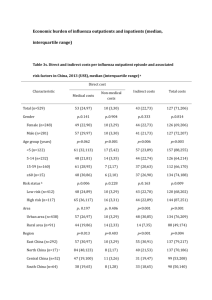
Comparison of rt-RT-PCR and MDCK cell culture for detection of
advertisement

N.Naranbold, National Influenza Laboratory, National Center of Communicable Diseases, Mongolia The 10th International Congress of the Asian Society of Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine September 10-11, 2009 in Ulaanbaatar Mongolia. Introduction Rapid detection and identification of causal agents is essential for timely actions to control of outbreaks and successful clinical management of the disease cases. Introduction However the traditional methods of virology are time-consuming and costly, making them less successful for practicising epidemiologists and clinicians, especially to control shortduration infections like influenza. Background In this report we share with you our results in the last 2 years with real-time Reversetranscriptase (r-RT) PCR for this purpose. Background In our laboratory, we have been introduced real time PCR since 2008. The study aim is to compare r-RT PCR and traditional method to satisfy epidemiological and clinical needs. We are trying to find out sensitive, rapid and cheaper methods for the reliable detection of A (H3, H1) and B influenza viruses. Methods and Materials • Samples – 565 clinical nasal samples from patients with ILI collected in ISSSs from Baganuur District, UB and Selenghe aimag in 2008/2009 cold season. • r-RT-PCR – – – – – Instrument RNA purification Primer Probe? ! Master-mix (ABI 7300) (QUIAGEN mini RNA kit) (Invitrogen®A (H1), A(H3), B, M? (TaqMan) (Invitrogen) • Traditional method – Influenza virus isolation – Serological tests (MDCK cell culture) (HA and HIT) Traditional influenza detection method Specimen collection Virus Isolation on MDCK cell culture ~6-7days Detection: HA Subtyping: HIT MDCK cell culture ready for virus inoculation MDCK cell culture with virus CPE r-RT-PCR influenza detection method Specimen collection RNA isolation 4-5 hours r-RT-PCR r-RT-PCR Thermal cycler protocol r-RT-PCR Results Detection percentage Duration Expenses Conclusion r-RT-PCR •6 times more sensitive •30 times quicker •2.5 times cheaper Traditional method (virus isolation on cell culture) for influenza virus detection Conclusion On the basis of the obtained results r-RT_PCR is recommended for routine influenza virus surveillance.